Oral cancer is a malignant tumor that can affect any part of the mouth or throat, including the tongue, lips, gums, cheeks, roof, and floor of the mouth. It can also manifest as cancer in the salivary glands, tonsils, and pharynx.
What Causes Oral Cancer?
Although the exact cause of oral cancer is not known, certain factors may increase a person’s risk of developing the disease.
Tobacco Use
The use of tobacco in any form (smoking, chewing, or snuffing) significantly increases the risk of oral cancer. Smokers are six times more likely to develop oral cancer than non-smokers.
And, people who smoke cigars or pipes are at a higher risk of developing cancer of the lips, tongue, or throat.
Alcohol Consumption
Drinking alcohol regularly and in excess can also increase the risk of developing oral cancer. Heavy drinkers are at least twice as likely to get oral cancer than non-drinkers.
Human Papillomavirus (HPV)
HPV is a sexually transmitted infection that can cause oral cancer. It is most commonly spread through oral sex. People who have HPV-16 are at a higher risk of developing oral cancer than those who do not have it.
Individuals who have multiple sexual partners and those who engage in oral sex are at a greater risk of getting HPV infection.
Poor Oral Hygiene
Poor oral hygiene can also contribute to oral cancer development. People who do not brush their teeth, floss, or have regular dental checkups are more likely to develop oral cancer.
Poor oral hygiene can lead to the buildup of harmful bacteria that can cause inflammation and other oral problems that increase the risk of oral cancer.
Early Detection and Treatment of Oral Cancer
Early detection of oral cancer is critical to successful treatment and prognosis. Treatment is most effective when the cancer is detected in the earliest stages and has not spread to other parts of the body.
The goal is to detect cancer before it has a chance to grow, spread, and become more difficult to treat.
Signs and Symptoms of Oral Cancer
It’s important to be aware of the signs and symptoms of oral cancer so you can report them to your doctor or dentist as soon as possible. The most common symptoms of oral cancer include:.
