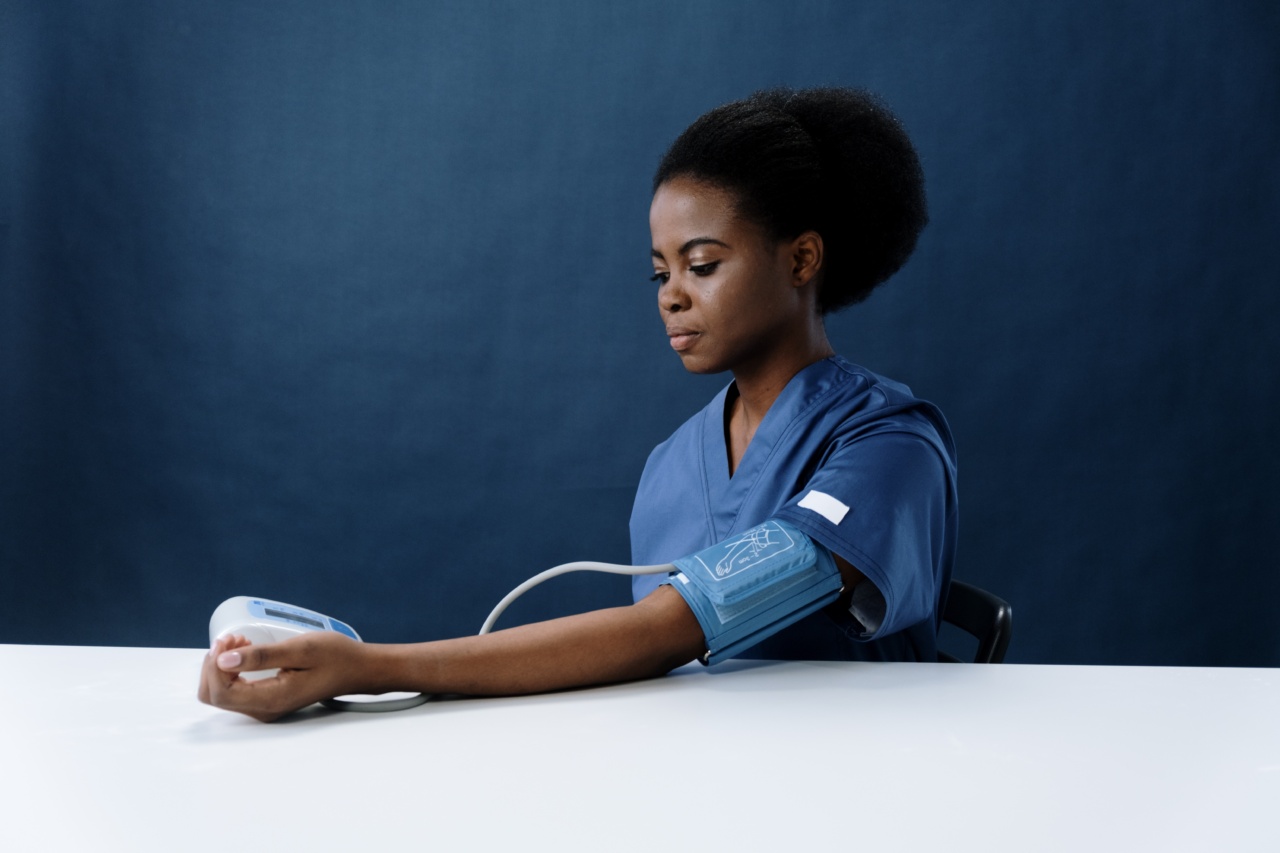
Blood pressure is one of the most essential indicators of our overall health. High blood pressure is linked to several health complications, including cardiovascular disease, stroke, and kidney failure.
Therefore, it’s crucial to measure blood pressure accurately to diagnose and treat potential health issues.
However, several common mistakes can affect accuracy when measuring blood pressure. Here are seven common mistakes to avoid:.
1. Failing to Rest Before the Test
Blood pressure is sensitive to activity, so it’s important to rest for at least five minutes before taking a measurement.
Avoid doing any vigorous activity, consuming caffeine or alcohol, or smoking cigarettes just before taking a reading as this can raise your blood pressure.
2. Improper Cuff Size
A cuff that’s too small or big can affect blood pressure measurement. An improperly sized cuff may result in readings that are either higher or lower than your actual blood pressure.
Always use the appropriate cuff size by measuring the circumference of your upper arm.
3. Taking Measurements Too Close Together
It’s best to wait at least two minutes between blood pressure readings to allow your blood vessels to return to their normal state. Consistent measurements over time are more likely to indicate actual changes in blood pressure.
4. Uncalibrated or Uncalibrated Equipment
The equipment (sphygmomanometer) must be calibrated, and the device used to measure blood pressure must also be recently calibrated to ensure accurate readings. Devices used at home or in clinics should be checked regularly.
It’s also essential to calibrate the equipment after replacing its batteries or tubing.
5. Holding Your Breath During the Measurement
You should breathe normally and avoid holding your breath during a blood pressure reading. Holding your breath can raise your blood pressure and lead to inaccurate results.
6. Incorrect Arm Placement
The arm cuff must be positioned at the correct level relative to the heart for accurate blood pressure measurement.
The cuff should be placed on your upper arm, with the lower edge of the cuff approximately one inch above the antecubital fossa (the space between your elbow and upper arm), and not below the elbow or over clothing.
7. Failing to Take Multiple Measurements
It’s preferable to take multiple readings during each blood pressure assessment and use an average to get a more accurate measure of your blood pressure.
You can take your measurements multiple times at the same time each day and note the readings over time to identify whether your blood pressure is consistently high or low.
In Conclusion
By avoiding these common mistakes, you can ensure that the blood pressure readings are as accurate as possible.
Blood pressure measurements can be helpful in detecting potential health problems, making the early identification of hypertension a crucial aspect of maintaining your overall health.