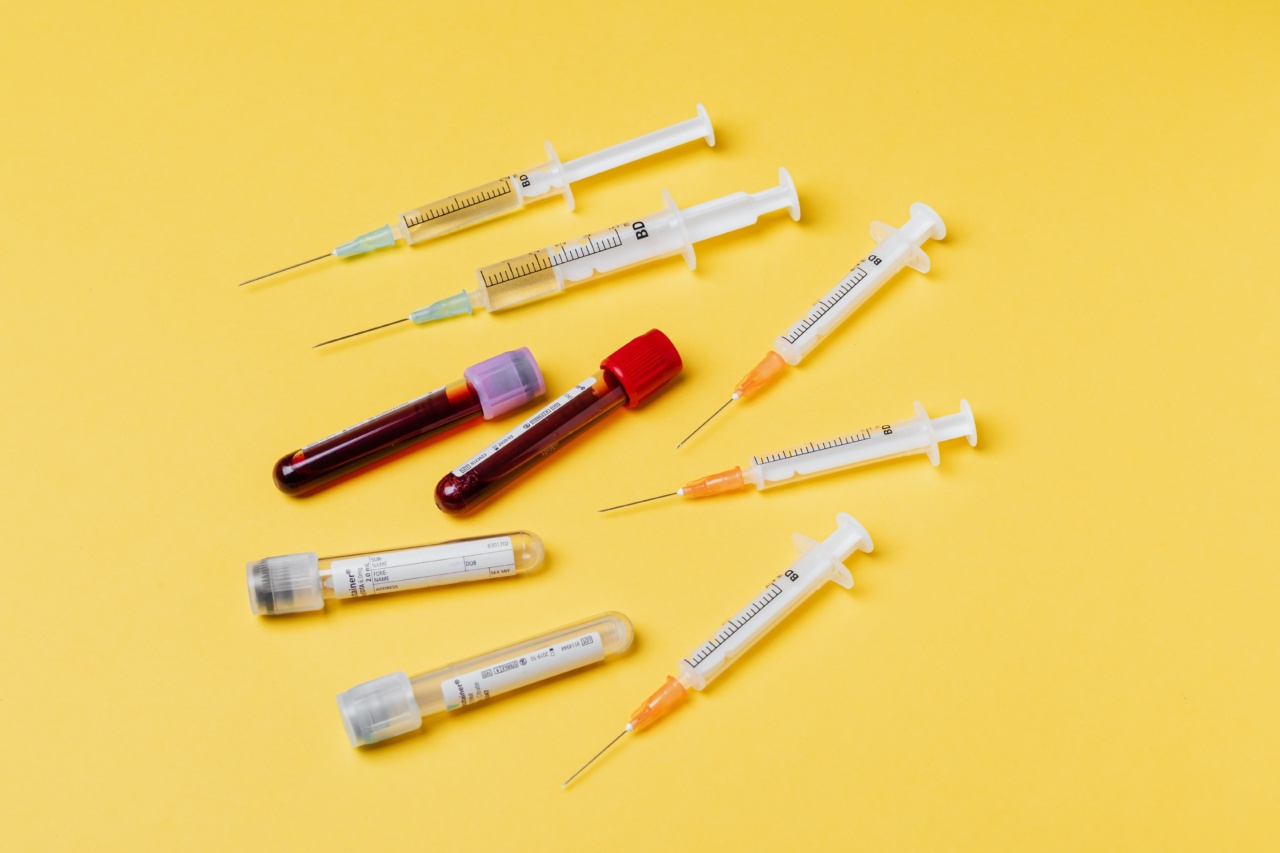
Blood transfusion is a medical procedure that involves transferring blood or blood components from one individual (donor) to another (recipient).
This procedure is commonly performed in hospitals to treat various medical conditions such as severe blood loss, anemia, and certain diseases that affect the body’s ability to produce or maintain healthy blood cells. In this article, we will explore the detailed process and coverage of hospital blood transfusion procedures.
1. Pre-Transfusion Assessment
Prior to the blood transfusion, a thorough assessment of the recipient’s health condition is conducted to ensure the procedure’s safety and efficacy.
This assessment includes evaluating the recipient’s medical history, current vital signs, and laboratory test results. It aims to identify any potential risks or contraindications that may prevent the transfusion.
2. Blood Type and Compatibility Testing
Once the pre-transfusion assessment is completed, the hospital laboratory will perform blood typing and compatibility testing. Blood typing determines the recipient’s blood group (A, B, AB, or O) and Rh factor (positive or negative).
Compatibility testing involves matching the recipient’s blood type with the appropriate blood product, considering factors such as the presence of antibodies or previous transfusion reactions.
3. Blood Product Selection
Based on the recipient’s blood type and specific medical needs, the healthcare team will select the appropriate blood product for transfusion. These products can include packed red blood cells, platelets, plasma, or cryoprecipitate.
Each blood product serves a different purpose in addressing specific deficiencies or conditions.
4. Informed Consent
Prior to the blood transfusion, the healthcare provider will obtain informed consent from the recipient or their legal guardian. This process involves explaining the procedure, potential risks, benefits, and alternatives to the transfusion.
The recipient or guardian must provide written consent before proceeding.
5. Intravenous Access
To administer the blood product, the healthcare team will establish intravenous access by inserting a sterile needle or catheter into a vein. This access allows for the safe and efficient delivery of the transfusion.
The choice of vein and size of the catheter will depend on the recipient’s age, medical condition, and the type of blood product being transfused.
6. Vital Sign Monitoring
Throughout the transfusion process, the recipient’s vital signs, including heart rate, blood pressure, respiratory rate, and temperature, are closely monitored.
Regular assessments help detect any adverse reactions or complications, allowing for immediate intervention if necessary.
7. Transfusion Administration
Once the intravenous access is established, the transfusion process can begin. The blood product is slowly infused into the recipient’s vein, typically over a period of one to four hours, depending on the quantity and specific requirements.
Healthcare providers follow strict protocols to ensure the safe and accurate administration of the transfusion.
8. Transfusion Reaction Monitoring
During the transfusion, the healthcare team remains vigilant for any signs of transfusion reactions. Symptoms may include fever, chills, rashes, shortness of breath, or changes in vital signs.
Immediate action will be taken if a transfusion reaction is suspected, including stopping the transfusion and providing appropriate medical interventions.
9. Post-Transfusion Care
Once the transfusion is completed, the recipient will continue to be monitored for a period of time to ensure their stability. Vital signs are closely observed, and any symptoms of adverse reactions or complications are promptly addressed.
The healthcare team will record the transfusion details, including the amount and type of blood product administered, for accurate medical documentation.
10. Follow-Up and Recovery
After the blood transfusion, the recipient’s healthcare provider will assess their response to the procedure and monitor their recovery.
This may involve additional laboratory tests, such as blood counts, to evaluate the effectiveness of the transfusion in addressing the underlying condition. The recipient’s progress will be closely monitored, and any necessary adjustments to their treatment plan will be made accordingly.