Choosing a contraceptive method is a crucial decision for anyone who wants to prevent unwanted pregnancy. There are several options available for both men and women, each with varying effectiveness rates.
In this article, we will explore different contraception options and how effective they are.
Barrier Methods
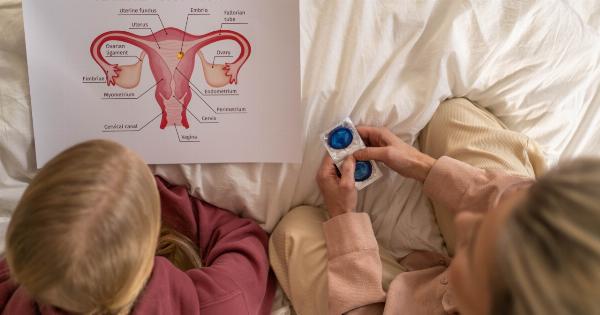
Barrier methods, as the name suggests, create a barrier between the sperm and the egg, preventing fertilization. These methods include condoms, diaphragms, and cervical caps.
Condoms
Condoms are one of the most popular contraceptive methods used around the world. When used correctly, condoms are highly effective in preventing unwanted pregnancy, as well as sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
The effectiveness rate of condoms is approximately 98% with correct and consistent use. However, the failure rate increases with incorrect or inconsistent use.
Diaphragms and Cervical Caps
Diaphragms and cervical caps are barrier methods that are placed inside the vagina to cover the cervix. Like condoms, they prevent the sperm from coming into contact with the egg.
The effectiveness rate for diaphragms and cervical caps is approximately 92-96%. However, effectiveness can decrease with incorrect use.
Hormonal Methods
Hormonal contraceptives use hormones, such as estrogen and progestin, to prevent pregnancy. These methods include birth control pills, patches, injections, vaginal rings, and hormonal IUDs.
Birth Control Pills
Birth control pills are taken orally and work by preventing the ovulation process. When used correctly, birth control pills are approximately 99% effective. However, effectiveness can decrease with missed pills or certain medications.
Patches and Vaginal Rings
Patches and vaginal rings are hormonal methods that work in the same way as birth control pills. The contraceptive patch is worn on the skin and releases hormones into the body. The vaginal ring is placed inside the vagina and also releases hormones.
Both methods are approximately 99% effective when used correctly.
Hormonal IUDs
Hormonal IUDs are small T-shaped devices that are inserted into the uterus by a healthcare provider. They release hormones that prevent ovulation and thicken the cervical mucus, making it difficult for sperm to reach the egg.
Hormonal IUDs are approximately 99% effective.
Depo-Provera Injection
The Depo-Provera injection is a hormonal method that is administered once every three months by a healthcare provider. The injection works by preventing ovulation and thickening the cervical mucus.
When used correctly, the Depo-Provera injection is approximately 99% effective.
Permanent Methods
Permanent methods of contraception are designed for people who no longer wish to have children. These methods include tubal ligation for women and vasectomy for men.
Tubal Ligation
Tubal ligation, also known as “getting your tubes tied,” is a surgical procedure that involves cutting or blocking the fallopian tubes to prevent the sperm from fertilizing the egg.
Tubal ligation is approximately 99.5% effective, but it is considered to be a permanent method of contraception.
Vasectomy
Vasectomy is a surgical procedure that involves cutting or blocking the vas deferens, which are the tubes that carry the sperm from the testicles to the urethra.
Vasectomy is considered to be a permanent method of contraception for men and is approximately 99.9% effective.
Emergency Contraception
Emergency contraception is a form of contraception that is used after unprotected sex. These methods include emergency contraceptive pills (also known as the “morning-after pill”) and the copper IUD.
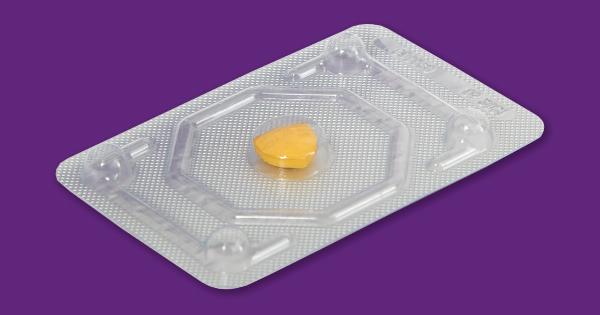
Emergency Contraceptive Pills
Emergency contraceptive pills are taken orally and work by preventing or delaying ovulation. When used correctly, emergency contraceptive pills are approximately 85% effective.
However, they are not as effective as regular contraceptives and should not be used as a regular form of contraception.
Copper IUD
The copper IUD is a non-hormonal method of emergency contraception that is placed inside the uterus by a healthcare provider. It can be inserted up to five days after unprotected sex and is also effective as a regular form of contraception.
The copper IUD is approximately 99.9% effective in preventing pregnancy.
Conclusion
Choosing the right contraceptive method is important for anyone who wants to prevent unwanted pregnancy. Each method has its own benefits and drawbacks, and effectiveness rates can vary depending on correct and consistent usage.
It is important to speak with a healthcare provider to determine which method is best suited for individual needs and lifestyles.