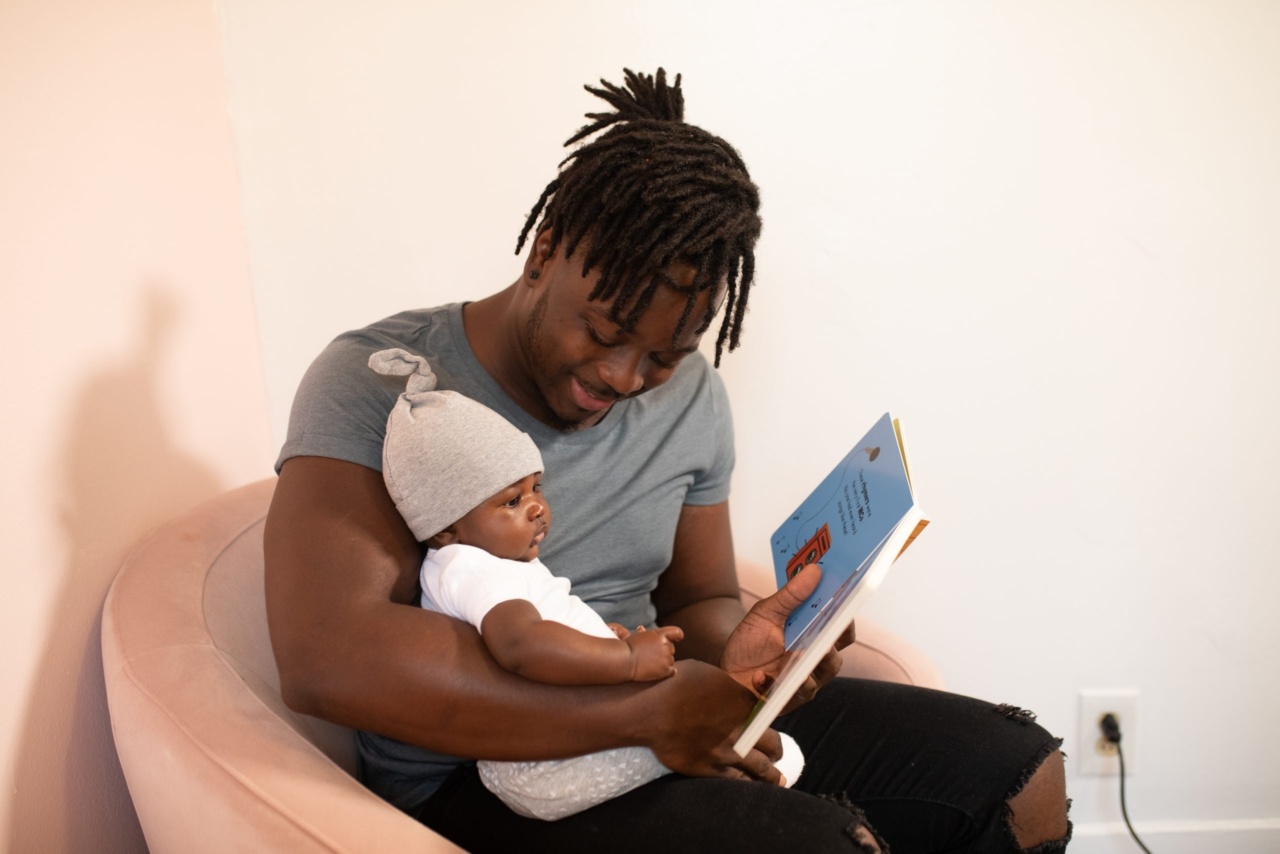
Dyslexia is a learning disorder that affects one’s ability to read, spell, and write. It is estimated that around 10% to 20% of the population worldwide has some degree of dyslexia.
People with dyslexia often struggle with decoding words, recognizing letters, and comprehending written information.
For individuals with dyslexia, learning English can be particularly challenging. English is notorious for its complex spelling rules, irregular word pronunciations, and ambiguous grammar.
These difficulties can make reading and writing tasks even more daunting for people with dyslexia.
The Impact of Dyslexia on Reading
Dyslexia affects reading in various ways. One of the primary difficulties for individuals with dyslexia is decoding words. They may have trouble associating sounds with letters, making it hard to recognize and pronounce unfamiliar words.
This can slow down their reading speed and make reading a frustrating experience.
Furthermore, dyslexia can hinder reading comprehension. The disorder impairs the ability to quickly process written information and extract meaning from text.
This makes it challenging to understand complex sentences, follow the flow of a story, or grasp the main ideas of a passage.
Strategies for Overcoming Dyslexia in English
Although dyslexia poses unique challenges when learning English, there are several strategies that can help individuals with dyslexia develop their reading skills:.
1. Multisensory Learning
Using multiple senses, such as sight, hearing, and touch, can enhance learning for individuals with dyslexia.
