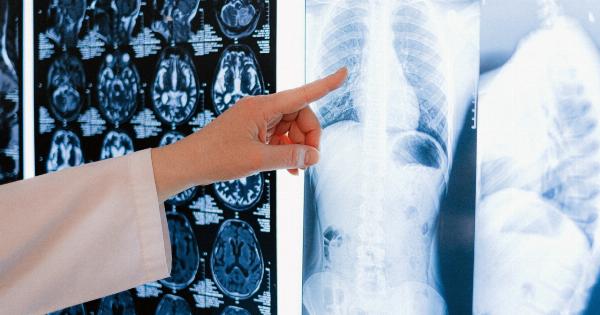
A burst blood vessel in the brain, also known as a cerebral hemorrhage or intracerebral hemorrhage, is a potentially life-threatening condition where blood leaks from a damaged blood vessel into the brain tissue.
This can result in significant damage to the brain and can lead to various neurological symptoms. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for a burst blood vessel in the brain is crucial for early detection and effective management of this condition.
Causes
Several factors can contribute to a burst blood vessel in the brain. The most common causes include:.
- Hypertension: High blood pressure is the leading cause of cerebral hemorrhages. Uncontrolled hypertension can weaken the walls of blood vessels, making them more susceptible to bursting.
- Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI): Severe traumatic brain injuries, such as those sustained in car accidents or falls, can rupture blood vessels in the brain.
- Abnormal Blood Vessels: Certain individuals may have weak or abnormal blood vessels in their brains from birth, predisposing them to a higher risk of hemorrhage.
- Aneurysm: A weakened area in a blood vessel wall can balloon and form an aneurysm. If an aneurysm ruptures, it can result in a cerebral hemorrhage.
- Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM): AVM is a congenital condition where abnormal connections between arteries and veins disrupt the normal blood flow, increasing the risk of bleeding in the brain.
- Blood Disorders: Certain conditions that affect the blood’s clotting ability, such as hemophilia or leukemia, can increase the likelihood of a burst blood vessel in the brain.
Symptoms
The symptoms of a burst blood vessel in the brain can vary depending on the location and extent of the hemorrhage. Common signs and symptoms include:.
- Severe headache
- Sudden onset of neurological deficits, such as weakness or numbness in the face, arms, or legs
- Difficulty speaking or slurred speech
- Loss of balance or coordination
- Confusion or changes in mental status
- Nausea and vomiting
- Seizures
- Vision disturbances
If you or someone you know experiences any of these symptoms, it is crucial to seek immediate medical attention, as prompt treatment can greatly improve the outcome.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing a burst blood vessel in the brain typically involves a combination of medical history assessment, physical examination, and imaging tests. The following diagnostic tests may be performed:.
- Computed Tomography (CT) Scan: This imaging test can help identify the presence and location of bleeding in the brain.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): MRI scans provide detailed images of the brain, helping to evaluate the extent of the hemorrhage and any associated brain damage.
- Cerebral Angiography: This test involves injecting a contrast dye into the blood vessels and taking X-ray images to detect abnormalities in the blood vessels, such as an aneurysm or AVM.
- Electroencephalogram (EEG): An EEG is used to assess brain activity and detect any abnormalities in electrical signals, especially in cases where seizures have occurred.
Treatment
The treatment for a burst blood vessel in the brain aims to stop the bleeding, stabilize brain function, and prevent further complications. The specific treatment options depend on the underlying cause and severity of the hemorrhage:.
- Medication: If the bleeding is caused by uncontrolled hypertension, medications may be prescribed to lower blood pressure and reduce the risk of further bleeding.
- Surgery: In cases of aneurysm or AVM, surgical procedures may be necessary to repair the blood vessels and prevent future ruptures.
- Endovascular Embolization: This minimally invasive procedure involves inserting a catheter into the blood vessels to block off the bleeding site or seal an aneurysm.
- Supportive Care: Patients with a burst blood vessel in the brain often require close monitoring in an intensive care unit, where measures can be taken to control intracranial pressure, manage seizures, and provide other supportive treatments.
Recovery and Rehabilitation
The recovery process following a burst blood vessel in the brain can be lengthy and challenging. The extent of recovery depends on various factors, including the size and location of the hemorrhage, as well as any subsequent brain damage.
Rehabilitation may involve:.
- Physical therapy to regain strength and mobility
- Occupational therapy to improve daily living skills
- Speech and language therapy to address communication difficulties
- Psychological support to cope with emotional and cognitive changes
Prevention
While not all cases of a burst blood vessel in the brain can be prevented, certain measures can reduce the risk:.