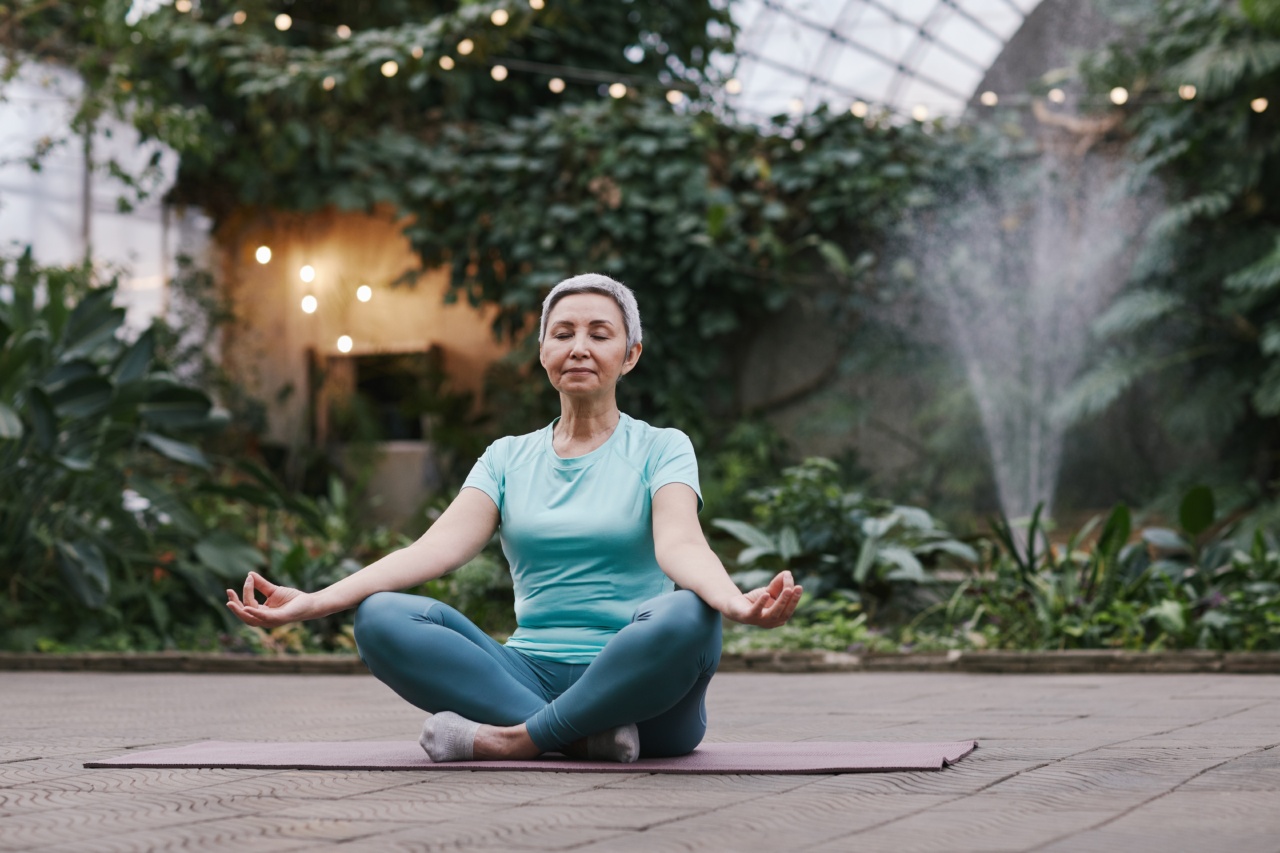Dementia is a progressive brain disorder characterized by a decline in cognitive functioning, memory loss, and difficulties with thinking, problem-solving, and language.
It affects millions of people worldwide, and the number is expected to rise significantly in the coming years. While there is no cure for dementia, various lifestyle factors, including physical exercise, have been found to play a crucial role in reducing the risk and delaying the onset of this debilitating condition.
