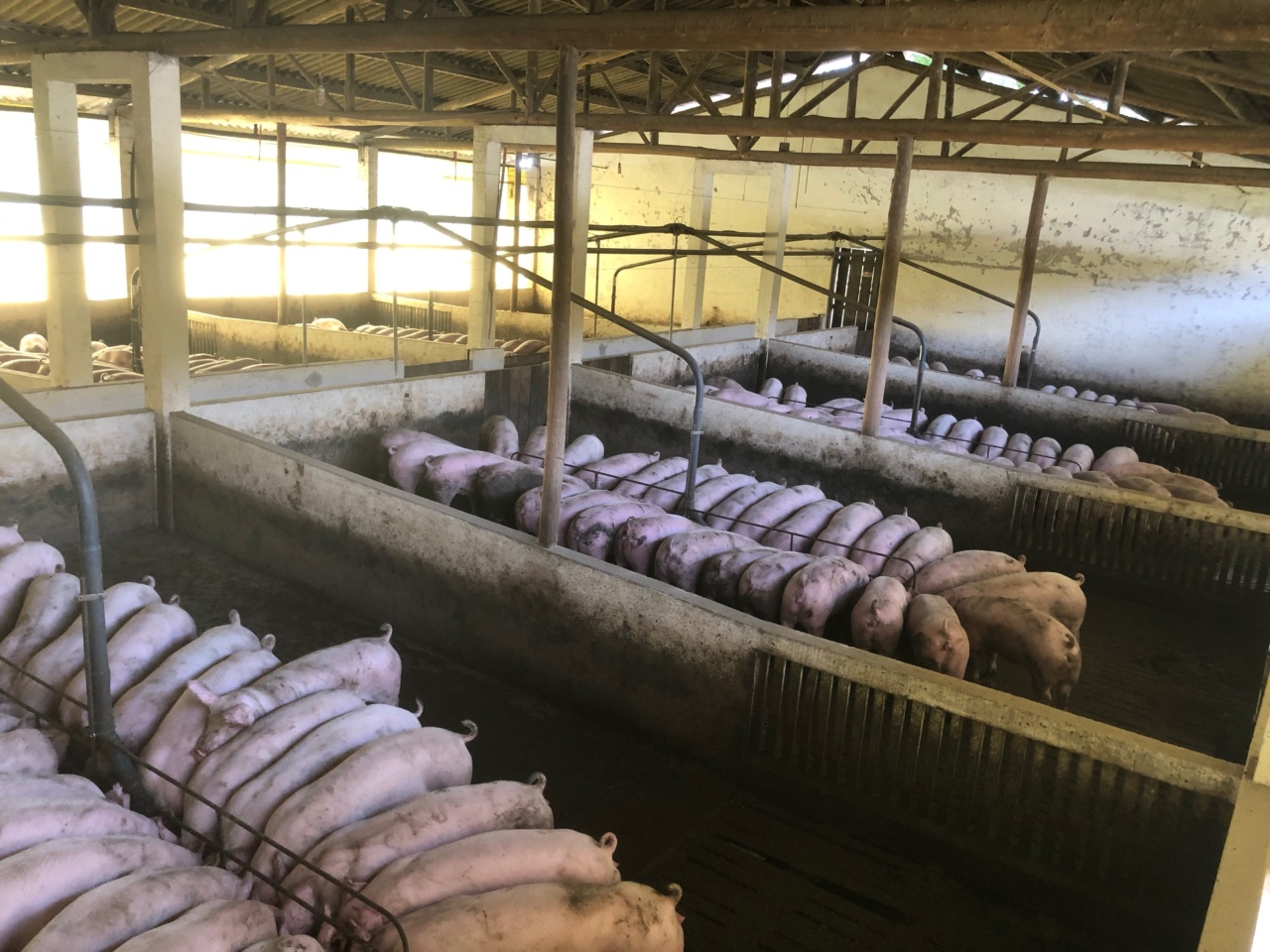
Lab-cultivated meat, also known as cell-based meat or cultured meat, is an innovative and promising solution to several challenges faced by the traditional animal agriculture industry.
This technology involves growing animal cells in a lab-controlled environment and cultivating them into edible meat products. In recent years, lab-cultivated meat has gained considerable attention due to its potential to address issues related to animal welfare, environmental sustainability, and global food security.
