Throughout pregnancy, the health and well-being of both mother and baby are of utmost importance. Regular prenatal care and monitoring are essential to ensure a healthy pregnancy and safe delivery.
One crucial aspect of this monitoring is fetal monitoring, which plays a significant role in assessing the well-being and development of the baby. In this article, we will explore the importance of fetal monitoring and its various methods and techniques.
The Purpose of Fetal Monitoring
Fetal monitoring involves tracking the baby’s heart rate, movements, and overall condition throughout pregnancy.
The primary purpose of this monitoring is to ensure that the baby is receiving sufficient oxygen and nutrients through the placenta and umbilical cord. By observing the baby’s heart rate and movements, healthcare professionals can detect any signs of distress or potential complications.
Methods of Fetal Monitoring
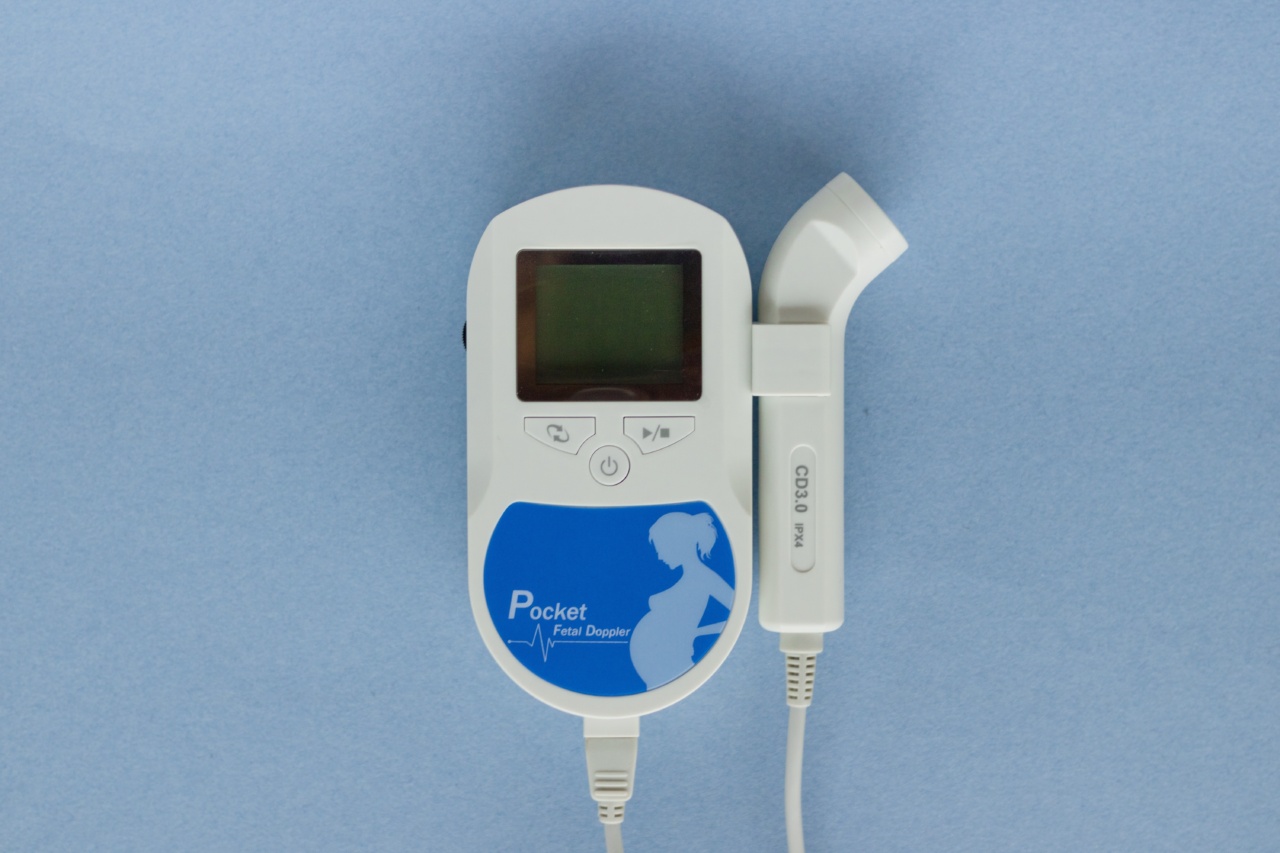
There are two main methods of fetal monitoring: external and internal. External monitoring involves using devices placed on the mother’s abdomen to monitor the baby’s heart rate and uterine contractions.
