Scoliosis is a condition that causes the spine to curve. It can affect people of all ages, but it’s usually diagnosed in children and teens. When parents first learn that their child has scoliosis, they may feel overwhelmed and unsure of what to do.
However, with the right management strategies in place, children with scoliosis can lead normal, healthy lives.
Understanding Scoliosis
Scoliosis is a complex condition that can be caused by a variety of factors. In some cases, scoliosis is caused by genetics, while in other cases it may be caused by other underlying medical conditions.
The curvature of the spine can range from mild to severe and can impact the health and well-being of the child as they grow and develop.
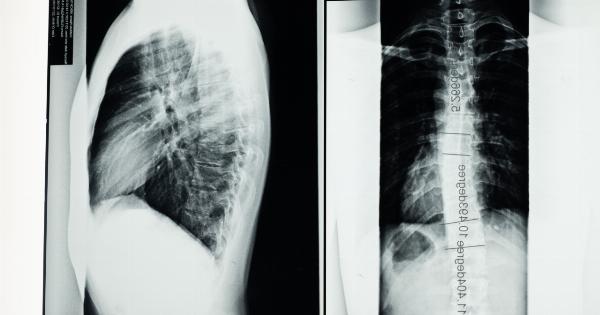
Diagnosing Scoliosis
Diagnosing scoliosis involves a physical examination from a healthcare professional. They will check the child’s spine for signs of curvature or asymmetry.
If scoliosis is suspected, the healthcare professional may order imaging tests such as an X-ray or MRI to confirm the diagnosis and determine the severity of the curvature.
Treatment Options
The treatment for scoliosis depends on several factors, including the child’s age, the severity of the curvature, and the underlying cause of the condition. Mild cases of scoliosis may not require treatment.
However, more severe cases may require braces or surgery to correct the curvature of the spine.
Bracing
Bracing is often used to treat scoliosis in growing children and teens. The goal of bracing is to prevent the curve from getting worse as the child grows.
Bracing involves wearing a special brace that fits around the torso and is designed to put pressure on the spine to prevent further curvature. The length of time the brace needs to be worn varies depending on the severity of the curvature and the child’s age.
Surgery
In more severe cases of scoliosis, surgery may be required. Surgery involves correcting the curvature of the spine using metal rods, hooks, or screws.
The goal of surgery is to straighten the spine as much as possible to prevent further health complications. Recovery from surgery can be lengthy, and the child may need to wear a brace for several months after the procedure.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy can be helpful for children with scoliosis, particularly after surgery. Physical therapy can help restore mobility and strength to the spine and surrounding muscles.
It can also help improve the child’s posture and reduce the risk of future complications.
Daily Living Tips
Managing scoliosis is not just about medical treatments or visits to the doctor. There are several things that parents can do at home to help their child live a healthy, fulfilling life with scoliosis.
Encouraging regular exercise and physical activity can help build strength and improve flexibility. Maintaining good posture is also important, as slouching can exacerbate the curvature of the spine. Additionally, eating a healthy and balanced diet can help support overall health and well-being.
Support Systems
Living with scoliosis can be challenging, both physically and emotionally. It’s important for children and families affected by scoliosis to have access to support systems that can provide encouragement, guidance, and resources.
Support groups can be a valuable resource for families affected by scoliosis, providing a network of people who share similar experiences and can offer advice and support.
The Importance of Regular Check-Ups
Managing scoliosis requires regular check-ups with a healthcare professional to ensure that the condition is properly managed. Healthcare professionals can monitor the curvature of the spine and ensure that treatment is working effectively.
Additionally, they can identify any potential health complications and recommend appropriate treatment options.
Conclusion
Scoliosis can be a challenging condition to manage, but with the right support and treatment options in place, children with scoliosis can lead happy, healthy lives.
Parents of children with scoliosis should work closely with healthcare professionals to develop a comprehensive treatment plan that addresses the child’s unique needs and supports their overall health and well-being.