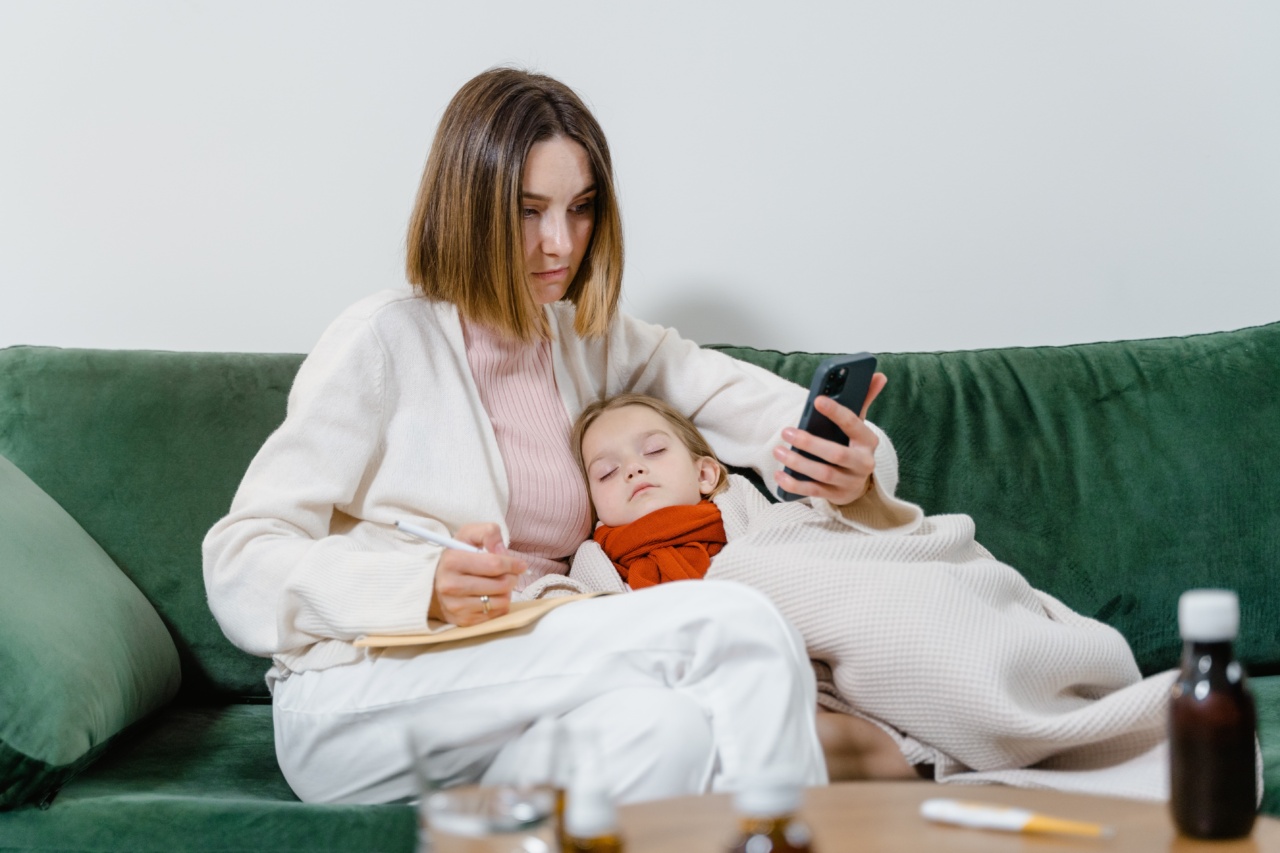
Bronchiolitis is a common respiratory illness among young children. It is an inflammation of the bronchioles, which are the smallest air passages in the lungs.
The illness is usually caused by a virus called respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), which is highly contagious. Bronchiolitis affects children under two years of age and is more common in the winter months. It is important for parents and caregivers to recognize the symptoms of bronchiolitis, as early intervention can help prevent complications.
Causes of Bronchiolitis
The primary cause of bronchiolitis is respiratory syncytial virus (RSV). RSV is a highly contagious virus that affects the respiratory system.
The virus is easily spread from person to person through contact with respiratory secretions, such as mucus and saliva, from infected individuals. Infants and young children are particularly susceptible to the virus as they have not developed immunity to it yet.
Symptoms of Bronchiolitis
The symptoms of bronchiolitis usually appear within two to three days of being infected with RSV. The symptoms may vary from child to child, but common symptoms include:.
- Coughing
- Sneezing
- Runny or stuffy nose
- Fever
- Rapid breathing
- Difficulty breathing
- Wheezing (a high-pitched sound when breathing)
- Irritability and fussiness
- Poor feeding
- Fatigue or lethargy
Diagnosis of Bronchiolitis
If your child is displaying symptoms of bronchiolitis, it is important to see a doctor for a diagnosis. A doctor will perform a physical exam and may order additional tests, such as a chest X-ray or blood tests, to confirm the diagnosis.
The doctor may also check the oxygen levels in your child’s blood using a pulse oximeter.
Treatment of Bronchiolitis
There is no cure for bronchiolitis, as it is a viral infection. Treatment is focused on relieving symptoms and preventing complications.
Mild cases of bronchiolitis can be treated at home with rest, fluids, and over-the-counter fever reducers, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen. In more severe cases, hospitalization may be necessary. This is especially true if your child is having difficulty breathing, experiencing a rapid heart rate, or has low oxygen levels.
In the hospital, your child may be given oxygen therapy, humidified air, or intravenous (IV) fluids to help manage symptoms. In rare cases, a ventilator may be necessary to help your child breathe.
Prevention of Bronchiolitis
There are several steps that parents and caregivers can take to prevent the spread of RSV and reduce the risk of bronchiolitis:.
- Wash your hands frequently, especially after blowing your nose or being in contact with someone who is sick
- Cover your mouth and nose with a tissue or your sleeve when coughing or sneezing
- Avoid close contact with individuals who are sick
- Clean and disinfect surfaces that may be contaminated with the virus, such as toys, doorknobs, and counters
- Keep your child away from large crowds, particularly during peak RSV season (usually from November to March)
- Avoid exposing your child to cigarette smoke, as this can worsen the symptoms of bronchiolitis
Conclusion
Bronchiolitis is a common respiratory illness among young children that is caused by a highly contagious virus called RSV. It is important for parents and caregivers to recognize the symptoms of bronchiolitis and seek medical attention if necessary.
Treatment is focused on relieving symptoms and preventing complications, and prevention strategies include frequent hand washing, avoiding close contact with sick individuals, and disinfecting surfaces. By taking these steps, parents and caregivers can help reduce the spread of RSV and protect young children from bronchiolitis.