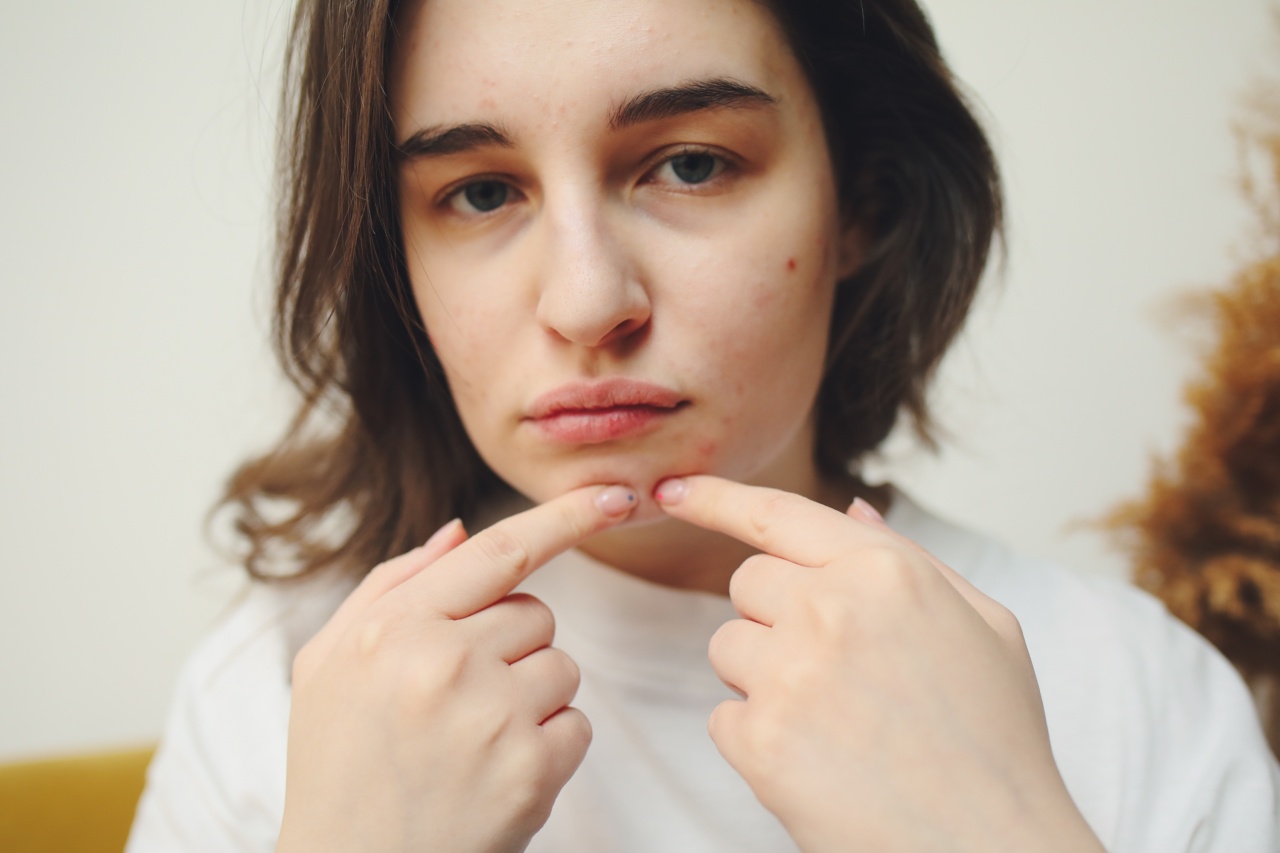
Almost everyone has experienced the satisfaction of popping a pimple, despite being warned against it by dermatologists. The sensation of releasing a burst of pus from a stubborn acne spot can be oddly gratifying.
But why is it so tempting to persistently pop pimples? And what does science have to say about this habit?.
The Anatomy of a Pimple
Before diving into the scientific explanation behind pimple popping, it’s important to understand the anatomy of a pimple.
