A team of researchers from the University of Bristol, UK has announced a breakthrough in the field of blood transplants.
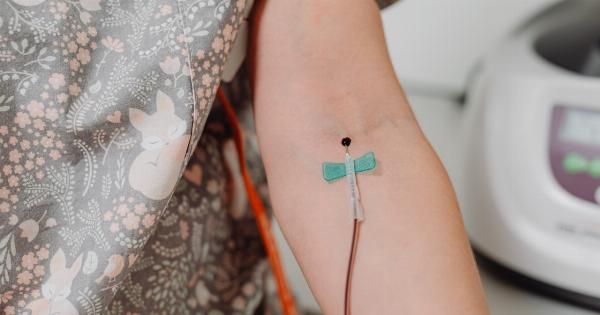
The team has been working on developing an artificial blood substitute that could be used as a replacement for human blood for transfusions. In a recent study, the team successfully transfused this revolutionary new artificial blood into human patients, marking a major milestone in the development of the technology.
What is Artificial Blood?
Artificial blood is a blood substitute that can be used to replace the need for human blood transfusions.
There are several different types of artificial blood, but the one developed by the University of Bristol team is based on a type of hemoglobin that is found in the human body. Hemoglobin is the protein responsible for carrying oxygen in the blood, and the artificial hemoglobin developed by the Bristol team is chemically modified to make it more stable and able to transport oxygen more efficiently than natural hemoglobin.
The Study
In the study conducted by the Bristol team, the artificial blood was successfully transfused into a small number of human patients.
The team evaluated the safety and effectiveness of the blood substitute by monitoring the patients for several weeks following the transfusions. The results of the study were overwhelmingly positive, with no adverse effects reported and a significant increase in oxygen levels observed in the patients.
The study was only a small-scale trial, conducted on a relatively small number of patients, so further research and development will be needed to fully assess the potential of artificial blood.
However, the success of this initial study is a major step forward in the development of this groundbreaking technology.
Potential Benefits of Artificial Blood
The development of artificial blood has the potential to revolutionize the field of blood transfusions and has numerous potential benefits over traditional donor blood. Some of the potential benefits of artificial blood include:.
1. Elimination of Blood Donor Shortages
One of the biggest challenges faced by the medical community is a shortage of donor blood. This can be particularly problematic during times of national emergencies or disasters when large amounts of blood may be needed.
Artificial blood would eliminate the need for donor blood altogether, ensuring that there is always a ready supply of blood available for transfusions.
2. Increased Safety of Blood Transfusions
While blood transfusions are generally safe, there is always a risk of infection or other complications. Artificial blood eliminates this risk, as it is sterilized and free from any potential pathogens or contaminants.
3. Improved Compatibility
One significant issue with human blood transfusions is compatibility. Blood types must be carefully matched to avoid the risk of a dangerous reaction.
Artificial blood, on the other hand, is not subject to the same compatibility concerns and could potentially be used universally.
4. Long Shelf Life
Traditional donor blood has a relatively short shelf life and must be used within a certain timeframe. Artificial blood, on the other hand, has a much longer shelf life and could potentially be stockpiled for use in emergency situations.
Conclusion
The successful transfusion of artificial blood into human patients marks a major milestone in the development of this groundbreaking technology.
While further research and development will be needed to fully assess the potential of artificial blood, it has the potential to revolutionize the field of blood transfusions and address some of the major challenges faced by the medical community in this area.