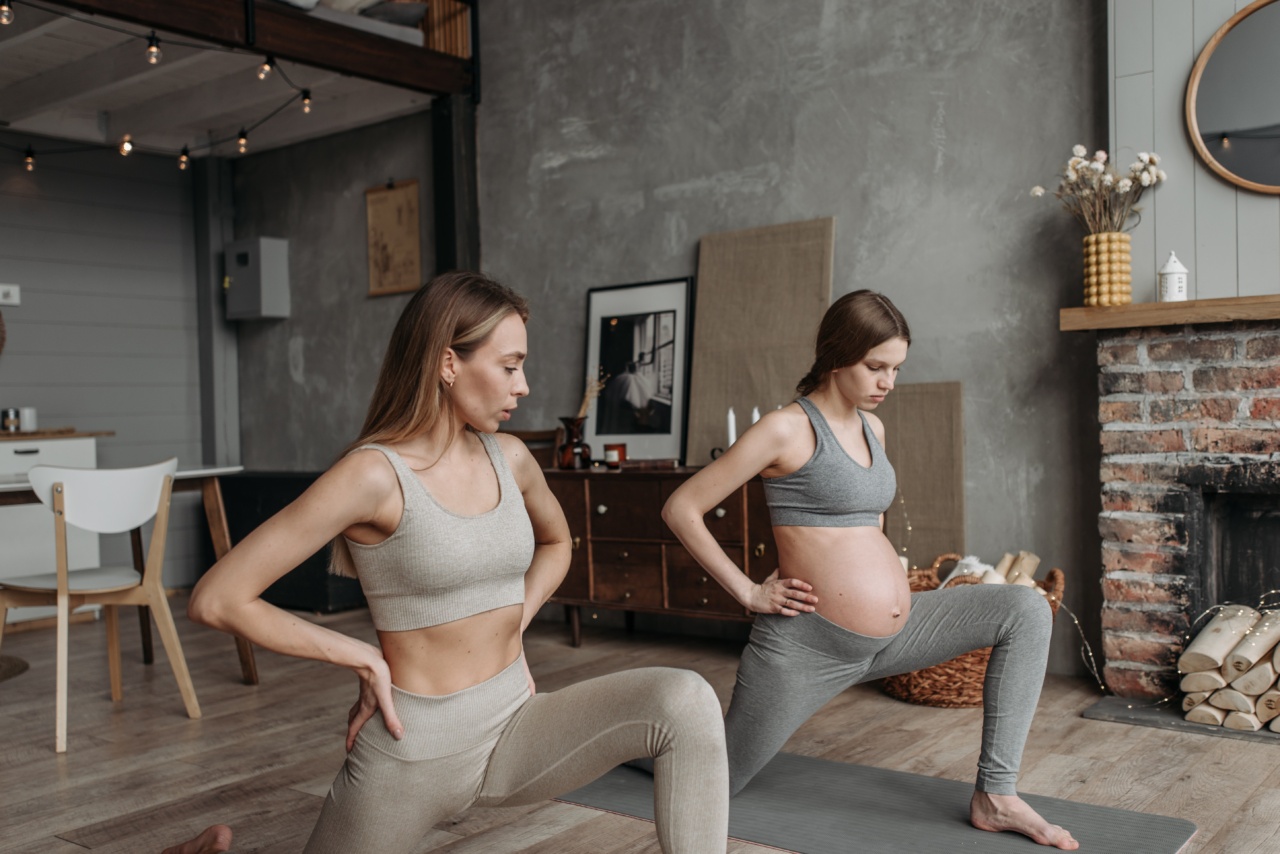
Exercise during pregnancy is not only safe but also beneficial for both the mother and the baby. Regular physical activity helps to alleviate common pregnancy discomforts, maintain a healthy weight, and prepare the body for labor and childbirth.
However, it is important to approach exercise during pregnancy with caution and consult with a healthcare professional to ensure safe and appropriate activities. In this guide, we will explore the importance of exercise during pregnancy, guidelines for safe workouts, and suitable exercises for each trimester.
Why Is Exercise Important during Pregnancy?
Engaging in regular exercise during pregnancy offers numerous benefits for both the mother and the growing baby:.
- Improved cardiovascular health: Regular exercise helps strengthen the heart, improving blood circulation and reducing the risk of high blood pressure and gestational diabetes.
