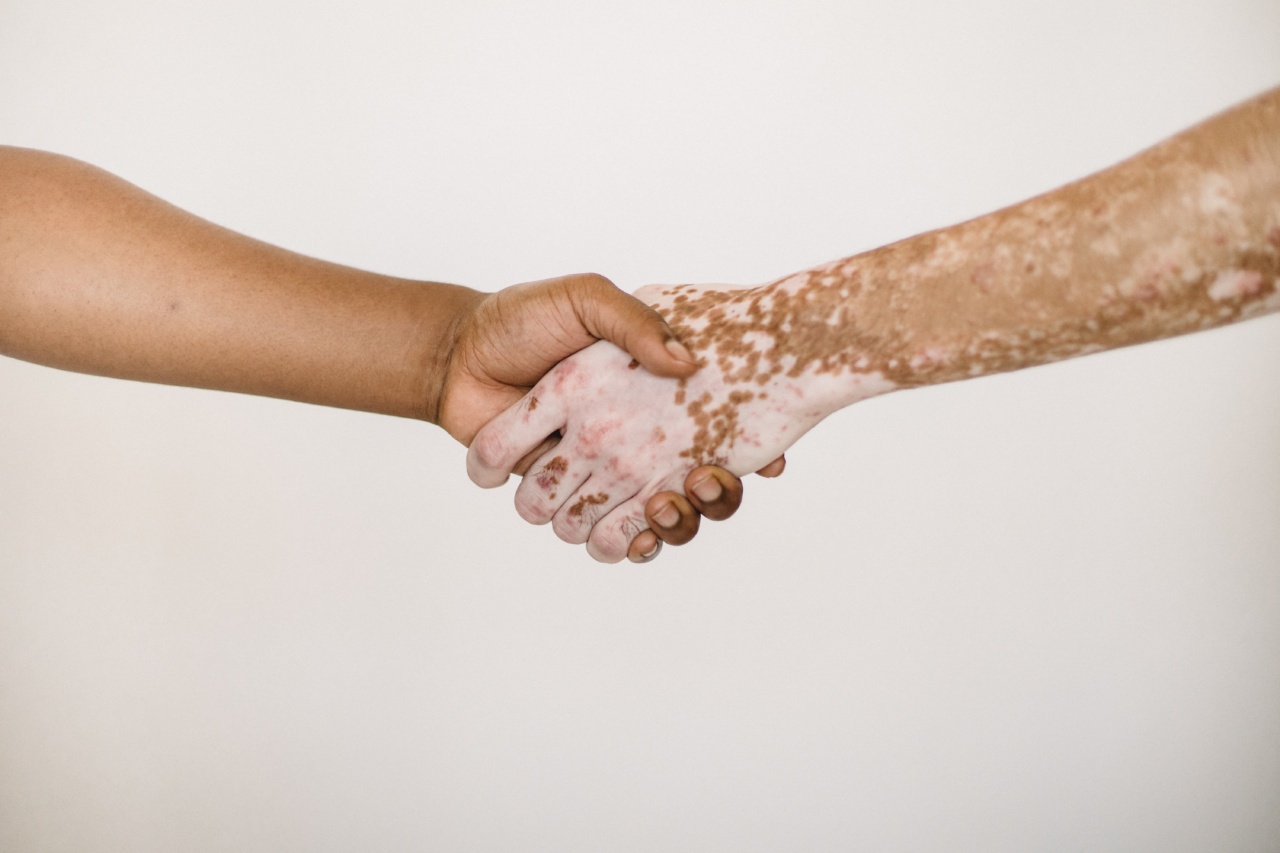
Living with psoriasis can be challenging on its own, but when it comes to managing life alongside other autoimmune diseases, the difficulties can multiply.
Autoimmune diseases occur when the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy cells in the body, leading to various health complications. Psoriasis is one such autoimmune disease that affects the skin and sometimes joints. While there is no cure for these conditions, there are ways to effectively manage the challenges they bring.
