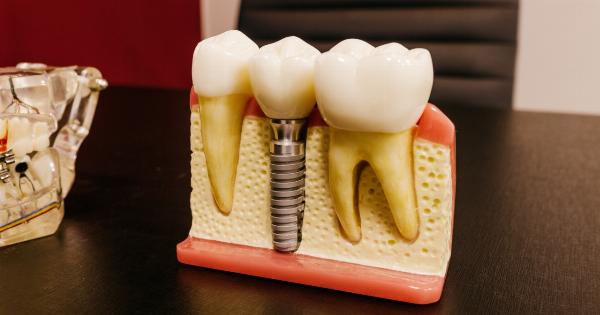
Gum cells have long been known to play a crucial role in maintaining oral health, but recent advancements in stem cell research have opened up new possibilities when it comes to tooth regeneration.
Scientists are now harnessing the regenerative potential of gum cells to create new teeth, offering hope to millions of people who suffer from tooth loss.
The Promise of Stem Cell Research
Stem cells are undifferentiated cells that have the remarkable ability to develop into different types of specialized cells in the body. This unique characteristic has made them a focus of extensive research across various fields, including dentistry.
By harnessing the regenerative potential of stem cells, scientists aim to develop new treatments and therapies for a wide range of diseases and conditions.
Gum Cells as a Valuable Source of Stem Cells
Gum cells, also known as gingival cells, have recently emerged as a valuable source of stem cells for tooth regeneration.
These cells can be obtained easily and non-invasively from the oral cavity, making them an attractive option for research and potential clinical applications. By isolating and expanding these gum cells, scientists can stimulate their differentiation into the specific cells needed for tooth formation.
How Gum Cells Enable New Tooth Growth
The process of tooth regeneration using gum cells begins with the extraction of a small sample of gingival tissue from the patient. From this sample, researchers isolate the gum cells and culture them in a lab.
By providing the cells with the appropriate growth factors and signaling molecules, scientists can steer their differentiation towards tooth-forming cells.
Once the gum cells have transformed into tooth-forming cells, they are seeded onto a biodegradable scaffold designed to resemble the shape and structure of a natural tooth.
This scaffold acts as a framework for the cells to grow and organize themselves, guiding the formation of a new tooth. Over time, the cells deposit minerals and harden, mimicking the process of dental enamel development.
Promising Results in Early Studies
Early studies exploring the potential of gum cell-based tooth regeneration have shown promising results. In an animal study conducted on rats, researchers successfully regenerated fully functional teeth using isolated gum cells.
The regenerated teeth closely resembled natural teeth in terms of structure, hardness, and overall appearance.
These findings have sparked considerable excitement in the scientific community and have paved the way for further research and development in this field.
Although the technique still needs to undergo extensive clinical trials before it can be used in humans, the early success is a strong indicator of the potential of gum cell-based tooth regeneration.
Potential Applications and Benefits of Gum Cell-Based Tooth Regeneration
Gum cell-based tooth regeneration offers several potential applications and benefits that could revolutionize the field of dentistry:.
1. Treatment for Tooth Loss
One of the most significant implications of gum cell-based tooth regeneration is its potential to provide an alternative treatment for tooth loss.
Traditional methods for replacing missing teeth, such as dental implants and bridges, have their limitations and may not be suitable for everyone. If gum cell-based tooth regeneration proves successful in clinical trials, it could offer a more natural and personalized approach to replacing lost teeth, eliminating many of the drawbacks associated with current options.
2. Restoration of Dental Function
Regenerated teeth derived from gum cells have the potential to restore full dental function.
Unlike dentures or dental implants, which may restrict certain food choices or require additional maintenance, regenerated teeth would be integrated into the mouth naturally and function just like natural teeth. This could greatly enhance the quality of life for individuals with missing teeth, allowing them to eat, speak, and smile with confidence.
3. Prevention of Bone Loss
When a tooth is lost, the surrounding bone begins to deteriorate due to lack of stimulation. This can lead to further dental problems and even changes in facial structure over time.
Gum cell-based tooth regeneration has the unique advantage of promoting bone growth as part of the tooth regeneration process. By stimulating bone formation, this technique could prevent bone loss and preserve the integrity of the jaw, providing long-term oral health benefits.
4. Aesthetically Pleasing Results
Regenerated teeth have the potential to closely resemble natural teeth in terms of appearance.
The underlying goal of gum cell-based tooth regeneration is to create fully functional, aesthetically pleasing teeth that blend seamlessly with the existing dentition. This would not only restore dental function but also enhance the overall appearance of the smile, boosting self-confidence and improving the quality of life for individuals with missing teeth.
Challenges and Future Directions
While the early results of gum cell-based tooth regeneration are promising, several challenges need to be addressed before this technique can be widely adopted in clinical practice:.
1. Clinical Trials and Regulatory Approval
Before gum cell-based tooth regeneration can become a standard treatment option, it must undergo extensive clinical trials to ensure its safety and efficacy in humans.
Additionally, regulatory approval from health authorities is necessary to validate the technique and ensure compliance with established medical standards.
2. Optimization of the Regeneration Process
Researchers are continuously working to optimize the regeneration process to improve the outcomes of gum cell-based tooth regeneration.
This includes refining the techniques for isolating and expanding gum cells, developing better scaffolds to support tooth formation, and enhancing the methods for guiding cellular differentiation.
3. Cost and Accessibility
As with any emerging medical technology, cost and accessibility may pose challenges in the initial stages. However, advancements in research and technology often lead to greater affordability and availability over time.
It is expected that gum cell-based tooth regeneration will become more accessible as techniques improve and become more widespread.
Conclusion
Gum cells have emerged as a valuable source of stem cells for tooth regeneration, offering hope for individuals who suffer from tooth loss.
Early studies have shown promising results, and the potential applications and benefits of gum cell-based tooth regeneration are vast. While several challenges need to be addressed before it can become a mainstream treatment option, the future looks promising for this groundbreaking technique.
As research and technology continue to advance, gum cell-based tooth regeneration may soon become a reality, revolutionizing the field of dentistry and providing a natural, personalized approach to restoring dental function and aesthetics.