- Managing weight gain: Exercise helps to control excessive weight gain during pregnancy, contributing to a healthy pregnancy and minimizing the risk of complications.
- Reduced discomforts: Physical activity can help alleviate common pregnancy discomforts such as backaches, constipation, mood swings, and fatigue.
- Enhanced mood and mental well-being: Exercise releases endorphins, which can help combat pregnancy-related hormonal changes and promote a positive mood.
- Improved stamina and endurance: Maintaining a fitness routine during pregnancy can prepare the body for the physical demands of labor and childbirth.
- More restful sleep: Regular physical activity promotes better sleep patterns and aids in relaxation.
Guidelines for Safe Exercise during Pregnancy
While exercise is generally safe during pregnancy, it is essential to follow these guidelines to ensure the safety of both the mother and the baby:.
- Consult with your healthcare provider: Before starting or continuing an exercise routine, consult with your healthcare provider to obtain personalized recommendations based on your health status and any specific pregnancy conditions.
- Warm-up and cool-down: Always begin your workout with a warm-up session to prepare the body and finish with a cool-down period to gradually lower heart rate and prevent dizziness or fainting.
- Stay properly hydrated: Drink plenty of water before, during, and after exercise to prevent dehydration.
- Listen to your body: Pay attention to your body’s signals and adjust the intensity or duration of your workout if needed. Avoid overexertion and take breaks as necessary.
- Avoid lying on your back: After the first trimester, avoid exercises that involve lying flat on your back for extended periods, as it can reduce blood flow to the uterus.
- Wear appropriate attire: Choose comfortable, breathable clothing and supportive footwear to prevent injuries and improve stability.
- Choose low-impact activities: Opt for low-impact exercises that reduce stress on the joints, such as walking, swimming, stationary biking, or prenatal yoga.
- Avoid contact sports or activities with a high risk of falling: Protect yourself and the baby by avoiding contact sports, activities with a risk of abdominal trauma, or those prone to falls.
- Modify exercises as the pregnancy progresses: As your body changes, modify exercises to accommodate your growing belly and shifting center of gravity. Avoid deep abdominal twists and high-impact movements.
- Don’t push beyond comfort: If an exercise feels uncomfortable, causes pain, or impacts your breathing, stop immediately and consult with your healthcare provider.
Safe Exercises for Each Trimester
First Trimester
During the first trimester, most exercises that were part of your pre-pregnancy routine are generally safe to continue. However, pay attention to your body and make modifications as necessary. Some safe exercises for the first trimester include:.
- Walking: Brisk walking helps maintain cardiovascular fitness without putting excessive strain on the joints.
- Swimming: Swimming is a low-impact exercise that provides a full-body workout and supports your joints.
- Prenatal yoga: Prenatal yoga classes focus on gentle stretching, breathing, and relaxation techniques specifically designed for pregnant women.
- Low-impact aerobics: Joining a prenatal exercise class or following a pregnancy-specific aerobic routine can help maintain fitness levels.
Second Trimester
As the belly grows and the body changes, certain exercises may need modification or avoidance during the second trimester. Opt for exercises that maintain balance, stability, and minimize the risk of falling. Suitable exercises for this stage include:.
- Prenatal strength training: Utilize light weights or resistance bands and focus on exercises that target the major muscle groups while avoiding lying flat on your back.
- Water aerobics: Join a water aerobics class specifically designed for pregnant women to improve strength, flexibility, and cardiovascular health.
- Stationary biking: Cycling on a stationary bike provides a low-impact cardio workout without the risk of falling.
- Modified Pilates: Participate in pregnancy-specific Pilates classes that emphasize core strength while avoiding exercises lying flat on your back.
Third Trimester
During the third trimester, the emphasis shifts towards maintaining comfort and avoiding exercises that put excessive pressure on the joints or abdomen. Focus on gentle movements and exercises designed to prepare the body for labor, such as:.
- Prenatal swimming: Continued swimming helps relieve discomfort, reduce swelling, and support the extra weight of the belly.
- Pelvic floor exercises: Kegels and other pelvic floor exercises can help strengthen the muscles needed for labor and prevent or treat urinary incontinence.
- Prenatal yoga: Participate in gentle prenatal yoga classes that focus on relaxation, stretching, and breathing techniques.
- Walking: Continue walking as long as it remains comfortable, adjusting pace and distances as needed.
Remember to consult with your healthcare provider for personalized recommendations on suitable exercises during each trimester.