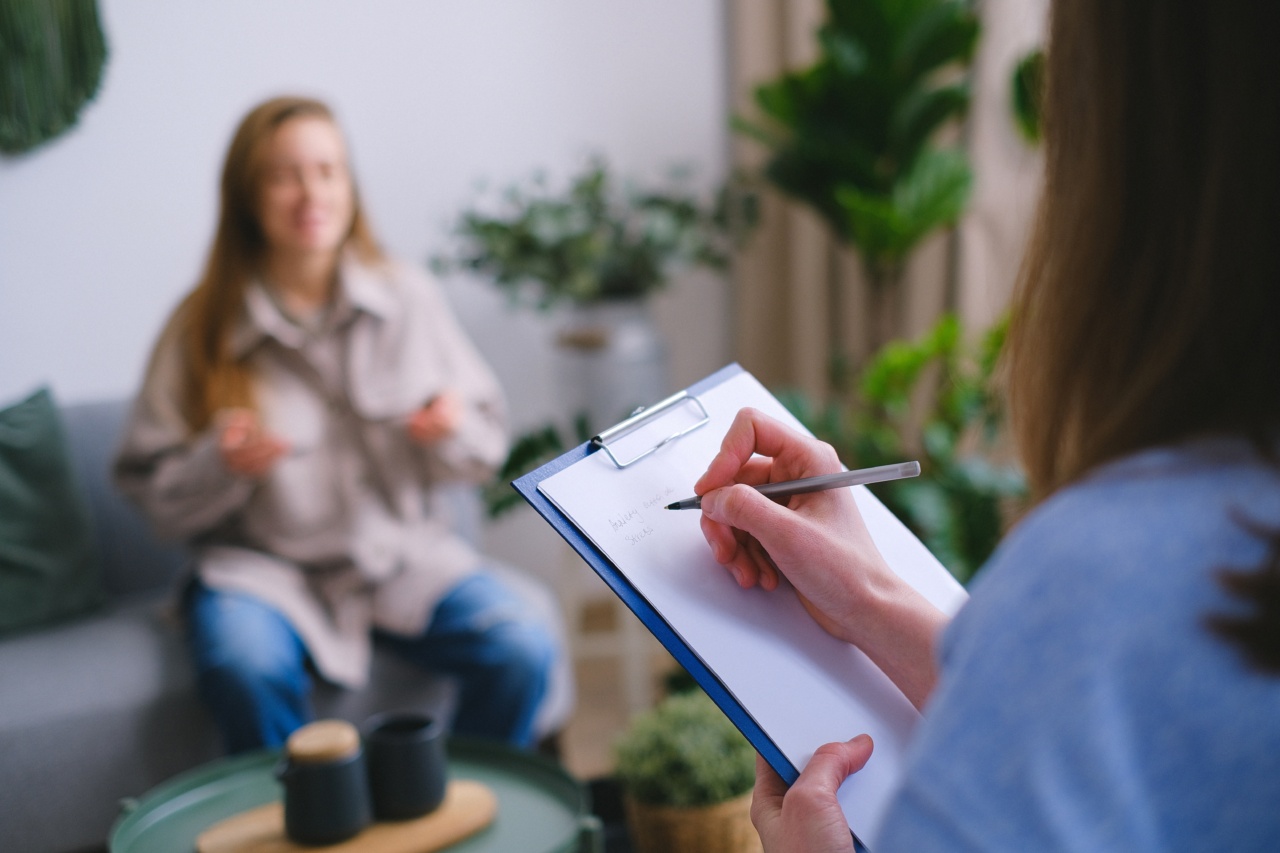
Language plays a crucial role in communication, enabling us to express our thoughts, emotions, and ideas effectively. However, in some cases, individuals may experience linguistic difficulties which hinder their ability to communicate efficiently.
Linguistic aid refers to the initial treatment and solutions available for individuals experiencing such challenges. This article explores the various approaches and techniques used to address linguistic impairments and promote better communication.
1. Speech Therapy
Speech therapy is a widely recognized and effective method of linguistic aid. It focuses on diagnosing and treating communication disorders, such as speech sound disorders, fluency disorders, and voice disorders.
A speech therapist employs various techniques, exercises, and activities to improve speech clarity and overall communication skills.
2. Language Intervention
Language intervention aims to enhance and develop an individual’s language skills, including listening, speaking, reading, and writing.
This form of linguistic aid is commonly used for individuals experiencing language delays, disorders, or difficulties related to comprehension, vocabulary, or syntax. Language intervention may involve one-on-one therapy sessions, group activities, or specialized programs tailored to individual needs.
3. Augmentative and Alternative Communication (AAC)
Augmentative and Alternative Communication (AAC) refers to a range of tools and strategies used to support individuals with severe communication impairments.
AAC systems can include sign language, symbol-based communication boards, picture exchange systems, or high-tech voice output devices. These aids facilitate communication for individuals who have limited or no speech capabilities, enabling them to express their needs, thoughts, and emotions effectively.
4. Multilingual Support
For individuals facing linguistic challenges due to language barriers or learning difficulties in multiple languages, multilingual support can be invaluable.
This type of linguistic aid provides assistance in acquiring and developing proficiency in multiple languages. It includes language immersion programs, bilingual education, tutoring, and specialized interventions designed to promote language skills in various languages.
5.
Accent Modification
Some individuals may face communication obstacles due to their accents. Accent modification programs are designed to help individuals improve their pronunciation, intonation, and overall speech patterns to be better understood by others.
These programs use techniques such as vocal exercises, speech drills, and auditory perception training to refine speech clarity and reduce accent-related communication challenges.
6. Occupational Therapy
While occupational therapy is primarily associated with physical rehabilitation, it can also play a role in linguistic aid.
Through activities designed to enhance fine motor skills, cognitive abilities, and overall sensory processing, occupational therapy can complement other linguistic interventions. This holistic approach helps individuals improve their ability to communicate effectively in their daily lives.
7. Assistive Technology
Assistive technology provides individuals with linguistic disabilities access to specialized tools, software, and devices that facilitate communication.
This includes text-to-speech software, speech recognition tools, communication apps, and alternative input devices. These technologies empower individuals to participate fully in conversations, express themselves, and engage in various social and professional settings.
8. Reading and Writing Interventions
Some individuals may struggle specifically with reading and writing due to linguistic impairments. Reading and writing interventions focus on improving literacy skills, including decoding, fluency, vocabulary, and comprehension.
These interventions can involve targeted exercises, personalized instruction, and the use of assistive technologies to enhance individuals’ ability to understand written language and express their thoughts effectively through writing.
9. Social Skills Training
Language is not only about words but also about effective communication within social contexts. For individuals who struggle with social interactions and pragmatic language skills, social skills training can be invaluable.
This form of linguistic aid helps individuals develop appropriate conversational skills, interpret social cues, initiate and maintain friendships, and navigate social situations confidently.
10. Parental and Caregiver Involvement
Parents and caregivers play a crucial role in supporting individuals with linguistic difficulties. Their involvement in treatment plans, therapy sessions, and home practice is pivotal for successful outcomes.
Linguistic aid programs often include education and guidance for parents and caregivers to enhance their understanding of the challenges faced by individuals and promote effective strategies for communication support.