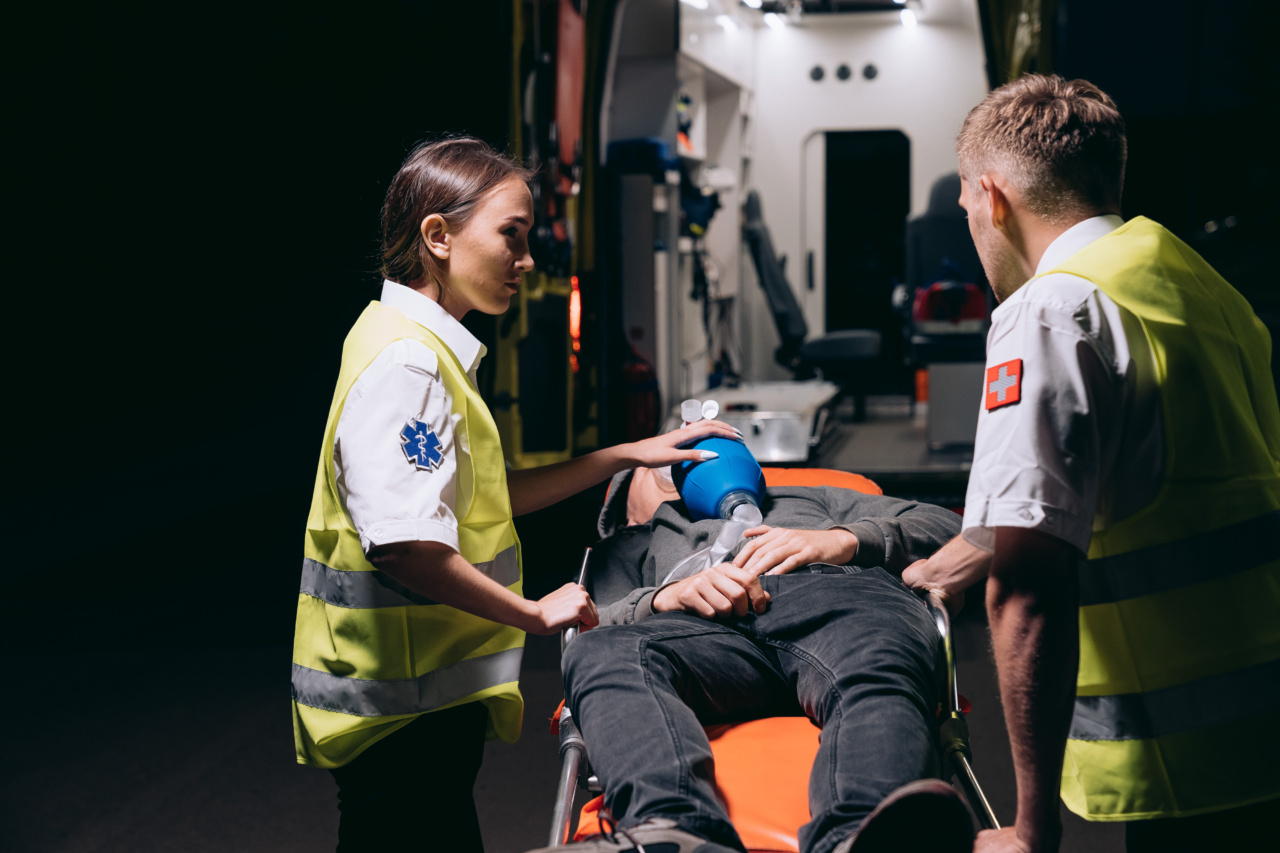
Patient transport is an integral part of medical settings, allowing for the transfer of patients within a healthcare facility or between different healthcare facilities.
This process ensures that patients receive the necessary care and treatment in a timely and efficient manner. While patient transport might seem like a routine task, it carries its own set of risks and challenges. In some cases, these risks can go unnoticed, potentially leading to adverse events or patient harm.
Undetected Perilous Risks in Patient Transport
Despite the crucial role that patient transport plays, there are several undetected perilous risks associated with this process. These risks can compromise patient safety and the overall quality of care provided.
It is essential for healthcare professionals involved in patient transport to be aware of these risks and take appropriate measures to mitigate them.
1. Inadequate Communication
Effective communication is key during patient transport. Lack of clear and concise communication between healthcare professionals can lead to misunderstandings, delays, and errors.
For example, if the patient’s condition deteriorates during transport, and the transport team fails to communicate this information to the receiving healthcare facility, essential interventions may be delayed, jeopardizing the patient’s well-being.
2. Failure to Adhere to Safety Protocols
Adherence to safety protocols is crucial in patient transport to minimize the risk of accidents or adverse events.
Failure to follow these protocols, such as improper securing of medical equipment or not utilizing appropriate protective equipment, can cause harm to patients and transport staff. Without proper adherence to safety protocols, the risk of falls, injuries, and infections significantly increases.
3. Inadequate Training and Skills
Healthcare professionals involved in patient transport should possess the necessary skills and undergo continuous training.
It is essential to understand the proper techniques for transferring patients, utilizing assistive devices, and responding to emergencies that may occur during transport. Without adequate training, healthcare professionals may not be equipped to handle unexpected situations, potentially endangering both the patient and themselves.
4. Lack of Standardized Processes
Standardization is crucial in patient transport to ensure consistency and minimize errors. However, many healthcare facilities lack standardized processes for patient transport, leading to inconsistencies and increased risks.
