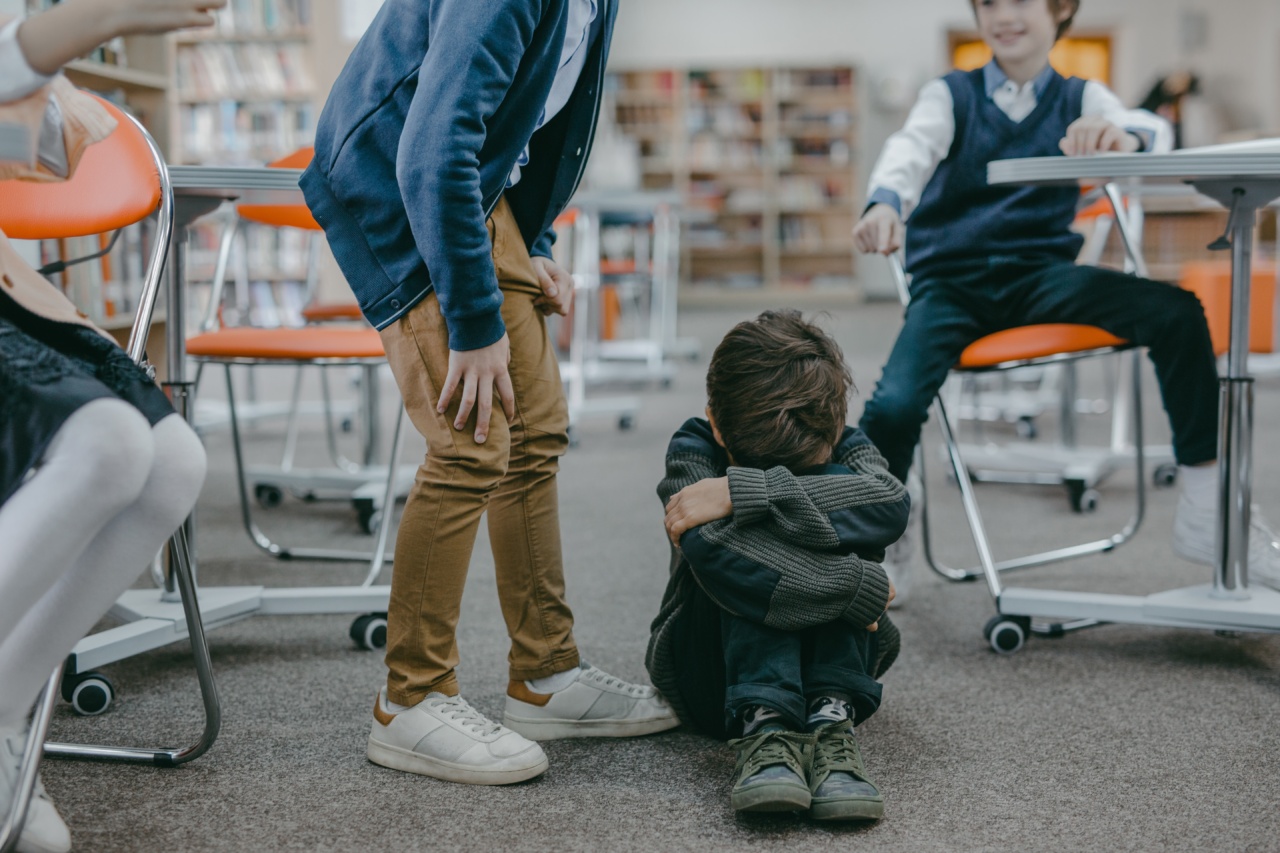
Bullying is a pervasive issue that affects millions of children worldwide. It is characterized by repeated aggressive behavior, intended to harm or disturb others. This behavior can take various forms, resulting in different types of bullying.
Understanding these types can help identify and address the specific challenges faced by child-victims. This article delves into the different types of bullying and explores the characteristics often exhibited by child-victims.
1. Physical Bullying
Physical bullying involves the use of physical force or aggression to harm or intimidate others. This can include hitting, kicking, pushing, pinching, or other forms of physical assault.
Child-victims of physical bullying often exhibit visible signs of abuse, such as bruises, cuts, or scrapes. They may also become more withdrawn, fearful, or anxious.
