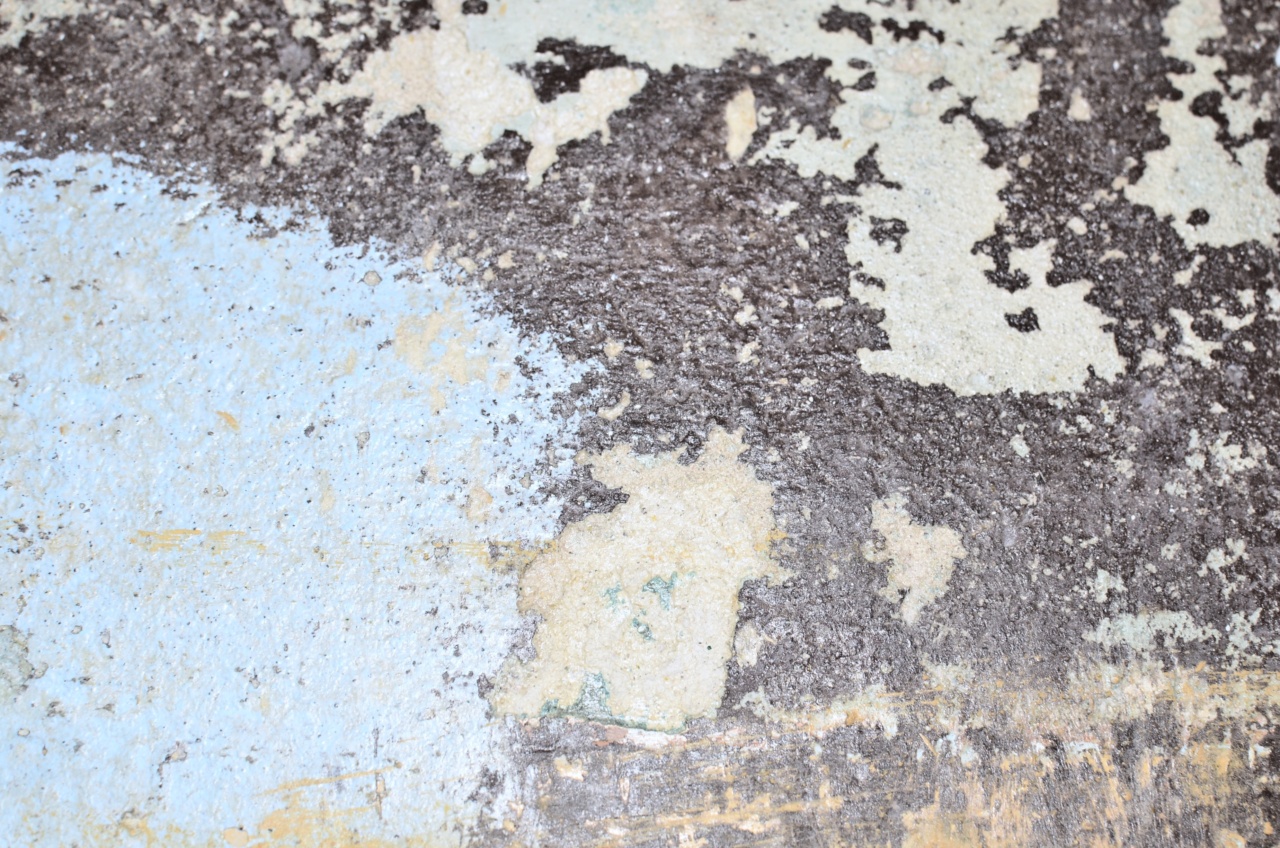
Black mold, also known as Stachybotrys chartarum, is a type of fungus that can grow in damp and humid environments. It is notorious for its dark black or greenish-black color and musty odor.
Black mold is commonly found in areas with water damage, such as leaky roofs, basements, and bathrooms. Exposure to black mold can lead to a variety of health problems, but one question that often arises is whether it can damage the brain.
Understanding black mold
Black mold belongs to a group of molds known as toxic mold. These molds release toxic compounds called mycotoxins, which can cause severe health issues in humans.
While black mold is not the only type of mold that can produce mycotoxins, it is one of the most well-known and concerning types.
When black mold spores are released into the air, they can be inhaled by humans, leading to exposure.
Prolonged exposure to black mold and its mycotoxins can cause various health problems, including respiratory issues, allergies, skin irritation, and even neurological symptoms.
The brain and mold exposure
When it comes to the brain, there is limited scientific research specifically addressing the effects of black mold exposure. However, several studies have looked at the broader impact of mold exposure on neurological health.
One study published in the journal Neurotoxicology and Teratology found that exposure to mold in early childhood was associated with an increased risk of neurobehavioral problems, such as attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).
Another study published in the journal Environmental Health Perspectives found an association between mold exposure and cognitive impairments in adults.
While these studies did not specifically focus on black mold, they suggest that exposure to any type of mold may have negative effects on brain function. Black mold, with its potent mycotoxins, may pose an even greater risk.
Neurological symptoms associated with black mold exposure
Although research is limited, there have been numerous anecdotal reports and case studies linking black mold exposure to neurological symptoms. Some of the common neurological symptoms associated with black mold exposure include:.
- Headaches
- Dizziness
- Memory problems
- Difficulty concentrating
- Brain fog
- Fatigue
These symptoms can significantly impact a person’s quality of life and ability to perform cognitive tasks effectively.
However, it is important to note that these symptoms can also be caused by various other factors, so a comprehensive evaluation is necessary to determine the exact cause.
The mechanism behind brain damage
The exact mechanism underlying how black mold may damage the brain is not fully understood. However, it is believed that the mycotoxins produced by black mold could play a role.
These mycotoxins can enter the body through inhalation or ingestion and may potentially disrupt neural pathways and cause inflammation in the brain.
Inflammation is known to be a contributing factor to many neurological disorders.
Studies have shown that elevated levels of inflammation markers are associated with conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and multiple sclerosis. It is possible that the mycotoxins released by black mold contribute to chronic inflammation in the brain, leading to long-term damage.
Preventing and dealing with black mold
Preventing black mold growth is crucial for maintaining a healthy environment. Here are some measures you can take to prevent and deal with black mold:.
- Keep indoor humidity levels below 50%
- Fix any leaks or water damage immediately
- Ensure proper ventilation in bathrooms, kitchens, and other humid areas
- Regularly clean and dry areas prone to moisture
- Use mold-resistant paint and materials
- If you find black mold, hire professionals for safe removal
It is essential to address black mold promptly to prevent health issues, including potential brain damage.
Seeking medical help
If you suspect that black mold exposure is causing neurological symptoms or any other health problems, it is important to seek medical help.
A healthcare professional can evaluate your symptoms, conduct appropriate tests, and provide guidance on the proper course of action.
Remember that only a qualified healthcare professional can provide an accurate diagnosis and treatment plan based on your specific situation.
Conclusion
While the research on black mold’s specific effects on the brain is limited, it is clear that mold exposure, in general, can have detrimental impacts on neurological health. Black mold, with its toxic mycotoxins, may pose an even greater risk.
Neurological symptoms such as headaches, dizziness, memory problems, and difficulty concentrating have been associated with black mold exposure.
Prevention and prompt action are crucial when dealing with black mold. Keeping humidity levels low, addressing water damage promptly, and ensuring proper ventilation can help prevent black mold growth.
If you suspect black mold exposure is causing health issues, seek medical help for a thorough evaluation and guidance.