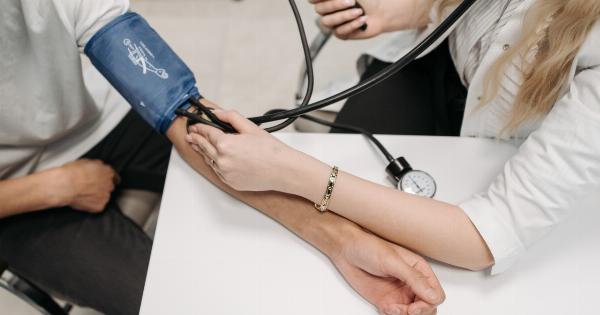
Taking accurate blood pressure measurements is crucial for monitoring and managing hypertension. High blood pressure, also known as hypertension, is a common condition that can increase the risk of heart disease, stroke, and other health problems.
In this guide, the Hellenic Hypertension Company provides valuable tips on how to accurately measure blood pressure at home or in a clinical setting.
Understanding Blood Pressure
Before learning how to take blood pressure, it’s important to understand what blood pressure is and how it is measured. Blood pressure refers to the force of blood pushing against the walls of the arteries as the heart pumps it around the body.
It is measured using two values – systolic pressure and diastolic pressure.
The Importance of Accurate Measurements
Accurate blood pressure measurements are essential for diagnosing hypertension and determining the effectiveness of treatment. Inaccurate readings can lead to incorrect diagnoses and improper management of the condition.
It is crucial to follow proper techniques and guidelines to obtain reliable measurements.
Preparing for a Blood Pressure Measurement
Before taking your blood pressure, it is important to prepare properly. Here are a few essential steps to follow:.
- Choose the Right Equipment: Select a validated blood pressure monitor that suits your needs. Automatic digital monitors with cuffs that fit around the upper arm are generally considered more accurate than wrist or finger monitors.
- Select a Quiet Environment: Find a calm and quiet place to perform the measurement. Avoid distractions and ensure the room temperature is comfortable.
- Rest and Relax: Sit quietly for at least 5 minutes before taking your blood pressure to calm your body and mind. Avoid smoking, drinking caffeine, or engaging in any strenuous activity before measurement as these can affect the readings.
- Position and Posture: Sit with your back straight and supported, feet flat on the floor, and arm resting on a table or armrest at heart level. Remove any tight clothing from your upper arm.
Measuring Blood Pressure
Now that you are prepared, follow these steps to measure your blood pressure accurately:.
- Apply the Cuff: Wrap the cuff around your upper arm so that the lower edge is about an inch above the bend of your elbow. The cuff should fit snugly but not be too tight.
- Find Your Pulse: Locate the radial artery on your wrist or the brachial artery on the inside of your elbow and place your index and middle fingers over it.
- Start Inflation: Press the start button on the blood pressure monitor to begin the inflation of the cuff. The cuff will gradually tighten around your arm.
- Listen for Heart Sounds: As the cuff deflates, listen carefully for the first pulse sound using a stethoscope placed over the brachial artery, or wait for the monitor to display the readings.
- Record the Measurements: Note down the systolic and diastolic pressure readings. Systolic pressure is the higher number, and diastolic pressure is the lower number. For example, a reading of 120/80 mmHg indicates a systolic pressure of 120 and a diastolic pressure of 80.
Tips for Accurate Measurements
Follow these additional tips to ensure accurate and reliable blood pressure measurements:.
- Consistency: Take your blood pressure at the same time each day to establish a consistent baseline for tracking changes over time.
- Noisy Environments: Avoid taking measurements in noisy environments as it can interfere with accurate readings.
- Multiple Readings: Take two to three readings with a short gap in between and calculate the average for a more precise result.
- Avoid Movement: Remain still and avoid talking or moving during the measurement as it can affect the accuracy.
- Check Both Arms: Occasionally measure your blood pressure in both arms to ensure consistency. If there is a significant difference, consult a healthcare professional.
Seeking Professional Help
While measuring blood pressure at home is convenient, it is still important to consult with a healthcare professional regularly.
They can provide guidance, interpret the results, and recommend any necessary lifestyle modifications or medications to manage hypertension effectively.
Taking Control of Hypertension
Accurate blood pressure measurements are vital for monitoring and managing hypertension.
By following the tips provided by the Hellenic Hypertension Company, individuals can take control of their blood pressure and work towards maintaining a healthy cardiovascular system.