- Persistent mouth sores
- White or red patches inside the mouth or on the lips
- Swelling or lumps in the mouth or throat
- Bleeding in the mouth
- Pain or difficulty swallowing
- Chronic sore throat
- Difficulty speaking
- Numbness in the mouth or tongue
If you experience any of these symptoms, see your doctor or dentist promptly for a diagnosis.
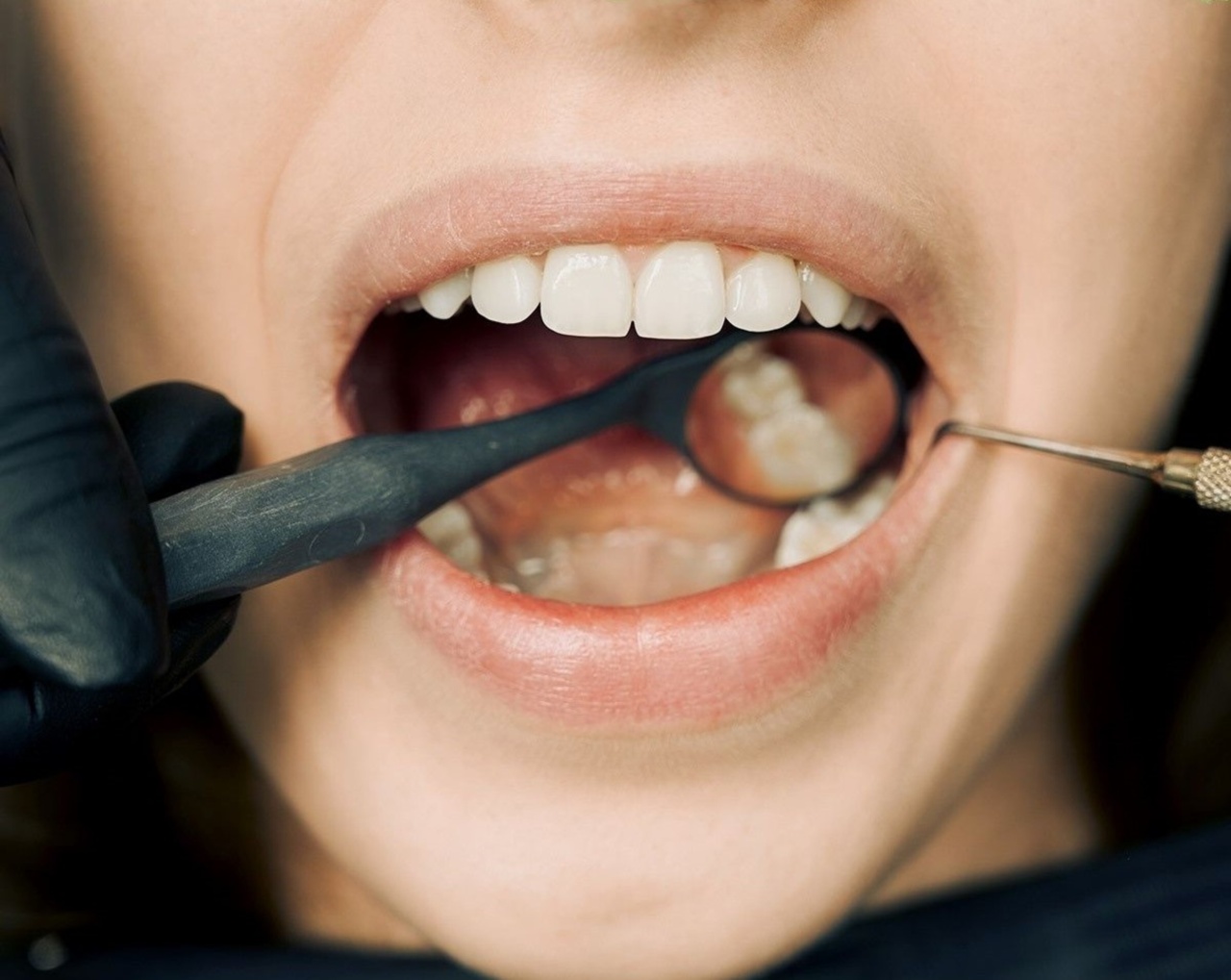
Mouth Examination for Early Detection of Oral Cancer
Your dentist or doctor can perform a simple mouth examination that can detect the early signs of oral cancer.
The examination involves checking the mouth and tongue for abnormalities, feeling the inside of the mouth with a gloved finger, and examining the neck for lumps or swelling.
Using Ferries for the Early Detection of Oral Cancer
Fluorescence visualization (FV) is a new technology used in the early detection of oral cancer. FV uses a special light and a mouthwash that causes abnormal cells in the mouth to appear as bright spots, making them easier to detect.
Ferries, which are small portable lights, can be used to examine the mouth for signs of oral cancer.
The ferry is used to emit a blue light in the oral cavity that can distinguish between normal and abnormal tissue and make it easier for the doctor to identify any suspicious areas that need further evaluation.
Treatment for Oral Cancer
The treatment for oral cancer depends on the stage and location of the cancer. Treatment may include:.
- Surgery to remove the cancerous cells
- Radiation therapy to kill the cancerous cells
- Chemotherapy to remove the cancerous cells
- Targeted therapy to treat specific types of oral cancer
Your doctor will recommend the most appropriate treatment plan for your type and stage of oral cancer.
Prevention of Oral Cancer
The best way to prevent oral cancer is to make healthy choices that reduce your risk of developing the disease.
- Quit smoking or using tobacco products
- Limit alcohol consumption
- Practice good oral hygiene by brushing and flossing regularly and visiting the dentist for checkups and cleanings at least twice a year
- Get vaccinated against HPV
By taking these steps, you can significantly reduce your risk of developing oral cancer.