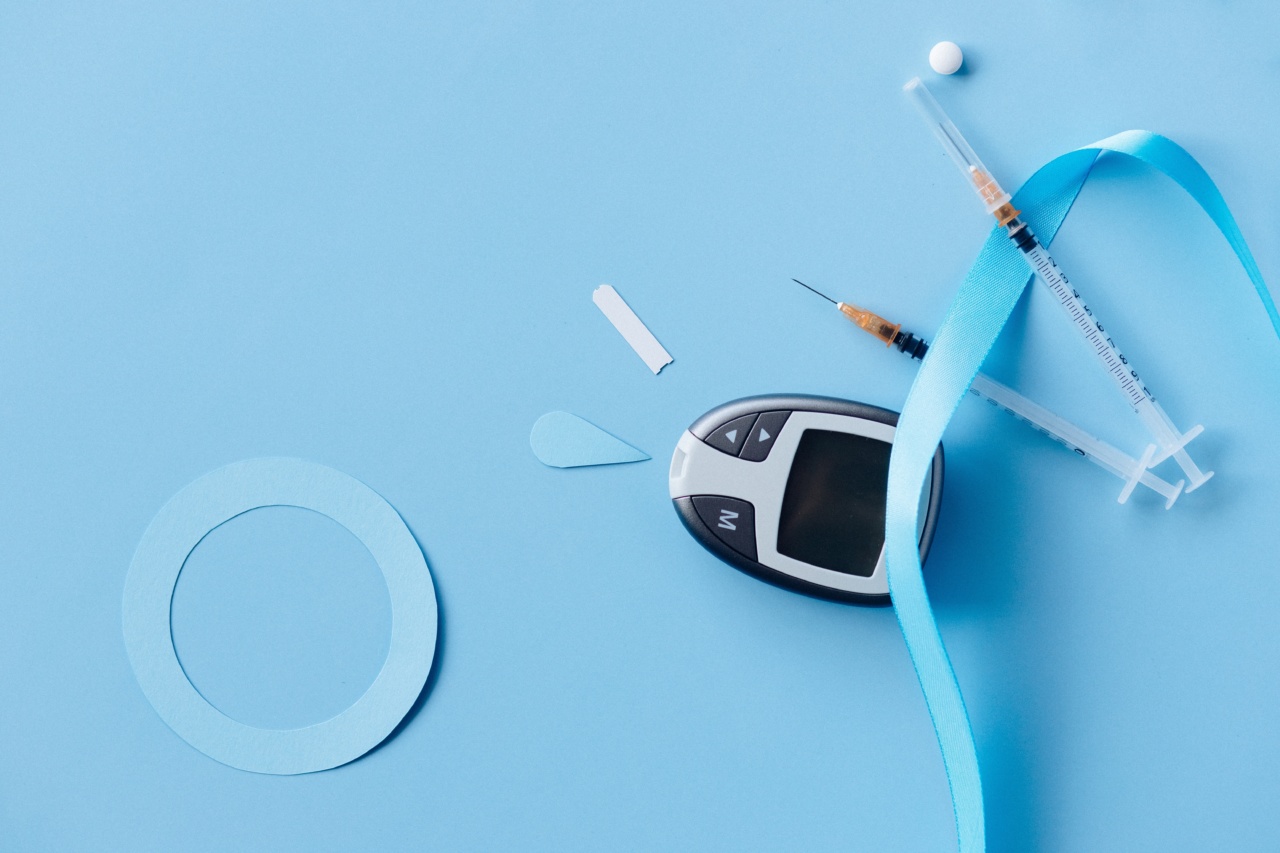
Diabetes is a chronic disease that affects millions of people worldwide. It is a condition in which the body is unable to produce or properly use insulin, a hormone needed to regulate blood sugar levels.
For decades, injections have been the primary method for managing diabetes, but now, a new revolution in diabetes management is taking place, with the development of pill-based therapies.
The Current State of Diabetes Management
Currently, people living with diabetes must rely on daily insulin injections to manage their blood sugar levels. Insulin is a hormone that is produced by the pancreas, which helps the body to convert glucose into energy.
In people with diabetes, either the pancreas does not produce enough insulin or the body does not properly use the insulin that is produced, leading to high blood sugar levels.
The most common form of insulin therapy is the use of an insulin pen or syringe, which involves injecting insulin into the body multiple times a day.
This can be a painful and time-consuming process, and requires regular monitoring of blood sugar levels and insulin doses to ensure proper control of the condition.
The Revolution in Diabetes Management
In recent years, there have been exciting developments in diabetes management, with the development of pill-based therapies.
These new medications are designed to help improve blood sugar control in people with diabetes, and are much less invasive than traditional insulin injections.
One of the most promising new treatments for diabetes is the use of GLP-1 agonists.
These medications work by stimulating the production of insulin, reducing the amount of glucose produced by the liver, and slowing down the rate at which food is absorbed by the stomach. By doing so, GLP-1 agonists can help improve blood sugar control in people with diabetes, without the need for daily injections.
Another type of medication that is changing the landscape of diabetes management is SGLT2 inhibitors. These medications work by blocking the reabsorption of sugar by the kidneys, leading to a decrease in blood sugar levels.
SGLT2 inhibitors are taken in pill form, making them a much more convenient and less invasive option for people with diabetes.
The Benefits of Pill-Based Therapy for Diabetes
The development of pill-based therapies for diabetes has the potential to revolutionize the way in which the condition is managed. Some of the key benefits of these medications include:.
Convenience
Pill-based medications are much more convenient than daily insulin injections.
They can be taken at home, without the need for medical supervision, and do not require the constant monitoring of blood sugar levels and insulin doses that is necessary for insulin therapy.
Less Invasive
Pill-based medications are much less invasive than daily insulin injections. They do not require needles or syringes, making them a more comfortable option for people with diabetes.
Improved Compliance
Many people with diabetes struggle to adhere to their treatment regimen, due to the inconvenience and discomfort associated with daily insulin injections.
Pill-based therapies offer a more convenient and less invasive option for managing the condition, which may improve compliance rates.
The Future of Diabetes Management
The development of pill-based therapies is just the beginning of a new era in diabetes management.
Researchers are constantly working to develop new treatments and therapies that can improve blood sugar control and reduce the burden of diabetes on those living with the condition.
One potential area for further research is the development of artificial pancreas systems. These systems use advanced sensors and software to monitor blood sugar levels and deliver insulin automatically, eliminating the need for manual injections.
Conclusion
The development of pill-based therapies for diabetes is changing the landscape of diabetes management.
These new medications offer a more convenient and less invasive option for managing the condition, which has the potential to improve compliance rates and patient outcomes. With ongoing research and development, the future of diabetes management looks bright.