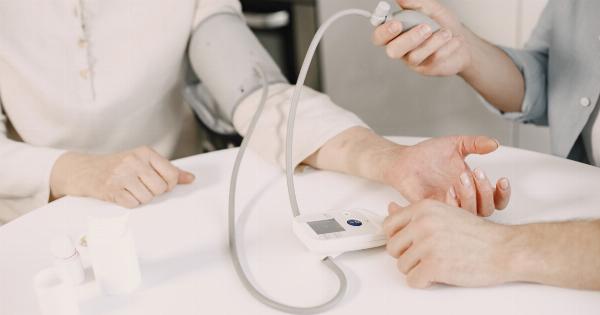
Pressure measurement is the measurement of force per unit area. Pressure is defined as force per unit area, and it is an important physical quantity that has applications in many fields, including science, engineering, medicine, and industry.
In this article, we will explore the science behind pressure measurement and the different methods used to measure pressure.
What is Pressure?
In physics, pressure is defined as force per unit area. It is the force acting perpendicularly on a unit area of surface. Pressure is a scalar quantity, which means that it has only magnitude and no direction.
The SI unit of pressure is the pascal (Pa), which is equal to one newton per square meter (N/m2). Other common units of pressure include pounds per square inch (psi), atmospheres (atm), and bars (bar).
How is Pressure Measured?
There are several different methods used to measure pressure, each of which has its own advantages and disadvantages. The most common methods are:.
1. Manometer
A manometer is a simple device used to measure pressure. It consists of a U-shaped tube filled with a liquid, typically mercury or water. One end of the tube is connected to the pressure source, and the other end is open to the atmosphere.
By measuring the difference in height between the two sides of the tube, the pressure can be calculated using the equation:.

where h is the height difference between the two sides of the tube, and ρ is the density of the liquid.
2. Bourdon Gauge
A Bourdon gauge is a mechanical device used to measure pressure. It consists of a curved tube that is closed at one end and connected to the pressure source at the other end.
As the pressure increases, the tube straightens out, which moves a pointer on a dial to indicate the pressure. Bourdon gauges are commonly used in industry to measure the pressure of fluids and gases.
3. Strain Gauge
A strain gauge is an electronic device used to measure pressure. It consists of a thin strip of metal that changes shape when pressure is applied.
As the metal changes shape, its electrical resistance changes, which can be measured and used to calculate the pressure. Strain gauges are commonly used in industries where the pressure needs to be measured continuously, such as in oil and gas pipelines.
4. Piezoelectric Sensor
A piezoelectric sensor is an electronic device that uses the piezoelectric effect to measure pressure. This effect occurs when a material, such as quartz crystal, is subjected to pressure, which causes it to generate an electrical charge.
The charge can be measured and used to calculate the pressure. Piezoelectric sensors are commonly used in industries where high accuracy pressure measurements are required, such as in the aerospace industry.
Applications of Pressure Measurement
Pressure measurement has a wide range of applications in science, engineering, medicine, and industry. Some of the most common applications include:.
1. Meteorology
In meteorology, pressure is an important measure of atmospheric conditions. Barometers are used to measure the air pressure, which is a key factor in weather forecasting.
2. Automotive Industry
Pressure measurement is important in the automotive industry for measuring tire pressure and engine oil pressure, which can affect vehicle performance and safety.
3. Medical Industry
Pressure is an important measure in the medical industry. Blood pressure is a key indicator of cardiovascular health, and devices such as sphygmomanometers are used to measure it.
4. Aviation Industry
Pressure measurement is critical in the aviation industry for measuring air pressure and altitude. Instruments such as altimeters and airspeed indicators rely on pressure measurement to function properly.
Conclusion
Pressure measurement is an important physical quantity that has applications in many fields, including science, engineering, medicine, and industry.
There are several different methods used to measure pressure, each of which has its own advantages and disadvantages. The most common methods include manometers, Bourdon gauges, strain gauges, and piezoelectric sensors. By understanding the science behind pressure measurement, we can better appreciate its importance in our daily lives.