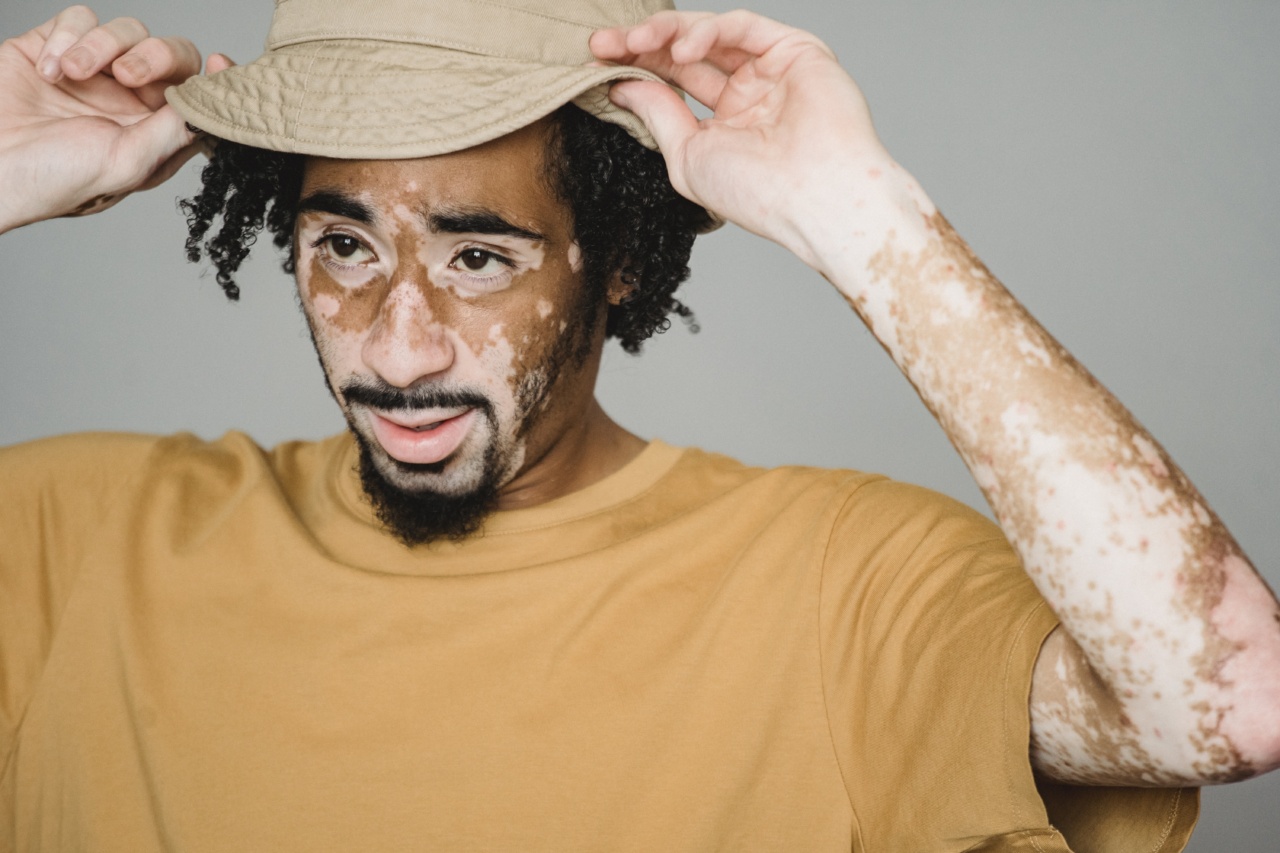
Autoimmune diseases are a group of disorders in which the immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys healthy body tissues. These conditions can affect various organs and systems in the body, leading to a wide range of symptoms and complications.
In this article, we will explore everything you need to know about autoimmune diseases, including their causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and more.
What are Autoimmune Diseases?
Autoimmune diseases occur when the immune system, which is designed to protect the body from harmful substances, instead starts attacking healthy cells and tissues.
This abnormal immune response causes inflammation and damage to various organs or systems.
Common Types of Autoimmune Diseases
There are over 80 known autoimmune diseases, each affecting different parts of the body. Some of the most common autoimmune diseases include:.
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Lupus
- Multiple sclerosis
- Celiac disease
- Type 1 diabetes
- Psoriasis
- Inflammatory bowel disease
- Hashimoto’s thyroiditis
- Graves’ disease
- Sjögren’s syndrome
Causes of Autoimmune Diseases
The exact causes of autoimmune diseases are still not fully understood. However, researchers believe that a combination of genetic and environmental factors play a role in their development. Some potential triggers for autoimmune diseases include:.
- Genetic predisposition
- Infections
- Environmental factors
- Hormonal imbalances
- Chronic stress
Signs and Symptoms
Autoimmune diseases can affect multiple organs and systems in the body, and their symptoms can vary widely depending on the specific condition. However, some common signs and symptoms may include:.
- Fatigue
- Pain and stiffness in joints
- Swelling
- Redness or discoloration of the skin
- Abdominal pain and digestive issues
- Unexplained weight loss or gain
- Frequent infections
- Hair loss
- Difficulty concentrating or memory problems
Diagnosis of Autoimmune Diseases
Diagnosing autoimmune diseases can be challenging because their symptoms often overlap with other conditions. To determine the presence of an autoimmune disease, healthcare providers may use a combination of the following methods:.
- Medical history evaluation
- Physical examination
- Blood tests to detect specific antibodies
- Imaging tests
- Tissue biopsy
Treatment Options
While there is no cure for autoimmune diseases, treatment aims to manage symptoms, reduce inflammation, and prevent further damage. The treatment approach may vary depending on the specific autoimmune disease and its severity.
Common treatment options include:.
- Medications to suppress the immune system
- Pain relievers
- Anti-inflammatory drugs
- Immunosuppressive drugs
- Physical therapy
- Dietary changes
- Stress management techniques
Lifestyle Tips for Managing Autoimmune Diseases
Along with medical treatment, making certain lifestyle changes can help individuals with autoimmune diseases manage their condition and improve their overall well-being. Here are some tips:.
- Eat a balanced and nutritious diet
- Get regular exercise
- Manage stress levels
- Get enough rest and sleep
- Avoid exposure to triggers or allergens
- Join support groups or seek counseling
Prevention of Autoimmune Diseases
Preventing autoimmune diseases entirely may not be possible due to their complex nature and the involvement of various factors. However, some measures that may lower the risk or delay the onset of certain autoimmune diseases include:.
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle
- Minimizing stress
- Avoiding exposure to harmful substances
- Getting vaccinated as recommended
Research and Future Directions
Research in the field of autoimmune diseases is ongoing, and scientists are continuously working towards a better understanding of these conditions.
There is hope that improved knowledge and advancements in treatment options will lead to more effective management and potentially even a cure for some autoimmune diseases in the future.