Glaucoma is a group of eye conditions that damage the optic nerve, which is responsible for transmitting visual information from the eye to the brain. It is often associated with a buildup of pressure inside the eye, known as intraocular pressure (IOP).
If left untreated, glaucoma can lead to irreversible vision loss and even blindness. Early-stage glaucoma may have no noticeable symptoms, making regular eye exams crucial for early detection and treatment.
The Importance of Early Detection
Early detection of glaucoma can significantly improve treatment outcomes and preserve vision. Regular eye exams, especially for individuals with a higher risk of developing glaucoma, such as those with a family history or advanced age, are essential.
Timely diagnosis allows for appropriate interventions to reduce the risk of vision loss.
Risk Factors for Glaucoma
Several factors increase the likelihood of developing glaucoma. It is important to be aware of these risk factors and take appropriate measures to protect your vision:.
1. Family History
If you have a close relative with glaucoma, you are at a higher risk for developing the condition. Make sure to inform your eye doctor about any family history of glaucoma during eye examinations.
2. Age
Glaucoma becomes more common as you age, with the risk increasing significantly after the age of 40. As you grow older, it is crucial to have regular eye exams to detect any signs of glaucoma early on.
3. High Intraocular Pressure
Elevated intraocular pressure is a typical characteristic of glaucoma, although not all individuals with high IOP develop the condition. Regular eye pressure checks and comprehensive eye exams can help determine if you are at risk.
4. Thin Corneas
People with thin corneas are more susceptible to developing glaucoma. Eye care professionals can measure corneal thickness during routine eye exams to assess your risk.
5. Ethnic Background
Certain ethnicities, such as African Americans, Hispanics, and Asians, have a higher risk of developing glaucoma. It is essential for individuals from these backgrounds to be diligent in scheduling regular eye exams.
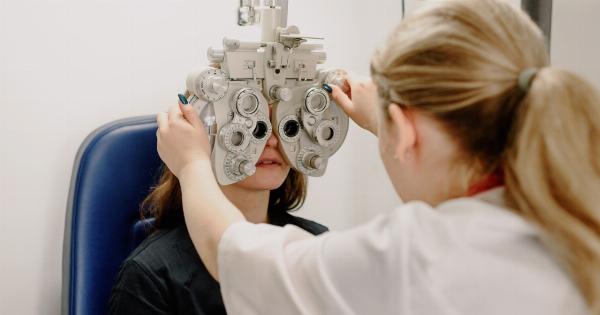
Regular Eye Exams
Regular eye exams are crucial for early detection and monitoring of glaucoma. Eye care professionals can perform various tests to assess your eye health and detect any signs of glaucoma. These tests may include:.
1. Tonometry
Tonometry measures the pressure inside your eye by using a device called a tonometer. It is a quick and painless procedure that helps evaluate your risk for glaucoma.
2. Visual Field Testing
Visual field testing assesses your peripheral vision. Changes in peripheral vision often occur in individuals with glaucoma.
By performing this test regularly, any early signs of glaucomatous vision loss can be detected and appropriate treatment initiated.
3. Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT)
OCT uses light waves to capture detailed images of the optic nerve and retina. This imaging test helps in early diagnosis and monitoring of glaucoma.
Treatment Options
While there is no cure for glaucoma, various treatment options can manage the condition and prevent further vision loss. The choice of treatment depends on the type and severity of glaucoma. The most common treatment options include:.
1. Eye Drops
Prescription eye drops can be used to reduce intraocular pressure and slow or prevent damage to the optic nerve. It is essential to follow the prescribed regimen and attend regular follow-up visits to monitor the effectiveness of the eye drops.
2. Oral Medications
In some cases, oral medications may be prescribed alongside or instead of eye drops. These medications work by reducing intraocular pressure and preventing optic nerve damage.
3. Laser Therapy
Laser therapy, such as trabeculoplasty or selective laser trabeculoplasty (SLT), can help increase drainage of fluid from the eye, lowering intraocular pressure.
This procedure is typically performed as an outpatient procedure and can reduce the need for long-term medication use.
4. Surgery
In advanced cases or when other treatments are ineffective, surgical intervention may be necessary. Surgical options for glaucoma include trabeculectomy, drainage implants, and minimally invasive glaucoma surgery (MIGS).
These procedures aim to improve the outflow of fluid from the eye, reducing intraocular pressure.
Lifestyle Changes and Prevention
While certain risk factors for glaucoma, such as age and family history, cannot be changed, you can take steps to reduce your overall risk and protect your vision:.
1. Regular Exercise
Engaging in regular exercise and leading an active lifestyle can help maintain healthy intraocular pressure levels and overall eye health.
2. Eating a Balanced Diet
A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and leafy greens is beneficial for maintaining eye health. Antioxidant-rich foods, such as those containing vitamins C and E, help protect against glaucoma.
3. Avoid Smoking and Excessive Alcohol Consumption
Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption have been linked to an increased risk of glaucoma. Quitting smoking and minimizing alcohol intake can help safeguard your vision.
4. Protect Your Eyes
Wearing protective eyewear, such as safety goggles or sunglasses, can shield your eyes from potential injuries and harmful ultraviolet (UV) rays.
Conclusion
Early detection and intervention are crucial for preserving vision and managing glaucoma effectively.
By understanding the risk factors, scheduling regular eye exams, and adopting a healthy lifestyle, you can significantly reduce your risk of developing glaucoma. Remember, your eyesight is a precious gift, and taking proactive measures to keep your vision safe from early-stage glaucoma is an investment in your long-term eye health.