Teachers and tutors often employ techniques that involve writing words in the air, tracing letters on textured surfaces, or using colored overlays to aid reading comprehension.
2. Phonics Instruction
Phonics instruction focuses on teaching the relationship between sounds and letters. By explicitly teaching the sounds of English letters and letter combinations, individuals with dyslexia can improve their ability to decode unfamiliar words.
Breaking down words into smaller phonetic units helps them understand the building blocks of English spelling.
3. Assistive Technology
Advancements in technology have provided individuals with dyslexia numerous tools to assist them in their reading journey.
Text-to-speech software, specialized dyslexia fonts, and spell-check applications can alleviate some of the challenges associated with dyslexia. These tools can read text aloud, provide visual aids, and correct spelling errors in real-time.
4. Structured Literacy Programs
Structured literacy programs are designed specifically for individuals with dyslexia. These programs provide systematic and explicit instruction in phonics, spelling, and decoding skills.
They often break down the English language into manageable components and gradually introduce more complex concepts, ensuring a solid foundation for language acquisition.
5. Reading Support and Accommodations
Providing ongoing support and accommodations for individuals with dyslexia is essential. Extra time during exams, audiobooks, and the use of assistive devices such as reading rulers can level the playing field for students with dyslexia.
Accessible reading materials, such as books with larger fonts or dyslexia-friendly formatting, can also make reading less arduous.
6. Building a Love for Reading
Despite the challenges, it is important to foster a love for reading in individuals with dyslexia. Encouraging a positive reading experience can help them overcome their difficulties and develop a lifelong passion for literature.
Here are some ways to promote a love for reading:.
a) Finding the Right Reading Material
Choosing books that match a dyslexic reader’s interest and reading level can make reading more enjoyable. Shorter books or books with larger fonts may be less overwhelming, allowing for a sense of accomplishment.
Graphic novels, audiobooks, and magazines are also excellent alternatives.
b) Reading Aloud
Reading aloud can make the reading experience interactive and enjoyable. It helps dyslexic individuals associate spoken words with written words, improving overall reading fluency.
Parents, teachers, or reading partners can take turns reading chapters or paragraphs, creating a shared experience.
c) Joining Reading Clubs
Participating in reading clubs or book clubs can provide a sense of community and foster a love for reading. Being able to discuss books with others and share their thoughts and ideas can enhance the reading experience for dyslexic individuals.
d) Using Assistive Devices
Assistive devices, such as e-readers or tablets, can provide dyslexic individuals with customizable reading experiences.
These devices offer font adjustments, background color changes, and text-to-speech functionalities that cater to individual preferences and needs.
e) Celebrating Achievements
Recognizing and celebrating the achievements of dyslexic readers is vital. Even small milestones should be acknowledged and praised.
This positive reinforcement boosts self-confidence and motivates individuals with dyslexia to continue their reading journey.
f) Incorporating Reading in Daily Life
Integrating reading activities into daily life can make reading a regular and enjoyable habit.
Encouraging dyslexic individuals to read recipes, newspapers, or even captions on TV shows helps them realize that reading is an essential skill for everyday living.
The Benefits of Cultivating a Love for Reading
Cultivating a love for reading has numerous benefits for individuals with dyslexia:.
1. Improved Vocabulary and Language Skills
Reading exposes individuals to various words, phrases, and sentence structures, expanding their vocabulary and enhancing their language skills.
Exposure to diverse reading materials also helps dyslexic readers become more comfortable with different writing styles and genres.
2. Enhanced Critical Thinking and Problem-Solving Abilities
Engaging with different perspectives, characters, and storylines in books stimulates critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
Reading allows dyslexic individuals to exercise their analytical abilities and develop creative strategies for various situations.
3. Increased Empathy and Emotional Intelligence
Reading fiction exposes individuals to different emotions, experiences, and perspectives.
Dyslexic readers can develop empathy and emotional intelligence by connecting with the characters and understanding their struggles, fostering social and emotional growth.
4. Stress Reduction and Relaxation
Reading can be a form of escapism, providing a break from everyday stressors. Engaging in a captivating book can help dyslexic individuals relax, unwind, and reduce anxiety. It serves as a healthy coping mechanism and promotes mental well-being.
5. Lifelong Learning and Personal Development
When individuals with dyslexia cultivate a love for reading, they embark on a journey of lifelong learning and personal development.
Reading exposes them to new ideas, different cultures, and a wealth of knowledge, empowering them to grow intellectually and emotionally throughout their lives.
Conclusion
While dyslexia presents unique challenges when it comes to reading and learning English, there are effective strategies and techniques that can help individuals overcome these obstacles.
By implementing multisensory learning, structured literacy programs, and assistive technology, individuals with dyslexia can improve their reading skills and build confidence.
It is crucial to foster a love for reading by providing dyslexic individuals with appropriate reading materials, encouraging reading aloud, and involving them in reading communities.
Developing a passion for reading offers numerous benefits, including enhanced language skills, critical thinking abilities, and personal growth.