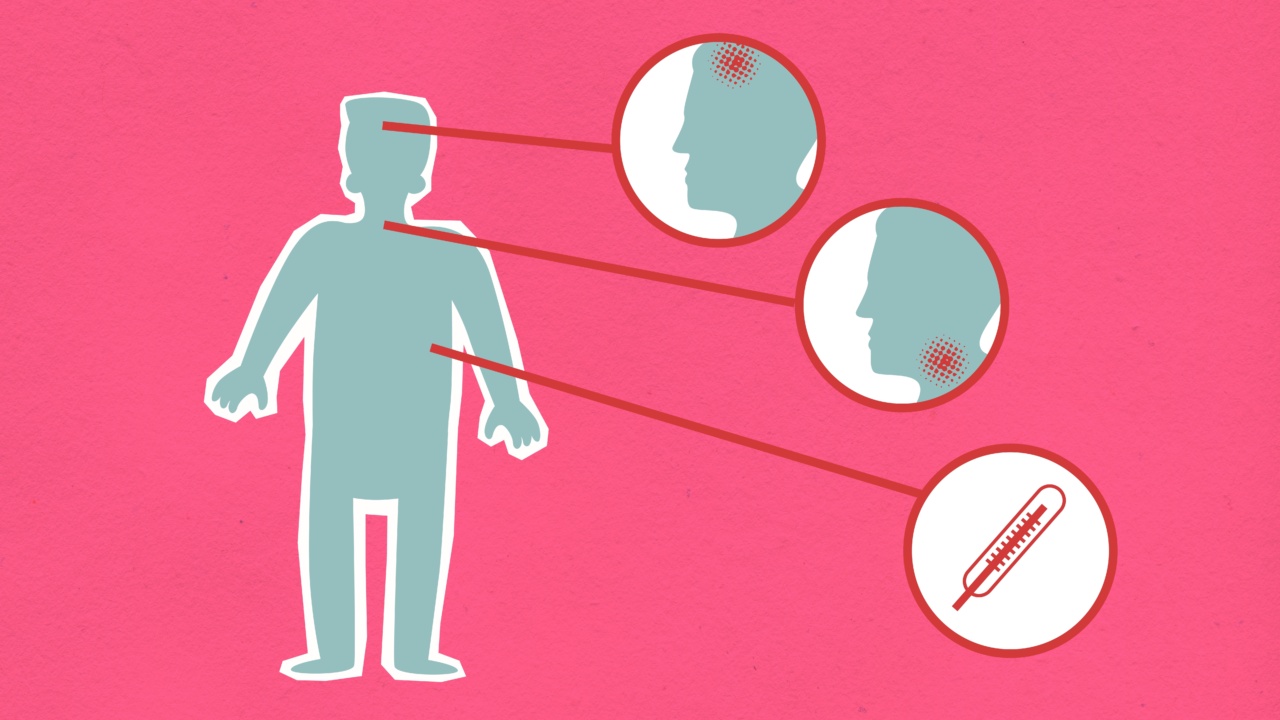
When it comes to healthcare, symptoms and indications are very important in determining the diagnosis and treatment for a patient. However, some people are not aware of the differences between the two terms.
In this article, we will discuss the dissimilarities between differential symptoms and indications.
Doctors and healthcare professionals do not jump to a conclusion when they encounter a patient with symptoms. They utilize a differential diagnosis to evaluate symptoms to find out the best possible diagnosis.
To conduct a differential diagnosis, doctors will make a list of potential illnesses or diseases that could potentially be causing the symptoms the patient is experiencing.
Differential Symptoms
Differential Symptoms are symptoms that are displayed when a person is affected by a particular condition.
When a patient visits the doctor, the professional examines them physically, listens to them explain their symptoms, and afterward creates a diagnosis by considering the possible conditions that could cause these symptoms.
For instance, a patient who is experiencing severe headaches and nausea may also be experiencing other symptoms that could either contrast with those symptoms or belong to the same category.
The other symptoms may include sleeplessness; this symptom does not usually go alongside migraines, but it is a symptom that falls under pain and discomfort. In this situation, the doctor would carefully consider the differential symptoms along with the other symptoms to make a diagnosis.
Indications
Indications are the signs or occurrences that show the possible presence of an ailment. The symbols may take place during a medication, or they may be a result of a physical assessment.
Doctors typically use indications to predict a specific diagnosis, which they can then examine through a differential diagnosis.
For instance, your doctor may decide to conduct an HIV test if you have an indication such as a rash that is present in HIV patients.
Therefore, clinicians would take note of every possible indication and weigh them with differential diagnosis possibilities as they work through the process to come up with the right diagnosis.
The Differences Between Differential Symptoms and Indications
After carefully analyzing the two terms mentioned above, it is clear that there is a specific contrast between the definitions of the term. The following are the differences between differential symptoms and indications.
Differential Symptoms
Differential symptoms are the symptoms displayed by someone who is experiencing a particular health issue.
The symptoms can be observable or observable, occurring for a short or extended time and be related to physical or cognitive causes.
Symptoms that the patient may experience before a diagnosis includes a flu-like illness, experiencing frequent nausea or vomiting, and loss of appetite.
The symptoms are just there to indicate that something is wrong, and a differential diagnosis is required to identify the underlying disorder.
Indications
An indication can be defined as a symptom, characteristic sign, or other manifestation of a disease. Indications are a flag for the presence of some issue in the body.
In general, an ‘indication’ is a sign that can alert clinicians to the fact that a differential diagnosis may be needed to get to the root of the problem.
Indications can be seen during a physical exam or discovered during the patient’s clinical history. Medical laboratory test results may also serve as indications to medical staff that further testing is needed.
The Importance of Differential Symptoms and Indications
The differential diagnosis is critical in determining the right treatment for a patient. It is crucial to identify whether a patient’s symptoms indicate an infection, a disease, or another underlying problem.
The first step in creating a differential diagnosis is to gather information about the patient’s clinical history. This includes the patient’s symptoms, medical history, lifestyle habits, and any available medical test results.
Once the clinician has gathered all the necessary information, they create a list of possible diagnoses. The next step is to determine which diagnosis is most likely based on the patient’s symptoms and clinical history.
Making Use of Differential Symptoms and Indications
Medical staff must make use of differential symptoms and indications to perform a proper diagnosis and treatment.
This procedure determines the right medical decision to make, providing guidance toward the specific treatment to take, depending on the underlying issue.
An assurance of a successful and accurate diagnosis involves an adequate examination of the affected patient. Medical clinicians must document every symptom that the patient presents with.
They must also use observation, medical history taking, laboratory test results to assess the patient’s condition to create a comprehensive diagnosis specific to that patient.
The Bottom Line
The knowledge of the differences between differential symptoms and indications is essential for everyone, especially in the healthcare system.
It assists healthcare providers in treating and providing patients with various healthcare options according to their health situation.
Overall, differential diagnosis is not easy. It requires adequate attention to detail and a great deal of time, especially in instances where a patient’s health issues are increasingly complicated.
Accurate symptom readings, medical history taking, laboratory test results all play a crucial role in making an accurate diagnosis.