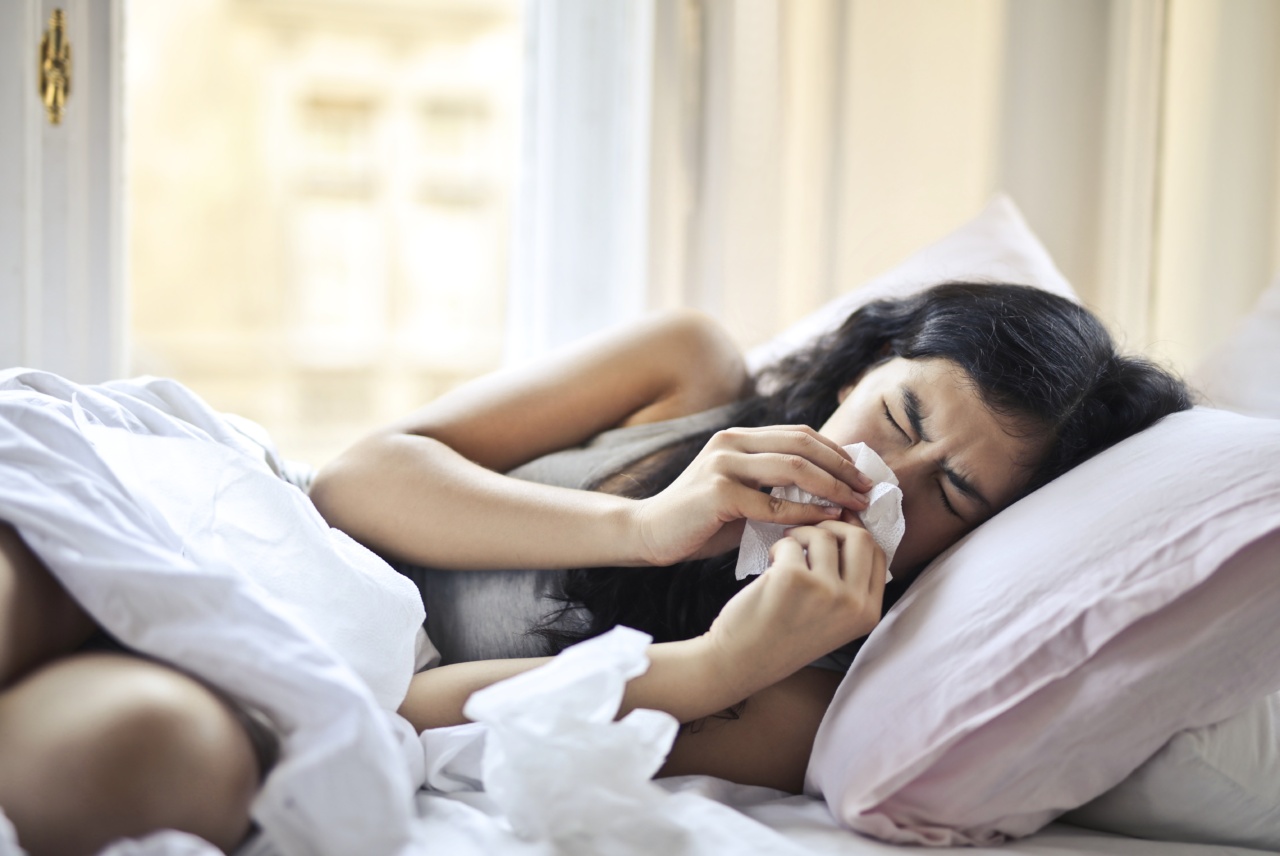
The sneezing reflex is a natural mechanism of the body that helps in expelling irritants, allergens, and foreign substances from the nasal passages. Sneezing is a protective reflex that plays a crucial role in maintaining respiratory health.
However, there are situations where people intentionally or unintentionally try to suppress or interrupt the sneezing reflex. In this article, we will explore the risks associated with interrupting the sneezing reflex and why it’s important to allow the body to go through the sneezing process.
