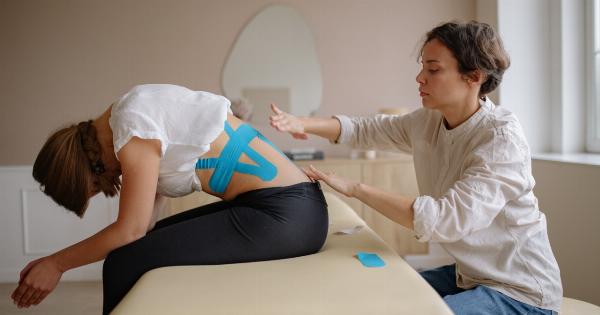
Repetitive movements are patterns of motion that are repeated over and over again. Repetitive movements can be caused by a wide range of activities, including daily work or activities such as sports.
Repetitive movements are not harmful in moderation, but excessive repetition can lead to injuries and long-term health problems such as musculoskeletal disorders. In this article, we will examine the effects of repetitive movements on different age groups.
Children and Adolescents
Children and adolescents are the most vulnerable to repetitive movement injuries due to the rapid growth and development of their bodies. Repetitive movements can cause damage to the growth plates as well as muscles, tendons, and ligaments.
Studies have found that intensive training in sports such as gymnastics, swimming, and baseball can increase the risk of repetitive movement injuries in young athletes.
To prevent repetitive movement injuries in children and adolescents, it is important to take precautions, including proper warm-up and cool-down procedures, stretching, and the use of proper equipment and protective gear.
Parents and coaches should implement a safe training regimen that emphasizes proper technique and form to reduce the risk of injury. They should also monitor any pain or discomfort experienced by their children and seek medical attention if necessary.
Young Adults
Young adults are at risk of repetitive movement injuries due to their active lifestyles and possible risk in the workplace.
Jobs involving repetitive movements or static postures can lead to carpal tunnel syndrome, tendinitis, and other musculoskeletal disorders. In addition, recreational activities such as tennis, golf, and weightlifting can also lead to repetitive movement injuries in young adults.
To prevent repetitive movement injuries in young adults, it is important to take regular breaks and stretch, practice good posture and ergonomics in the workplace, and seek medical attention if any pain or discomfort is experienced.
Using proper equipment and tools, such as wrist pads and ergonomic chairs, can also help reduce the risk of injury.
Middle-aged Adults
Middle-aged adults are at risk of repetitive movement injuries from daily tasks such as typing on a computer, carrying heavy objects, and performing repetitive motions at work.
This age group is also more susceptible to musculoskeletal disorders such as arthritis, which can be exacerbated by repetitive movements.
To prevent repetitive movement injuries in middle-aged adults, it is important to practice good posture and ergonomics in the workplace and adopt a healthy lifestyle that includes regular exercise and a balanced diet.
Performing stretching exercises and taking regular breaks during repetitive tasks can also help prevent injury. It’s important to seek medical attention if any pain or discomfort is experienced.
Elderly Adults
Elderly adults are at risk of repetitive movement injuries from everyday tasks and activities such as gardening, housework, and walking.
Age-related changes in the musculoskeletal system such as decreased bone density and joint flexibility can increase the risk of injury. Repetitive movements can lead to chronic pain, joint stiffness, and reduced mobility.
To prevent repetitive movement injuries in elderly adults, it is important to stay physically active and practice good posture and ergonomics when performing daily tasks.
Regular exercise, particularly weight-bearing exercise, can help improve bone density and reduce the risk of injury. If any pain or discomfort is experienced, it is important to seek medical attention promptly.
Conclusion
Repetitive movements are an inevitable part of daily life, and while they are often harmless, excessive repetition can lead to injury and long-term health problems.
By staying physically active, practicing good posture and ergonomics, and seeking medical attention if any pain or discomfort is experienced, individuals of all ages can reduce their risk of repetitive movement injuries and maintain a healthy, active lifestyle.