2. Verbal Bullying
Verbal bullying centers on the use of words to humiliate, insult, or belittle others. This can include name-calling, teasing, mocking, or spreading rumors.
Child-victims of verbal bullying may experience a decline in self-esteem, feelings of shame, and social isolation. They may also exhibit changes in behavior, such as avoidance of certain situations or places.
3. Social Bullying
Social bullying, also known as relational bullying, involves manipulating relationships or social status to harm others. This can include excluding someone from a group, spreading gossip or rumors, or cyberbullying.
Child-victims of social bullying often experience a sense of loneliness, rejection, or loss of friendships. They may become increasingly isolated and may show signs of depression or other emotional distress.
4. Cyberbullying
Cyberbullying refers to bullying that occurs through electronic devices, such as computers, smartphones, or tablets. It can take various forms, such as sending threatening messages, spreading rumors online, or sharing embarrassing photos or videos.
Child-victims of cyberbullying may exhibit increased anxiety, depression, or withdrawal from social activities. They may also experience difficulties concentrating or sleeping.
5. Sexual Bullying
Sexual bullying involves any unwanted sexual behavior or comments that target others to assert power or control. This can include inappropriate touching, sexual harassment, or sexual coercion.
Child-victims of sexual bullying often feel violated, ashamed, or embarrassed. They may exhibit changes in behavior, such as avoiding certain individuals or locations, and may experience difficulties in maintaining healthy relationships.
6. Prejudicial Bullying
Prejudicial bullying targets individuals based on their race, religion, ethnicity, gender, or any other characteristic that makes them different. It can include discriminatory comments, exclusion from activities, or hate speech.
Child-victims of prejudicial bullying may experience a decline in self-esteem, increased anger, and a sense of alienation. They may also exhibit changes in academic performance or engage in self-destructive behaviors.
7. Psychological Bullying
Psychological bullying, also known as emotional bullying, involves the use of tactics to manipulate, control, or intimidate others emotionally. This can include threats, intimidation, manipulation, or humiliation.
Child-victims of psychological bullying may exhibit changes in behavior, such as increased aggression or withdrawal. They may also experience difficulties in regulating emotions and have an increased risk of developing mental health issues.
8. Covert Bullying
Covert bullying refers to subtle and hard-to-detect forms of bullying that often occur behind the scenes. It can include covert manipulation, spreading rumors discreetly, or socially excluding individuals without their knowledge.
Child-victims of covert bullying may exhibit changes in behavior or mood, such as increased irritability or sadness. They may also become highly vigilant or anxious, constantly on guard for potential threats.
9. Workplace Bullying
Workplace bullying involves the mistreatment of individuals within a professional setting, such as schools or extracurricular activities. It can include actions such as excessive criticism, sabotage, or withholding of resources.
Child-victims of workplace bullying may exhibit decreased motivation, a decline in academic performance, or physical symptoms such as headaches or stomachaches. They may also avoid attending school or participating in activities they once enjoyed.
10. Characteristics of Child-Victims
Child-victims of bullying often exhibit distinct characteristics that can help identify and support them. Some common characteristics include:.
1. Low self-esteem: Child-victims may have low confidence and a negative perception of themselves due to the ongoing bullying they endure.
2. Social withdrawal: They may become socially isolated, avoiding interactions and maintaining limited friendships.
3. Emotional distress: Child-victims often experience emotional distress, such as anxiety, depression, or increased irritability.
4. Physical symptoms: Bullying can manifest physically, leading to headaches, stomachaches, or sleep disturbances.
5. Academic difficulties: Child-victims may have difficulties concentrating, declines in academic performance, or a lack of interest in school.
6. Changes in behavior: They may exhibit changes in behavior, such as increased aggression, submission, or avoidance of certain situations.
7. Decreased self-worth: Persistent bullying can erode the child’s self-worth, making them feel powerless and insignificant.
8. Avoidance of school: Child-victims may try to avoid attending school to escape the bullying, leading to frequent absences or tardiness.
9. Fearfulness: They may become more anxious, constantly living in fear of encountering the bully or experiencing further harm.
10. Suicidal ideation: In severe cases, child-victims may develop thoughts of self-harm or suicide as a result of the relentless bullying.