As a parent, you always want what’s best for your child, and their health is no exception. While most parents are vigilant about monitoring their child’s growth and development, sometimes certain conditions can go unnoticed.
One such condition is scoliosis, a disorder that affects the spine and can cause significant discomfort and potential health complications if left untreated.
What is scoliosis?
Scoliosis is a medical condition characterized by an abnormal curvature of the spine.
Instead of the spine appearing straight when viewed from the front or back, it may exhibit a sideways curvature resembling an “S” or a “C” shape. This abnormal curvature can vary in severity, with some cases being mild and hardly noticeable, while others are more pronounced and can cause noticeable physical changes.
What causes scoliosis?
While the exact cause of scoliosis is often unknown, there are several factors that may contribute to its development. Some of the known causes include:.
1. Congenital scoliosis
This form of scoliosis is present at birth and is caused by abnormal spine development in the womb. It may be associated with other congenital disabilities or syndromes.
2. Neuromuscular scoliosis
Neuromuscular conditions such as cerebral palsy or muscular dystrophy can cause the muscles supporting the spine to weaken, resulting in an abnormal curvature.
3. Idiopathic scoliosis
This is the most common form of scoliosis and typically develops during adolescence or early teenage years. The exact cause is unknown, but it often occurs in families with a history of the condition.
4. Traumatic scoliosis
In some cases, scoliosis can be the result of an injury or trauma to the spine, such as a fracture or surgery.
Signs and symptoms of scoliosis
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of scoliosis is crucial for early detection and prompt treatment. Here are some common indicators that your child may have scoliosis:.
1. Uneven shoulders or hips
If you notice that your child’s shoulders or hips appear uneven or one side looks higher than the other, it may be a sign of scoliosis. A curvature in the spine can cause these asymmetries in the body.
2. Prominent shoulder blade or rib cage
An abnormally curved spine can cause one shoulder blade or one side of the ribcage to protrude more than the other.
3. Uneven waist
A visible curvature in the spine can cause the waistline to appear uneven, with one side being higher or more pronounced than the other.
4. Leaning to one side
If you observe that your child consistently leans or tilts to one side rather than standing upright, it may be an indication of scoliosis.
5. Back pain or discomfort
While not all cases of scoliosis are painful, some individuals may experience discomfort or pain in the back, particularly after prolonged periods of standing or sitting.
How to confirm a scoliosis diagnosis?
If you suspect that your child may have scoliosis based on the signs and symptoms mentioned above, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis.
The following steps are typically involved in confirming a scoliosis diagnosis:.
1. Physical examination
Your healthcare provider will conduct a physical examination, visually assess your child’s back, and check for noticeable curvature or asymmetry.
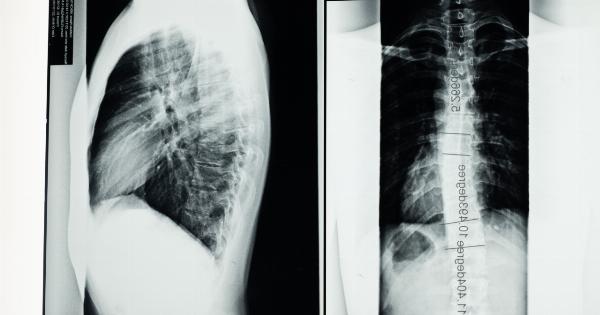
2. X-rays
X-rays are commonly used to confirm the presence of scoliosis and evaluate the degree of curvature. These images allow healthcare professionals to determine the severity of the condition and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
3. Other imaging tests
In some cases, additional imaging tests such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT) scans may be required to assess the spinal structures and identify any underlying causes.
Treatment options for scoliosis
The treatment approach for scoliosis largely depends on the severity of the curvature and the age of the individual. Here are some common treatment options:.
1. Observation and monitoring
For mild cases of scoliosis, especially in growing children, monitoring the condition may be the recommended approach.
Regular check-ups and periodic X-rays can help track the progression of the curvature and ensure appropriate intervention if it worsens.
2. Bracing
If the curvature progresses beyond a certain threshold, your child may be prescribed a brace. A brace is typically worn for several hours a day and can help slow down or halt the progression of the curvature as the child grows.
3. Physical therapy and exercise
Physical therapy exercises specifically designed for scoliosis can help improve posture, strengthen the back and core muscles, and alleviate discomfort associated with the condition.
4. Surgery
In severe cases of scoliosis where the curvature is significant and progressing rapidly, surgery may be recommended.
The main goal of surgery is to correct the curvature and stabilize the spine using various techniques, such as spinal fusion or the insertion of metal rods.
Preventing scoliosis
While it may not be possible to prevent all cases of scoliosis, there are some steps you can take to promote a healthy spine and reduce the risk of developing the condition:.
1. Encourage good posture
Incorporate good posture practices into your child’s routine from an early age. Emphasize the importance of sitting and standing up straight, avoiding slouching or hunching over.
2. Promote regular exercise
Encourage your child to engage in physical activities that promote overall body strength and flexibility. Exercises that focus on core muscles and back strength can help support a healthy spine.
3. Use proper backpack ergonomics
If your child carries a backpack to school, make sure they are using it correctly to minimize strain on their back. Opt for backpacks with padded straps and a waist belt to distribute the weight evenly.
4. Regular check-ups
Make sure your child attends regular check-ups with their healthcare provider. This allows for early detection of any potential health issues, including scoliosis.
Conclusion
Monitoring your child’s back and paying attention to any signs or symptoms of scoliosis is essential for early detection and timely intervention.
If you suspect your child may have scoliosis, consult with a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation and proper diagnosis. With early intervention and appropriate treatment, the long-term outcomes for individuals with scoliosis can be greatly improved.