Eggs are a staple of many diets around the world, and they are a great source of protein, vitamins, and minerals.
But have you ever wondered about the nutritional differences between the egg yolk and egg white? In this article, we will explore the caloric difference between the two parts of an egg and understand their distinct nutritional profiles.
The Composition of Eggs
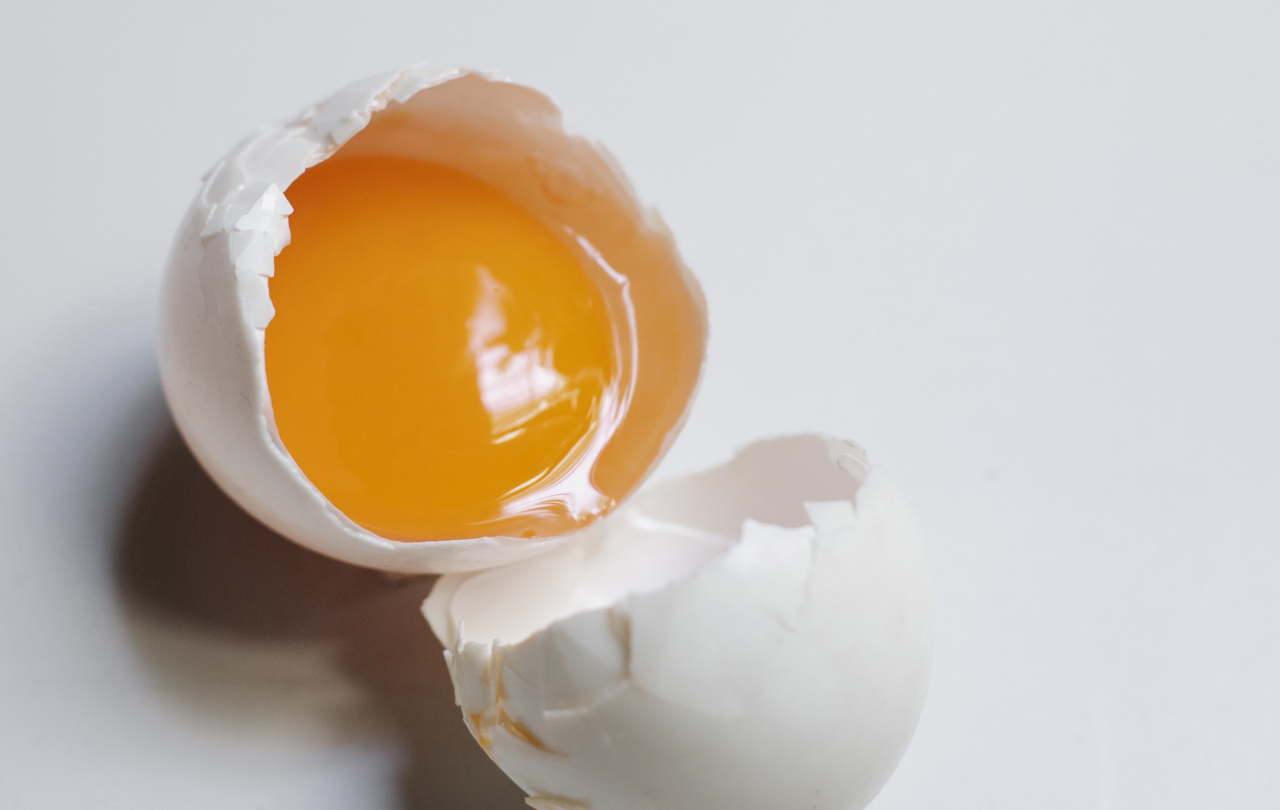
An egg is composed of both the yolk and the white, each with its own unique set of nutrients. The yolk is the yellow, circular part at the center of the egg, surrounded by the egg white or albumen.
The yolk contains all the fat and cholesterol found in the egg, while the white primarily consists of protein. Let’s delve into the caloric breakdown of these two components.
Caloric Content of Egg Yolk
The egg yolk is the part of the egg that contains the most calories due to its higher fat content. On average, a single large egg yolk contains around 55 calories.
These calories come from various nutrients present in the yolk, such as fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, and K), minerals (calcium, iron, and phosphorus), and healthy fats.
Caloric Content of Egg White
Compared to the egg yolk, the egg white contains significantly fewer calories. On average, a single large egg white contains around 17 calories.
The egg white is primarily composed of water and protein, making it a low-calorie, high-protein option for those watching their caloric intake.
Different Macronutrient Composition
While the caloric content of the egg yolk is higher than that of the egg white, the two components differ in their macronutrient composition.
Apart from calories, it is important to consider the amount of protein, fat, and carbohydrates present in each part.
Protein Content
Egg whites are considered an excellent source of high-quality protein. A single large egg white contains approximately 3.6 grams of protein.
The protein in egg whites is easily digestible and provides all the essential amino acids required for building and repairing body tissues, making it a valuable addition to any diet.
The egg yolk, on the other hand, contains a lower amount of protein compared to the egg white. A single large egg yolk contains approximately 2.7 grams of protein.
While the protein content is somewhat lower, the yolk compensates by providing other essential nutrients.
Fat Content
The egg yolk contains the majority of the fat found in an egg. A single large egg yolk contains around 4.8 grams of fat. However, it’s worth noting that not all fats are bad for our health.
The fat in egg yolks consists of monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, which are considered healthy fats that can benefit heart health and provide energy to the body.
On the flip side, the egg white is virtually fat-free, containing only a small trace amount of fat. This makes egg whites a great choice for individuals who are watching their fat intake, particularly those aiming for weight loss or weight maintenance.
Cholesterol Comparison
Egg yolks are known for their cholesterol content, with a single large egg yolk containing approximately 186 milligrams of cholesterol.
Cholesterol is a type of fat that plays essential roles in our body, such as hormone production and cell membrane formation. However, it is advisable for individuals with certain health conditions, such as high cholesterol levels or cardiovascular disease, to limit their intake of dietary cholesterol.
Egg whites, on the other hand, contain no cholesterol at all. Therefore, individuals who need to monitor their cholesterol intake can freely enjoy egg whites without worrying about negatively impacting their cholesterol levels.
Nutritional Benefits of Each Component
Both the egg yolk and egg white offer unique nutritional benefits, and incorporating them into your diet can contribute to a well-rounded nutrient intake.
The yolk contains essential fat-soluble vitamins, such as vitamin A for eye health, vitamin D for bone health, vitamin E for cell protection, and vitamin K for blood clotting.
Additionally, the yolk provides essential minerals like iron, which is necessary for the production of oxygen-carrying red blood cells, and phosphorus, which supports bone and teeth health.
The egg white, with its high protein content, supports muscle growth, repair, and maintenance.
It is also a versatile ingredient in cooking and baking, known for its ability to add volume and texture to various dishes without adding excessive fat or calories.
Conclusion
While the egg yolk and egg white differ in their caloric content, macronutrient composition, and cholesterol levels, both components of an egg offer valuable nutrients and can be consumed as part of a balanced diet.
Whether you prefer the richness of the egg yolk or the protein-packed egg white, eggs can be a nutritious addition to many meals, providing essential vitamins, minerals, and high-quality protein.