Understanding the Sneezing Reflex
Sneezing is a sudden and forceful expulsion of air from the nose and mouth. It is triggered by irritation to the nasal mucosa, which can be caused by various factors such as allergens, dust, smoke, cold air, or even bright light.
The purpose of sneezing is to clear the nasal passages from these irritants and protect the respiratory system.
1. Nasal Irritation
When we interrupt the sneezing reflex, the irritants and allergens that caused the initial stimulation of the reflex can remain in the nasal passages. This can lead to prolonged nasal irritation, which may result in discomfort, itching, and congestion.
Suppressing sneezes can prevent the body from effectively clearing these irritants, worsening the symptoms and potentially leading to sinus infections.
2. Sinus Infections
Allowing the sneezing reflex to occur naturally helps in preventing sinus infections. Sinusitis is a common condition that occurs when the nasal passages and the sinuses become inflamed and infected.
Suppressing sneezes can hinder the body’s ability to expel bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens from the nasal passages, increasing the risk of developing sinus infections.
3. Nasal Congestion
By interrupting the sneezing reflex, individuals may experience prolonged nasal congestion. Sneezing helps clear out excess mucus, allergens, and other irritants that can cause nasal congestion.
When the sneezing reflex is inhibited, these substances can accumulate in the nasal passages, leading to a stuffy nose, difficulty breathing, and discomfort.
4. Increased Eye Pressure
Sneezing generates a forceful release of air, which increases the pressure in the nasal passages and sinuses. This pressure can also affect the eyes.
When we suppress the sneezing reflex, it can cause the pressure to build up, potentially leading to increased intraocular pressure. This can be particularly risky for individuals with certain eye conditions such as glaucoma, as it can exacerbate their symptoms and potentially cause damage.
5. Middle Ear Problems
Sneezing also involves the activation of the muscles in the middle ear, which help equalize the pressure between the inner ear and the environment. When we intentionally hold back or interrupt a sneeze, we disrupt this natural equalization process.
This can result in an imbalance of pressure, leading to discomfort, earaches, and even ear infections.
6. Ruptured Blood Vessels
Suppressing a sneeze can cause a sudden and excessive increase in pressure within the blood vessels of the head and neck. This pressure can potentially lead to the rupture of small blood vessels, known as petechiae.
While petechiae are usually harmless and resolve on their own, severe cases may require medical attention.
7. Spread of Infections
Allowing the body to naturally go through the sneezing reflex helps in preventing the spread of infections. When we interrupt the sneezing process, the nasal and respiratory secretions containing infectious agents may not be expelled properly.
This increases the risk of spreading infections, such as the common cold or flu, to others in close proximity.
8. Discomfort and Pain
Suppressing sneezes can lead to feelings of discomfort and even pain. The force generated during a sneeze can reach speeds of up to 100 miles per hour.
When we try to halt or interrupt this forceful expulsion of air, it can cause discomfort in the nasal passages, throat, and even the chest. In some cases, it can lead to headaches, facial pain, and muscle strains.
9. Masking Underlying Conditions
Sneezing can sometimes be indicative of underlying health conditions such as allergies, colds, or respiratory infections.
By interrupting or suppressing the sneezing reflex, individuals may temporarily mask the symptoms of these conditions, making it difficult to identify and address the root cause. It is important to allow the body to go through the sneezing process to accurately assess any underlying health issues.
10. Disruption of Natural Defense Mechanisms
The sneezing reflex is part of the body’s natural defense mechanisms against irritants and foreign particles. By interrupting this reflex, we interfere with the natural safeguarding process of our respiratory system.
This can compromise the body’s ability to effectively filter and remove harmful substances, making us more susceptible to respiratory infections, allergies, and other respiratory problems.
Conclusion
Interrupting the sneezing reflex can pose various risks to our respiratory health. From nasal irritation and sinus infections to increased eye pressure and spread of infections, the consequences of suppressing sneezes should not be taken lightly.
It is important to allow the body to go through the natural process of sneezing to protect and maintain respiratory well-being.