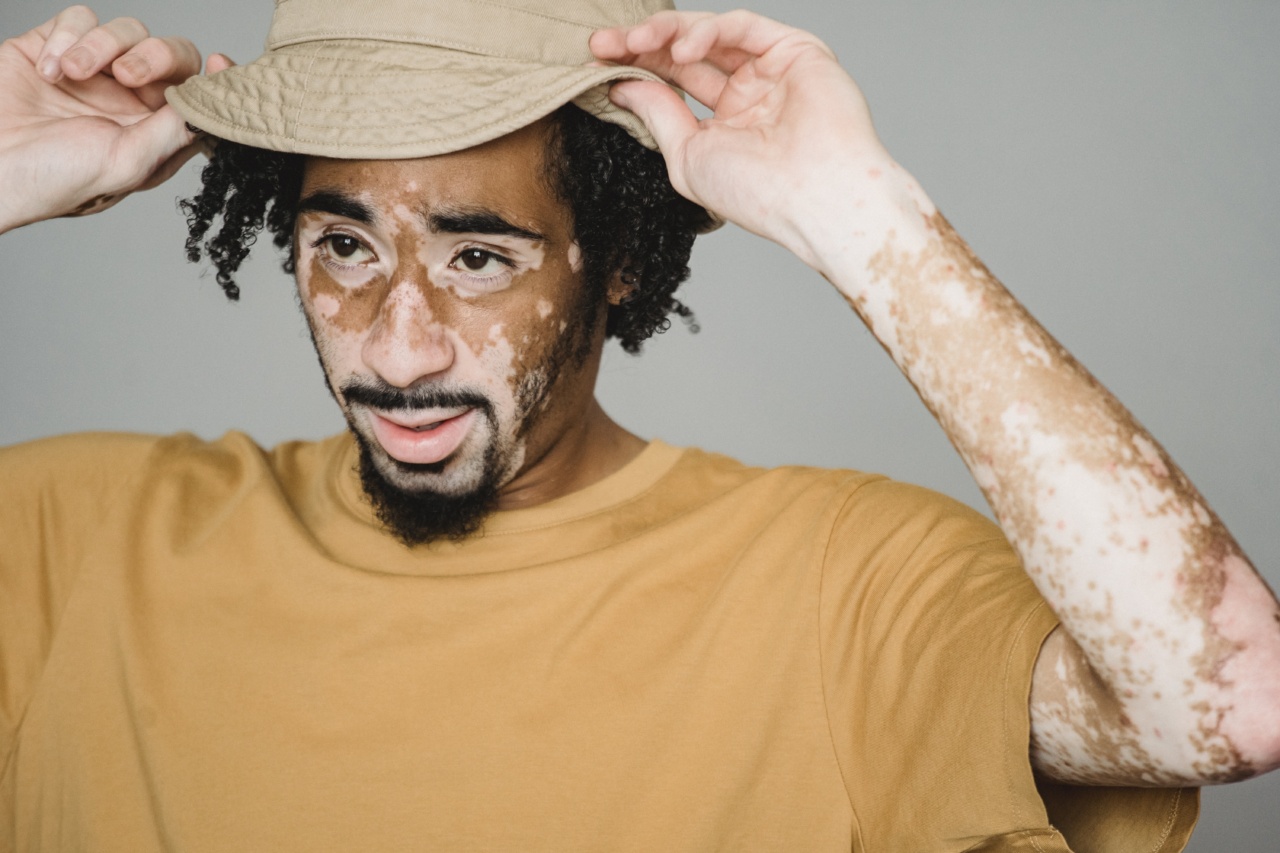
Autoimmune diseases affect millions of people worldwide, including in the United States. These conditions arise when a person’s immune system mistakenly attacks healthy cells in the body, resulting in chronic inflammation and tissue damage.
Common autoimmune diseases include rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, multiple sclerosis, and inflammatory bowel disease. While these conditions can be debilitating, they can also be expensive, and many people living with autoimmune diseases struggle to afford the care they need.
For this reason, understanding how health insurance coverage works for autoimmune diseases is crucial. In this guide, we’ll explore some of the key factors to keep in mind when navigating the intersection of autoimmune disease and insurance.
Pre-Existing Conditions
One of the most crucial factors to consider when it comes to autoimmune diseases and insurance coverage is whether your condition is considered a pre-existing condition.
A pre-existing condition is any ailment that you had before signing up for a particular insurance policy. In the past, many health insurance policies would exclude coverage for pre-existing conditions, leaving those with chronic illnesses struggling to afford care.
Thankfully, the Affordable Care Act (ACA) changed this and ensured that insurance companies could no longer deny coverage to people with pre-existing conditions.
This means that if you have an autoimmune disease, you cannot be denied coverage or charged more for your insurance policy simply because of your condition.
Out-of-Pocket Costs
Even with insurance coverage, many people with autoimmune diseases find that they still face significant out-of-pocket costs. This includes co-pays, deductibles, and co-insurance fees.
It’s essential to pay attention to the fine print in your insurance policy when it comes to these costs.
Some policies may have lower monthly premiums but higher out-of-pocket costs, while others may have higher premiums but lower out-of-pocket expenses.
If you’re struggling to afford your out-of-pocket expenses, there are some options available to you. For example, some drug manufacturers offer financial assistance programs to help cover the cost of medications.
Additionally, some states offer programs for low-income residents that can help pay for healthcare expenses.
Specialty Care
Many autoimmune diseases require specialized care, such as visits with rheumatologists, dermatologists, or gastroenterologists. These visits can be expensive, and not all insurance policies cover them.
When choosing a health insurance policy, it’s crucial to pay attention to which doctors and specialists are within the network covered by the policy.
Out-of-network care can be significantly more expensive, so it’s essential to ensure that the doctors you need are in-network.
Prescription Medications
Many autoimmune diseases require ongoing treatment with prescription medications. These drugs can be costly, and not all insurance policies cover them.
When evaluating insurance policies, be sure to look at the prescription drug coverage. Some policies may require you to pay a percentage of the cost of the medication, while others may have a set co-pay amount for each prescription.
Additionally, it’s worth noting that not all medications are created equal when it comes to insurance coverage.
Some insurance policies may cover only generic versions of medications, while others may cover name-brand drugs but require a higher co-pay.
Alternative Treatments
Many people with autoimmune diseases turn to alternative treatments, such as acupuncture, massage, or dietary supplements. While these treatments are often helpful, they can be expensive, and not all insurance policies cover them.
If alternative treatments are important to you, it’s essential to look for insurance policies that cover them. However, keep in mind that alternative treatments may be more challenging to find coverage for than traditional medical care.
Long-Term Disability Coverage
Autoimmune diseases can be debilitating, and in some cases, they may prevent individuals from working. Long-term disability coverage can help provide financial support in these situations.
When evaluating insurance policies, be sure to look at the long-term disability coverage options. Some policies may provide coverage for up to two years, while others may offer coverage for longer periods.
Conclusion
Autoimmune diseases can be challenging to live with, both physically and financially. However, understanding how health insurance coverage works can help you better navigate the challenges that come with these conditions.
By paying attention to factors such as pre-existing conditions, out-of-pocket costs, specialty care, prescription medications, alternative treatments, and long-term disability coverage, you can make an informed decision when selecting a health insurance policy.