Without clear guidelines and protocols, healthcare professionals may resort to different, potentially unsafe, transport practices, increasing the chances of adverse events.
5. Equipment Malfunctions
Medical equipment used during patient transport can face malfunctions, putting patients at risk. For instance, a malfunctioning oxygen tank or a defective stretcher can lead to serious complications during transport.
Regular maintenance and inspection of equipment are necessary to identify any potential issues and prevent equipment failures that could endanger patients.
6. Inadequate Staffing
Insufficient staffing is a common issue in healthcare settings, including patient transport. Inadequate staffing levels can result in rushed and poorly executed patient transfers.
When healthcare professionals are overwhelmed with numerous patients needing transport, they may overlook important details or fail to provide the necessary care and attention during the process. Inadequate staffing not only increases the risk of errors but also compromises patient safety.
7. Environmental Hazards
During patient transport, healthcare professionals must navigate through various environmental hazards. These hazards can include slippery floors, uneven surfaces, or obstructed pathways.
Failing to address and mitigate these hazards can lead to falls, injuries, or accidents, posing a danger to both the patient and the transport team.
8. Patient Anxiety and Psychosocial Stress
Patient transport can often induce feelings of anxiety, stress, and discomfort for patients. It is crucial for healthcare professionals to be mindful of these psychosocial factors and provide appropriate support and reassurance during transport.
Failing to address patient anxiety and psychosocial stress can result in compromised patient well-being and affect the overall patient experience.
9. Infection Control Breaches
Transporting patients can increase the risk of infection transmission if proper infection control practices are not followed.
Healthcare professionals involved in patient transport should adhere to hand hygiene protocols, utilize personal protective equipment, and follow appropriate cleaning and disinfection procedures. Infection control breaches during patient transport can lead to healthcare-associated infections and compromise patient safety.
10. Lack of Continuous Monitoring
Patient transport requires continuous monitoring of the patient’s vital signs and overall condition. However, due to distractions or insufficient resources, continuous monitoring may be lacking during transport.
Failing to monitor a patient adequately can delay the identification of potential complications or deteriorations in their condition, resulting in delayed interventions and compromised patient outcomes.
Mitigating Risks in Patient Transport
Despite the undetected perilous risks associated with patient transport, there are measures that can be taken to mitigate these risks and enhance patient safety:.
1. Enhanced Communication and Information Exchange
Improving communication between healthcare professionals involved in patient transport is essential.
Utilizing standardized communication tools and protocols can ensure that vital information is effectively exchanged and any changes in the patient’s condition are promptly communicated.
2. Training and Education
Providing comprehensive training and education to healthcare professionals involved in patient transport is crucial.
This training should cover proper transfer techniques, use of assistive devices, emergency response, infection control, and safety protocols. Continuous learning and skill development should be encouraged to ensure healthcare professionals remain up-to-date with best practices.
3. Standardized Transport Processes
Implementing standardized processes for patient transport helps minimize variability and reduce the risks associated with inconsistent practices.
Developing clear guidelines and protocols ensures that all healthcare professionals involved in patient transport follow the same safe practices, minimizing the potential for errors or adverse events.
4. Maintenance and Inspection of Equipment
Regular maintenance and inspection of medical equipment used during patient transport are essential. This helps identify any potential malfunctions or defects, allowing for timely repairs or replacements.
Healthcare facilities should establish routine equipment checks to ensure the safety and reliability of equipment during patient transport.
5. Adequate Staffing Levels
Addressing the issue of inadequate staffing is crucial for patient safety during transport.
Healthcare facilities should prioritize adequate staffing levels to ensure healthcare professionals can devote proper attention and care to each patient during the transport process. This reduces the likelihood of oversights and errors that could compromise patient well-being.
6. Environmental Risk Assessment
Prior to patient transport, healthcare professionals should conduct a comprehensive risk assessment of the environment to identify and address potential hazards.
This assessment should include evaluating the condition of floors, pathways, and any other environmental factors that might pose a risk during transport. By proactively addressing these hazards, the chances of accidents or injuries can be significantly reduced.
7. Patient-Centered Care
Adopting a patient-centered approach during patient transport can help alleviate patient anxiety and psychosocial stress.
Healthcare professionals should communicate with patients, address their concerns, and provide reassurance throughout the transport process. Creating a supportive and empathetic environment can enhance the overall patient experience and contribute to improved patient outcomes.
8. Adherence to Infection Control Practices
Infection control practices should be strictly followed during patient transport. This includes practicing proper hand hygiene, utilizing personal protective equipment, and adhering to appropriate cleaning and disinfection protocols.
By preventing infection transmission during transport, the risk of healthcare-associated infections can be minimized, ensuring patient safety.
9. Continuous Monitoring and Assessment
Healthcare professionals involved in patient transport should prioritize continuous monitoring and assessment of the patient’s vital signs and overall condition.
Utilizing portable monitoring equipment and maintaining close observation allows for early identification of any complications or changes, enabling prompt interventions and reducing the risk of adverse events.
Conclusion
Patient transport in medical settings carries undetected perilous risks that can compromise patient safety. However, by recognizing and addressing these risks, healthcare professionals can ensure safe and efficient patient transfers.
Effective communication, adherence to safety protocols, continuous training, and standardized processes are essential for mitigating the risks associated with patient transport. Additionally, maintaining equipment, ensuring adequate staffing, and providing patient-centered care contribute to promoting patient safety and enhancing the overall patient experience.