Understanding Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune disease that primarily affects the skin. It causes cells to build up rapidly on the surface of the skin, leading to the formation of thick, silvery scales and itchy, red patches.
These patches can be painful and may crack and bleed.
Psoriasis is thought to be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Certain triggers, such as infections, stress, and certain medications, can worsen the symptoms.
It is not contagious, but the impact on one’s quality of life can be significant.
Managing Psoriasis and Autoimmune Diseases
While psoriasis and other autoimmune diseases cannot be cured, they can be effectively managed through several approaches that focus on reducing inflammation, relieving symptoms, and improving overall well-being. Here are some strategies that can help:.
1. Medications
There are various medications available to manage psoriasis and other autoimmune diseases. Topical treatments, such as corticosteroids and vitamin D analogs, can be applied directly to the affected skin areas to reduce inflammation and promote healing.
Systemic medications, such as methotrexate and biologics, can be prescribed for more severe cases and when psoriasis affects the joints. These medications work by suppressing the immune system to alleviate symptoms.
However, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most suitable medication and monitor for potential side effects.
2. Phototherapy
Phototherapy involves exposing the skin to ultraviolet light under medical supervision. This treatment can help slow down the rapid growth of skin cells and reduce inflammation.
There are different types of phototherapy, including UVB therapy and psoralen plus ultraviolet A (PUVA) therapy. The choice of treatment depends on the severity and location of the psoriasis patches.
3. Lifestyle Modifications
Adopting a healthy lifestyle can play a crucial role in managing psoriasis and autoimmune diseases. This includes following a balanced diet, engaging in regular exercise, managing stress levels, and getting an adequate amount of sleep.
Certain dietary changes, such as reducing alcohol consumption and avoiding trigger foods, may also be beneficial.
It’s important to note that while lifestyle modifications can have a positive impact, they should complement medical treatments rather than replace them entirely.
4. Support Groups
Connecting with others who are going through similar experiences can provide invaluable support and understanding.
Joining support groups, whether in-person or online, can allow individuals with psoriasis and autoimmune diseases to share their challenges, gain insights, and access helpful resources. Additionally, healthcare professionals who specialize in these conditions can provide guidance and help devise effective management plans.
5. Skincare Routine
A proper skincare routine can help soothe psoriasis symptoms and prevent flare-ups. This includes using gentle, fragrance-free cleansers, moisturizing regularly, and avoiding harsh products that may irritate the skin.
It’s advisable to consult a dermatologist for personalized skincare recommendations based on the severity and type of psoriasis.
6. Stress Management
Stress can trigger or worsen psoriasis symptoms, making stress management techniques essential. Engaging in relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing exercises, yoga, and meditation, can help reduce stress levels.
Finding activities that bring joy and relaxation can also contribute to overall well-being.
7. Regular Medical Check-ups
Regular check-ups with healthcare professionals are crucial to monitor the condition’s progression, assess treatment effectiveness, and address any concerns.
They can also detect and manage any co-existing conditions or complications that may arise.
8. Education and Empowerment
Understanding psoriasis and autoimmune diseases is vital in managing them effectively.
Educating oneself about the conditions, available treatments, and lifestyle modifications can empower individuals to make informed decisions and actively participate in their own care. Being proactive and working closely with healthcare professionals is key in optimizing treatment outcomes.
9. Psychological Support
Living with psoriasis and autoimmune diseases can have a significant impact on mental health. It’s essential to seek psychological support when needed, whether through therapy, counseling, or support groups.
Managing the emotional and psychological aspects of these conditions can improve overall well-being and quality of life.
10. Patience and Self-Compassion
Managing psoriasis and other autoimmune diseases is a journey that requires patience and self-compassion. Finding the right treatment approach may take time, and there may be setbacks along the way.
Being kind to oneself, celebrating small victories, and seeking support from loved ones can make the journey more bearable.