Pimples, also known as acne vulgaris, occur when the hair follicles become clogged with sebum, dead skin cells, and bacteria. This leads to the formation of a small, raised lesion on the skin’s surface.
Pimples are classified based on their severity into three types: comedones, inflammatory acne, and cystic acne. Comedones are non-inflammatory and include both whiteheads and blackheads.
Inflammatory acne is characterized by redness, swelling, and the presence of pus, while cystic acne is the most severe form and involves deep, painful nodules beneath the skin.
The Appeal of Pimple Popping
Pimple popping, or the act of manually extracting the contents of a pimple, can be incredibly tempting due to several psychological factors. First and foremost, it offers immediate gratification.
The release of pus provides a sense of relief and can give the impression of improving the appearance of the skin.
Moreover, there is a human tendency to engage in repetitive behavior that provides tactile stimulation. Pimple popping offers a combination of tactile stimulation, visual feedback, and emotional satisfaction, triggering the reward center of the brain.
This can create a cycle of repetitive popping, as the brain seeks out the pleasurable sensation.
The Dangers of Pimple Popping
While popping a pimple may provide temporary satisfaction, it is not without risks. Dermatologists strongly advise against popping pimples due to the potential complications it can cause.
Firstly, when you pop a pimple, the pressure exerted can lead to the rupture of the follicle wall. This can cause the contents of the pimple to be pushed deeper into the skin, leading to an increased risk of infection and inflammation.
It can also result in the formation of acne scars, which can be difficult to treat and may persist long after the pimple has healed.
Additionally, popping pimples can introduce bacteria from your hands and nails into the skin, further increasing the risk of infection. It can also lead to the spread of bacteria to neighboring follicles, causing new pimples to form.
Furthermore, excessive popping can disrupt the skin’s natural healing process and prolong the time required for a pimple to resolve. It can also worsen inflammation, leading to increased redness and swelling.
The Science Behind the Temptation
The urge to pop pimples is driven by several scientific factors. Firstly, when a pimple is popped, the pressure applied to the skin triggers nerve endings.
These nerve endings send signals to the brain, resulting in the release of feel-good chemicals such as dopamine. This creates a rewarding sensation and can reinforce the behavior of pimple popping.
In addition, the act of popping a pimple can provide sensory stimulation, activating the brain’s reward circuitry.
This stimulation can create a pleasurable response, leading to a psychological attachment and increasing the likelihood of repeating the behavior in the future.
The Importance of Proper Pimple Care
Instead of resorting to popping pimples, practicing proper pimple care is essential for maintaining healthy skin and preventing the formation of acne scars. Here are some tips to help you deal with pimples effectively:.
1. Cleanse Your Face Regularly
Regularly cleansing your face helps remove excess oil, dead skin cells, and bacteria, reducing the risk of clogged pores and acne breakouts.
Use a gentle cleanser suitable for your skin type and avoid scrubbing too vigorously, as it can irritate the skin and worsen acne.
2. Use Topical Treatments
Topical treatments, such as over-the-counter creams or gels containing benzoyl peroxide or salicylic acid, can help control acne. These ingredients work by reducing inflammation, killing bacteria, and promoting the shedding of dead skin cells.
3. Avoid Touching Your Face
Touching your face with your hands can transfer bacteria and dirt, potentially leading to acne breakouts. Keep your hands away from your face as much as possible, especially when you have active pimples.
4. Do Not Squeeze or Pop Pimples
Resist the temptation to squeeze or pop pimples. Instead, allow them to heal naturally or seek professional help from a dermatologist if needed.
Dermatologists have specialized tools and techniques to safely extract pimples without causing additional harm to the skin.
5. Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle
Eating a balanced diet, getting enough sleep, managing stress levels, and avoiding excessive sun exposure can all contribute to overall skin health and reduce the risk of acne breakouts.
The Bottom Line
Pimple popping may provide temporary gratification, but it is not a recommended practice due to the potential risks and complications it can cause.
Understanding the science behind the temptation can help individuals make informed decisions about their skincare routine.