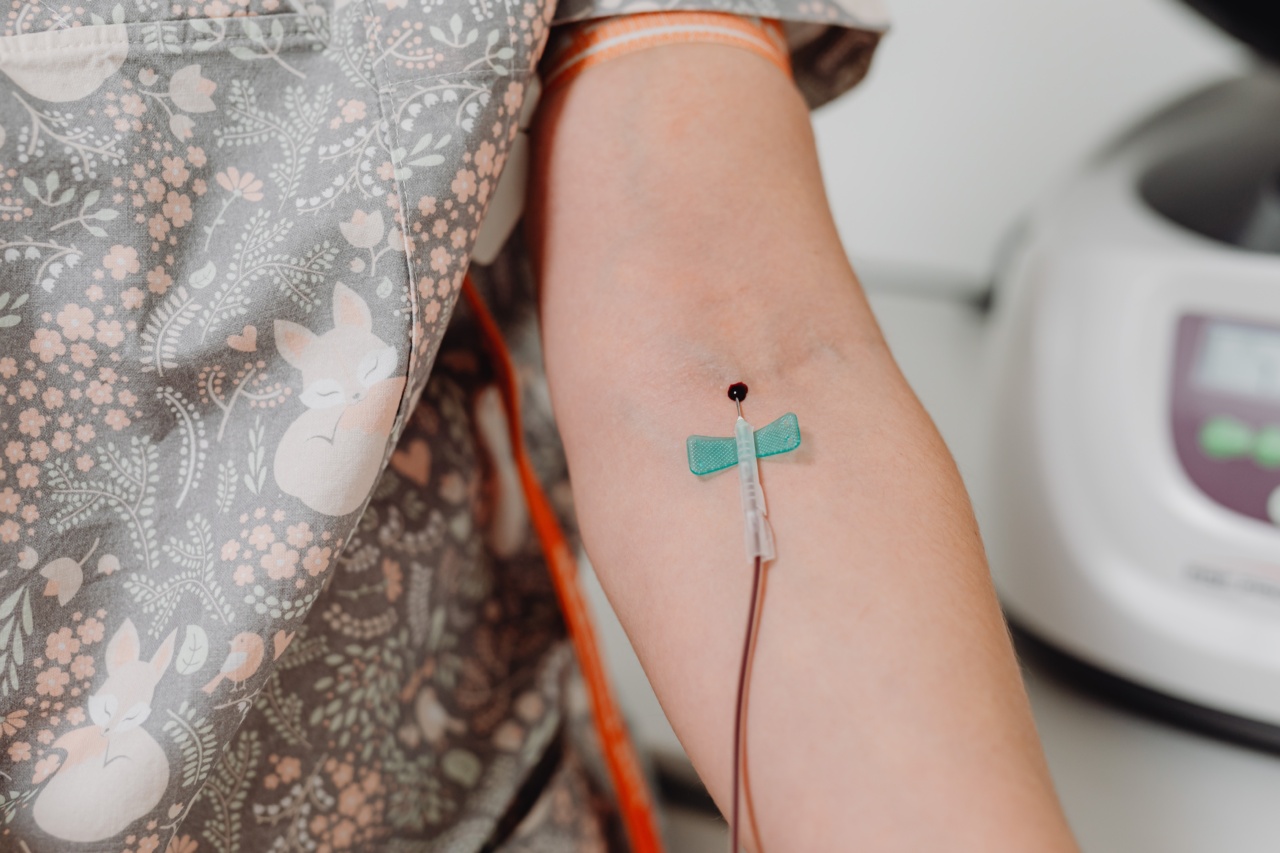
Peripheral injections are medications or fluids that are injected into the veins or other tissues outside the central nervous system.
These injections can have several therapeutic or diagnostic purposes, but they are generally used to treat various conditions and diseases. Peripheral injection is the administration of drugs through the veins in the arm, legs or hands or through other body sites such as the abdomen, chest, buttocks, or other parts of the body.
Purpose of Peripheral Injection
Peripheral injections are used to provide medications for the management of various conditions and diseases, such as dehydration, infections, joint pain, arthritis, cancer, and cardiovascular diseases.
These injections can provide faster and more effective results than oral medications as they go directly into the bloodstream, bypassing the digestive system. Some common uses of peripheral injections are:.
Fluid and Electrolyte Replacement
Peripheral injection is used to supply fluids and electrolytes to patients who are dehydrated or have lost fluids due to injury, illness, or surgery.
This technique can help restore body fluids, balance fluid and electrolyte levels, and prevent dehydration-related complications such as kidney problems, low blood pressure, and shock.
Medication Administration
Peripheral injection is used to administer a variety of medications, such as antibiotics, pain relief drugs, anti-inflammatory agents, and chemotherapy agents.
These drugs can be used to treat various conditions such as infections, inflammation, pain, and cancer. Peripheral injections are often used to control pain, fever and inflammation when oral medications are not effective.
Blood Transfusions
Peripheral injection is also used for the transfusion of blood products such as packed red blood cells, platelets, and plasma.
These blood products are used to treat conditions such as anemia, clotting disorders, and to replace lost blood due to injury or surgery.
Diagnostic and Imaging Procedures
Peripheral injection is used for diagnostic and imaging procedures such as CT scans, MRIs, and X-rays. Contrast agents are injected into the veins before the procedure to highlight specific organs or tissues in the images.
Types of Peripheral Injections
Peripheral injections are classified into several types based on the location of the injection site, the type of medication or fluid used, and the duration of treatment. Some common types of peripheral injections are:.
Intravenous (IV) Injection
IV injection is the most common type of peripheral injection. This involves injecting medication or fluids directly into the veins of the arms or hands using a needle or catheter.
This technique can provide fast and reliable delivery of medications to the bloodstream, but it requires a skilled healthcare professional to perform the injection reliably and safely.
Intramuscular (IM) Injection
IM injections are used to inject medications into the muscles of the arms, legs, or buttocks. This technique is used for medications that cannot be absorbed through the veins and require a longer period to take effect.
Common medications given via IM injection include vaccines, hormones, antipsychotics, and antibiotics.
Subcutaneous (SC) Injection
SC injection is used to inject medications under the skin in the fatty tissue layer. Common medications given via SC injection include insulin, vaccines, anticoagulants, and pain relief drugs.
SC injections are generally easy to perform, and the medications are slowly released into the bloodstream over time.
Intradermal (ID) Injection
ID injection is used to inject medications into the skin. This technique is commonly used for diagnostic purposes such as allergy testing, tuberculosis testing, and some vaccinations.
The medication is injected into the top layer of the skin, and the healthcare professional will monitor the reaction to the medication.
Risks and Precautions
Peripheral injections are generally considered safe and effective, but there are some risks associated with the procedure. Some potential risks are:.
- Bleeding, infection, or inflammation at the injection site
- An allergic reaction to the medication or fluid
- Damage to the veins or other tissues due to improper injection technique or insertion of the needle
- Side effects such as nausea, vomiting, fever, and chills
To avoid complications, healthcare professionals should follow strict guidelines for medication preparation, injection technique, and monitoring of patients.
Patients should inform their healthcare providers about any allergies, medical conditions, or medications they are taking before undergoing peripheral injection.
Conclusion
Peripheral injections are a common medical procedure used to treat various conditions and diseases. These injections can provide faster and more effective results than oral medications as they go directly into the bloodstream.
Peripheral injections can cause some side effects and risks, and patients should discuss the procedure with their healthcare provider before undergoing the treatment.