However, the advancement and adoption of this technology also come with several challenges that need to be overcome. In this article, we will explore the benefits and challenges associated with lab-cultivated meat.
The Benefits
1. Animal Welfare
One of the major benefits of lab-cultivated meat is its potential to significantly improve animal welfare. Traditional animal farming involves cramped and often stressful conditions, leading to the suffering of animals.
Lab-cultivated meat eliminates the need for raising and slaughtering animals, thereby minimizing animal cruelty and providing a more ethical solution for meat production.
2. Environmental Sustainability
The traditional meat production industry is known for its enormous environmental impact. It contributes to deforestation, greenhouse gas emissions, water pollution, and overconsumption of resources such as water and land.
Lab-cultivated meat has the potential to reduce these environmental burdens significantly. It requires fewer natural resources, emits fewer greenhouse gases, and eliminates the need for large-scale land and water use associated with traditional livestock farming.
3. Food Security
As the global population continues to grow, ensuring food security becomes a critical challenge. Lab-cultivated meat has the potential to provide a sustainable and efficient solution to meet the increasing demand for meat.
It can be produced year-round in controlled environments, irrespective of the geography or climate, reducing the dependence on traditional livestock farming and its associated limitations.
4. Health and Safety
Lab-cultivated meat can offer improved food safety compared to conventional meat production. The controlled lab environment reduces the risk of contamination by harmful pathogens commonly found in traditional meat.
Additionally, since the growing process is free from antibiotics and growth hormones, lab-cultivated meat offers the possibility of producing healthier and more wholesome products.
5. Ethical Considerations
Many individuals, due to religious, cultural, or personal beliefs, follow specific dietary restrictions or choose to avoid consuming meat. Lab-cultivated meat provides an alternative that aligns with these ethical considerations.
It allows people to enjoy meat products without compromising their values and beliefs, thereby increasing inclusivity in the food system.
The Challenges
1. Cost
Currently, lab-cultivated meat is significantly more expensive to produce compared to traditional meat. High production costs arise from the complex and resource-intensive processes involved in lab-grown meat production.
To ensure widespread adoption and accessibility, there is a need for technological advancements and economies of scale to reduce the cost of lab-cultivated meat.
2. Public Acceptance and Perception
Despite its potential benefits, lab-cultivated meat faces challenges in gaining acceptance and changing consumer perceptions.
Skepticism, fear, and hesitancy from the public regarding the safety and quality of lab-cultivated meat can hamper its market viability. Building trust and awareness through education and transparent communication will be crucial in overcoming these challenges.
3. Regulation and Labeling
The regulation of lab-cultivated meat poses a challenge for policymakers. The technology is relatively new, and existing regulations designed for traditional meat may not adequately address the unique characteristics of lab-cultivated meat.
Developing appropriate regulations and establishing clear labeling requirements will be essential to ensure consumer confidence and a level playing field for both traditional and lab-cultivated meat producers.
4. Scaling and Commercialization
Currently, lab-cultivated meat production is limited to small-scale operations. Scaling up production to meet the demands of a growing population presents significant technical and logistical challenges.
Developing efficient and scalable production processes, along with establishing large-scale production facilities, will be necessary to bring lab-cultivated meat to the mainstream market.
5. Cultural Acceptability
Many cultures and cuisines have deep-rooted traditions and preferences that revolve around conventional meat. Introducing lab-cultivated meat as an alternative may face resistance in such communities.
Tailoring the production and marketing strategies to address cultural acceptability will become crucial to increase consumer adoption and overcome cultural barriers.
Conclusion
Lab-cultivated meat holds significant potential to revolutionize the traditional meat industry and address the numerous challenges it faces.
The benefits of lab-cultivated meat, such as animal welfare improvement, environmental sustainability, food security, health and safety, and ethical considerations, are promising. However, the challenges of cost, public acceptance, regulation, scaling, and cultural acceptability must be diligently addressed to ensure its successful integration into the food system.
With continued research, investment, and collaborative efforts between scientists, industry stakeholders, and policymakers, lab-cultivated meat has the potential to become a viable and sustainable alternative to conventional meat production.