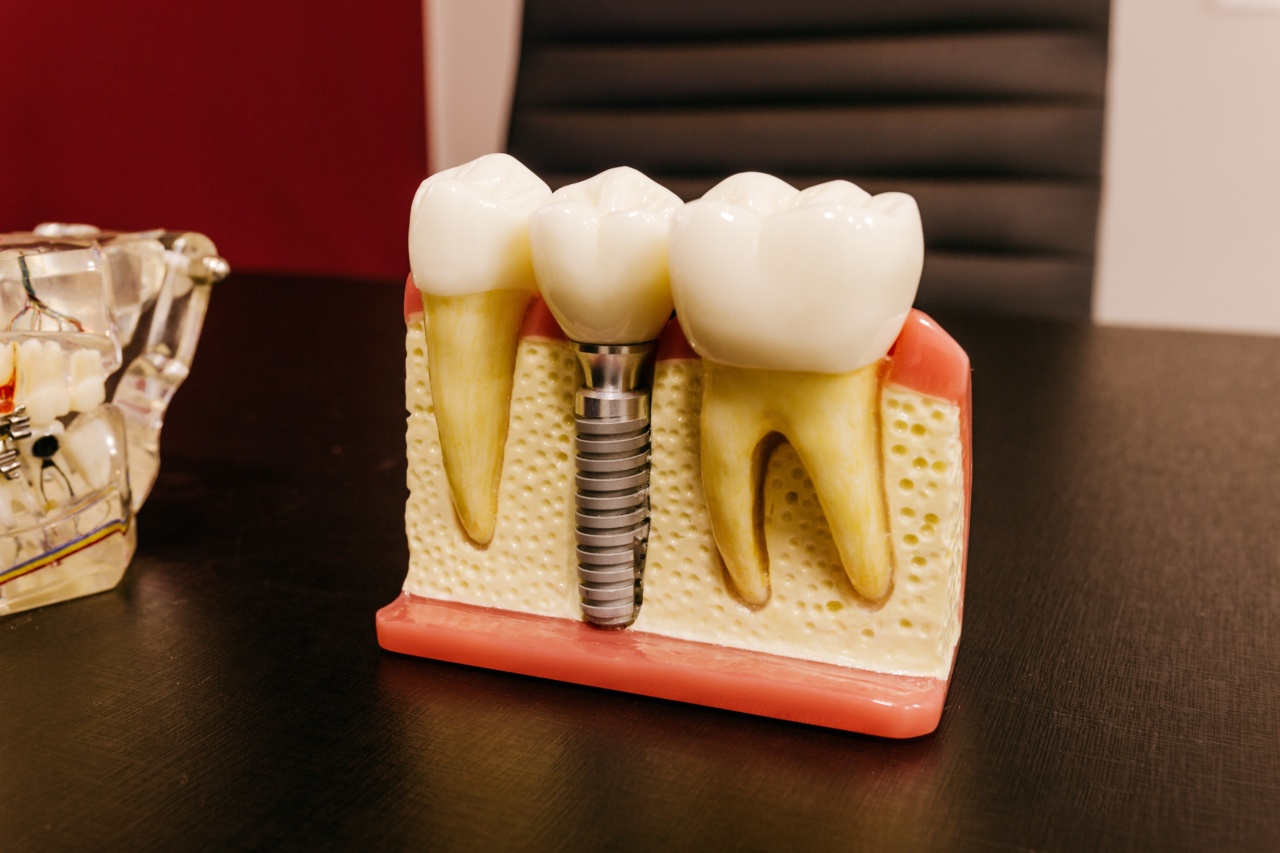
For centuries, dentists have been working tirelessly to find solutions for tooth loss.
While painful and expensive dental implants, bridges, and dentures have long been the standard options for those with missing or damaged teeth, recent advancements in regenerative medicine are offering a new and groundbreaking solution: regenerating teeth from gum tissue.
What is Regenerative Dentistry?
Regenerative dentistry is a rapidly developing field that focuses on using biological agents and materials to replace or regenerate lost or damaged teeth, gums, and bone tissues in the oral cavity.
The field of regenerative dentistry involves the use of stem cells, growth factors, and scaffolds to activate the body’s natural healing processes and regrow lost or damaged tissues.
Regenerative dentistry also involves tissue engineering, where new tissues can be grown in a laboratory and later implanted into the patient’s oral cavity.
Benefits of Regenerated Teeth
The benefits of regenerated teeth over traditional dental implants, bridges, and dentures are numerous. Some of the most significant advantages include:.
- Long-term durability – regenerated teeth have a higher chance of lasting a lifetime, unlike traditional dental implants, bridges, and dentures, which may require repairs or replacements over time.
- Natural appearance – regenerated teeth look and feel like natural teeth, which can significantly increase the patient’s self-confidence and quality of life.
- Less invasive – regenerated teeth do not require extensive surgery or extraction of the affected teeth, which can minimize the risk of complications and speed up the recovery process.
- Improved function – regenerated teeth offer a better chewing and biting function, which can improve the patient’s diet and overall health.
The Journey of Regenerated Teeth from Gum Tissue
Regenerating teeth from gum tissue is a complex process that involves several steps.
The journey of regenerated teeth from gum tissue starts with the extraction of the damaged or diseased tooth, followed by the creation of a scaffold and the placement of stem cells on it.
After the stem cells are placed on the scaffold, they are allowed to multiply and differentiate into different cell types, including odontoblasts, which are the cells responsible for producing dentin, the hard tissue that makes up the majority of a tooth.
The next step is to place the scaffold and stem cells into the tooth socket, where they will continue to grow and differentiate into different tooth tissues, including dentin, pulp, and enamel.
Once the new tooth has fully developed, it can be implanted into the patient’s oral cavity, where it will fuse with the surrounding tissues and become a permanent part of the patient’s smile.
The Future of Regenerated Teeth from Gum Tissue
The future of regenerated teeth from gum tissue is bright. Researchers and dental professionals are continuing to refine the process, making it more efficient, effective, and accessible to patients around the world.
The advancements in regenerative dentistry are paving the way for a world where tooth loss no longer means a lifetime of discomfort and embarrassment.
Instead, patients can look forward to a bright, healthy, and natural-looking smile, all thanks to the revolutionary breakthroughs in regenerative medicine.
The Bottom Line
Regenerating teeth from gum tissue is one of the most significant and groundbreaking advancements in modern dentistry.
With its long-term durability, natural appearance, less invasive nature, and improved function, regenerated teeth offer a superior alternative to traditional dental treatments. As researchers and dental professionals continue to refine the process, we can only look forward to a future where tooth loss is no longer a barrier to a happy and healthy life.