One common external monitoring technique is the Doppler ultrasound, which uses sound waves to detect and amplify the baby’s heartbeat. Another commonly used method is the use of electronic fetal monitors, which record the baby’s heart rate and uterine contractions on a graph.
Internal fetal monitoring, on the other hand, involves placing a probe directly on the baby’s scalp through the cervix.
This method provides more accurate and continuous readings of the baby’s heart rate and can also measure the strength and duration of uterine contractions. Internal monitoring is usually reserved for high-risk pregnancies or situations where external monitoring may not be sufficient.
When is Fetal Monitoring Necessary?
Fetal monitoring is typically performed during prenatal visits, especially in the later stages of pregnancy. However, there are specific situations where more intensive monitoring is necessary. These include:.
1. High-Risk Pregnancies
High-risk pregnancies, such as those involving pre-existing medical conditions, multiples, or a history of complications, often require more frequent and comprehensive fetal monitoring.
This ensures that any potential issues are detected and managed promptly.
2. Reduced Fetal Movement
If a mother notices a significant decrease in her baby’s movements, it may indicate a problem. Fetal monitoring can help assess the baby’s well-being in such cases and determine if any intervention is necessary.
3. Preterm Labor
When a woman experiences preterm labor or is at risk of premature delivery, fetal monitoring becomes crucial.
It helps determine the baby’s condition and assists healthcare providers in making decisions about interventions and treatments to support the baby’s development.
4. Post-Term Pregnancy
If a pregnancy exceeds the expected due date, fetal monitoring can help assess the baby’s well-being and ensure that the baby is not experiencing any distress due to prolonged gestation.
Benefits and Limitations of Fetal Monitoring
Fetal monitoring provides numerous benefits in ensuring the well-being of both the mother and baby. Some of the key advantages include:.
1. Early Detection of Problems
Continuous monitoring can detect any signs of distress, such as a decreased heart rate or inadequate oxygen supply, allowing healthcare providers to intervene promptly and prevent potential complications.
2. Evaluation of Contractions
Monitoring uterine contractions helps healthcare professionals assess the strength, duration, and frequency of contractions, which is crucial in managing labor and determining the progress of delivery.
3. Peace of Mind for Expectant Mothers
Fetal monitoring provides reassurance to expectant mothers, allowing them to monitor their baby’s well-being and be actively involved in their pregnancy journey.
Despite its benefits, fetal monitoring does have some limitations. It is important to understand that fetal monitoring provides information that must be interpreted by trained healthcare professionals.
In some cases, the monitoring may result in false alarms, causing unnecessary anxiety for expectant mothers. Additionally, continuous monitoring may restrict a woman’s movement during labor, making her feel anxious or uncomfortable.
The Future of Fetal Monitoring
Technological advancements continue to shape the field of fetal monitoring, paving the way for more accurate and non-invasive methods.
One such advancement is wireless fetal monitoring, where sensors are attached to the mother’s abdomen, allowing her to move more freely during labor. This type of monitoring provides real-time data and increases the comfort and satisfaction of expectant mothers.
Another promising development is the use of artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms to analyze fetal monitoring data.
AI algorithms can identify patterns and anomalies, helping healthcare providers make quicker and more accurate decisions about necessary interventions.
Conclusion
Fetal monitoring plays a vital role in assessing the well-being and development of the baby throughout pregnancy.
By tracking the baby’s heart rate, movements, and overall condition, healthcare professionals can detect any signs of distress or potential complications. Through both external and internal monitoring methods, expectant mothers and their healthcare providers can ensure a safe and healthy pregnancy journey.
Advancements in technology, such as wireless monitoring and AI algorithms, continue to enhance the accuracy and convenience of fetal monitoring.