Eggs are a versatile and nutritious food that is enjoyed by people all around the world. They are not only delicious but also packed with essential nutrients, making them a popular choice for breakfast or baking.
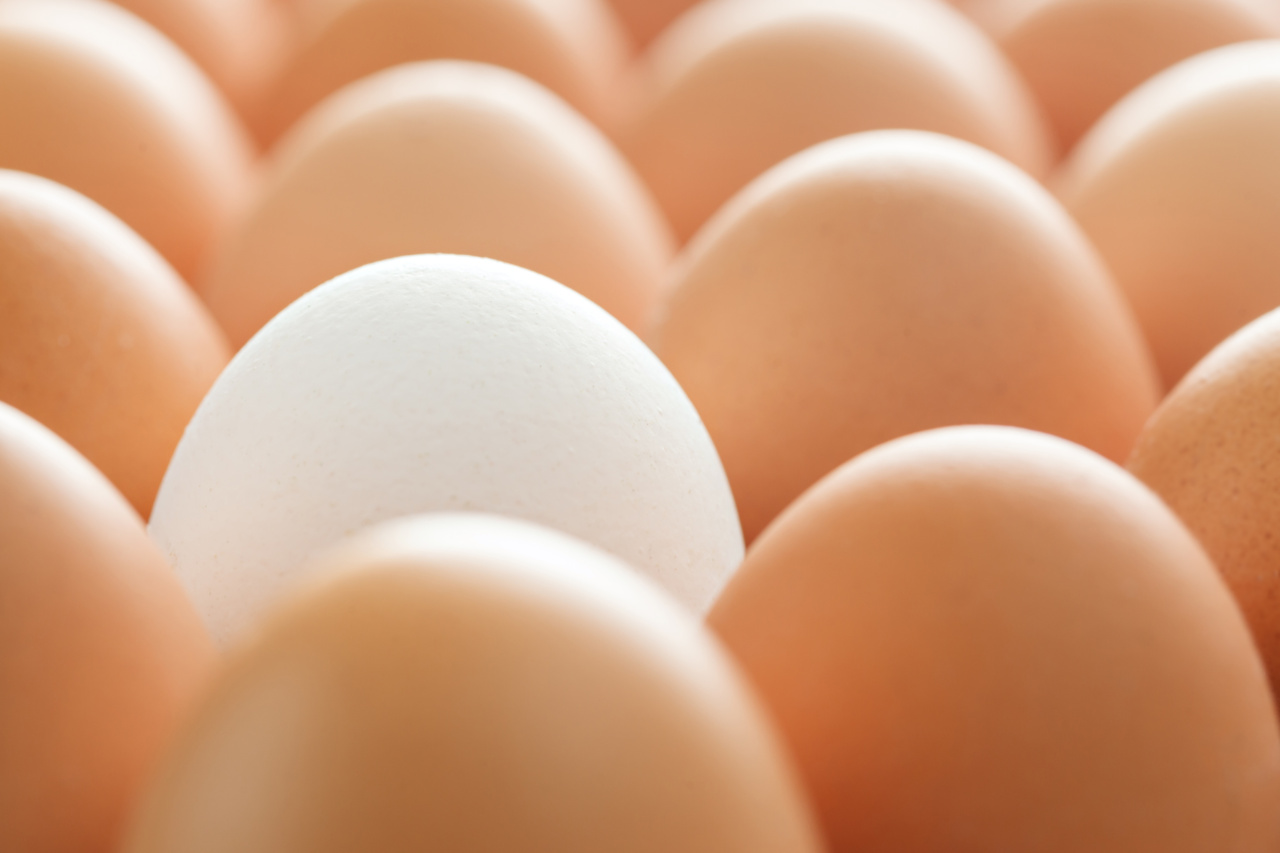
When shopping for eggs, you may notice that they come in different colors, with white and brown being the most common options. But does the color of the eggshell indicate any nutritional differences between the two? In this article, we will explore whether white and brown eggs are nutritionally different and debunk any myths surrounding this topic.
The Eggshell Color
The color of an eggshell is determined by the breed of the hen laying the egg. Hens with white feathers and white earlobes typically produce white eggs, while hens with red or brown feathers and red earlobes generally lay brown eggs.
However, the eggshell color has no correlation with its nutritional value or taste.
Nutritional Profile of Eggs
Eggs, regardless of their shell color, are highly nutritious. They are a rich source of high-quality protein, essential amino acids, vitamins, and minerals. Let’s take a closer look at the nutritional composition of eggs:.
Protein Content
Eggs are considered to be a complete protein source as they contain all the essential amino acids our body needs. A large egg contains approximately 6 grams of protein, making it an excellent choice to meet your daily protein requirements.
Vitamins and Minerals
Eggs are packed with various vitamins and minerals, making them a valuable addition to a balanced diet. Here are some key nutrients found in eggs:.
Vitamin B12
One large egg provides around 0.6 micrograms of Vitamin B12, which is essential for the normal functioning of the brain and nerve cells. It also plays a crucial role in the formation of red blood cells.
Vitamin D
Eggs are one of the few food sources that naturally contain vitamin D. This vitamin is essential for maintaining bone health and the absorption of calcium.
Vitamin A
Vitamin A is essential for maintaining healthy vision, promoting cell growth, and supporting the immune system. Eggs are a good source of this vitamin, with one large egg providing around 6% of the recommended daily intake.
Choline
Choline is an essential nutrient that plays a vital role in brain development and function. It is also involved in various metabolic processes in the body.
One large egg can provide approximately 147 mg of choline, which is almost a third of the recommended daily intake for adults.
Lutein and Zeaxanthin
Eggs are rich in two antioxidants known as lutein and zeaxanthin, which are beneficial for eye health. These antioxidants help reduce the risk of age-related macular degeneration and cataracts.
Dietary Cholesterol
Eggs have often been a topic of discussion due to their cholesterol content. One large egg contains approximately 186 milligrams of cholesterol.
However, it is essential to note that dietary cholesterol has minimal impact on blood cholesterol levels in most individuals. It is the saturated and trans fats in our diet that have a more significant impact on blood cholesterol.
Egg Yolk Color
Aside from the eggshell color, another aspect that often causes confusion is the color of the egg yolk. The yolk color can range from pale yellow to deep orange, and this variation is influenced by the hen’s diet.
Hens that have access to a diet rich in pigments like xanthophylls, found in foods such as leafy greens or marigold petals, tend to produce eggs with darker and more vibrant yolks. However, the yolk color does not signify any nutritional superiority.
Conclusion
In conclusion, there is no significant nutritional difference between white and brown eggs. The color of the eggshell does not affect the eggs’ nutritional composition, taste, or quality.
Both white and brown eggs are an excellent source of high-quality protein, vitamins, and minerals. When choosing eggs, focus on factors such as freshness, organic or free-range options, and the hen’s diet. Eggs should be a part of a balanced diet, and their consumption can contribute to a healthy and nutritious lifestyle.