The Impact of Dementia
Dementia not only affects the individuals who suffer from it but also places a significant burden on their families, caregivers, and healthcare systems.
The emotional, financial, and social implications are far-reaching, making it an urgent public health concern. Research has shown that engaging in regular physical activity and maintaining a healthy lifestyle can help protect against dementia and slow down its progression, providing hope for individuals and their loved ones.
The Link Between Fitness and Brain Health
Scientific evidence suggests that physical exercise has a significant impact on brain health.
Regular exercise improves blood circulation and increases the supply of oxygen and nutrients to the brain, promoting the growth of new neurons and enhancing synaptic plasticity. Exercise also triggers the release of endorphins, neurotransmitters that boost mood, reduce stress, and enhance overall cognitive function.
Cardiovascular Exercise and Dementia Prevention
Engaging in cardiovascular exercises, such as walking, running, swimming, or cycling, can have a profound effect on reducing the risk of dementia.
These activities improve cardiovascular health, lower blood pressure, and reduce the risk of developing conditions like hypertension, diabetes, and obesity, all of which are associated with a higher risk of dementia. Regular cardio exercise also enhances cognitive function and memory, making it a powerful tool in the fight against dementia.
Strength Training for Cognitive Enhancement
Strength training exercises, such as lifting weights, resistance training, or using resistance bands, not only help build muscle and improve overall physical strength but also offer significant cognitive benefits.
Studies have shown that strength training can enhance executive functioning, attention, and memory in older adults. By increasing muscle mass and improving metabolism, strength training indirectly strengthens the brain and reduces the risk of dementia. It also helps in minimizing age-related cognitive decline and enhancing overall quality of life.
Flexibility and Balance Exercises for Brain Health
Keeping the brain active and improving motor skills are essential in reducing the risk of dementia. Flexibility and balance exercises, such as yoga, tai chi, and Pilates, promote mindfulness, improve coordination, and enhance cognitive function.
These exercises focus on body movements that engage both the body and the mind, stimulating neuroplasticity and improving overall brain health.
Social Interaction and Mental Stimulation
In addition to physical exercise, maintaining social connections and engaging in mentally stimulating activities plays a crucial role in reducing dementia risk.
Social interaction helps combat loneliness, depression, and stress, all of which are linked to an increased risk of dementia. Participating in group fitness classes, joining community clubs, or volunteering can provide not only physical benefits but also social and mental well-being.
Creating a Senior Fitness Routine
It is never too late to start a senior fitness routine to reduce the risk of dementia. Before beginning any exercise program, seniors should consult with their healthcare providers to ensure they are physically capable of engaging in certain activities.
A well-rounded fitness routine should include a combination of cardiovascular exercises, strength training, flexibility and balance exercises, and mind-engaging activities. Gradually increasing the intensity and duration of exercises over time will help seniors maintain their fitness levels and enjoy the cognitive benefits.
The Importance of a Healthy Lifestyle
It’s important to note that while regular exercise is crucial, it should be complemented by a healthy lifestyle.
Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats provides essential nutrients that support brain health. Avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, getting enough quality sleep, and managing stress levels also contribute to reducing the risk of dementia.
The Role of Caregivers and Communities
Caregivers and communities play a vital role in promoting senior fitness for reducing the risk of dementia. Caregivers can help seniors establish and maintain an exercise routine, ensuring their safety and providing motivation and support.
Communities should prioritize creating accessible and safe environments for seniors to engage in physical activities, such as well-maintained parks, walking paths, and senior-friendly fitness programs.
Conclusion
Reducing the risk of dementia through senior fitness is a multifaceted approach that requires regular physical exercise, a healthy lifestyle, social interaction, and mental stimulation.
Engaging in cardiovascular exercises, strength training, flexibility and balance exercises, and mind-engaging activities can significantly contribute to brain health and prevent or delay the onset of dementia. By promoting senior fitness and adopting healthy lifestyle practices, individuals, caregivers, and communities can work together to combat the dementia epidemic and improve the overall well-being of seniors.