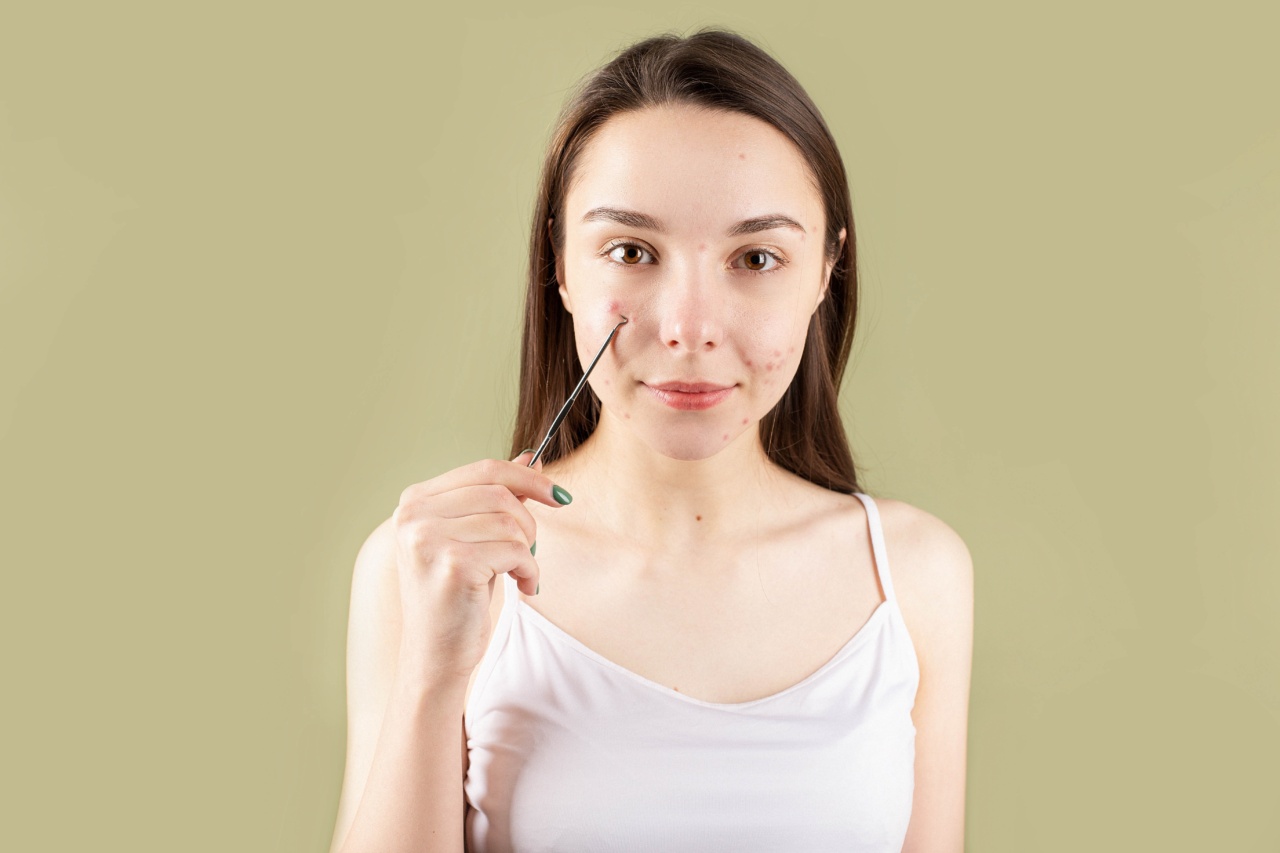
Acne is a common skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It can be a source of frustration and embarrassment, particularly when it occurs during adolescence, but it can also persist into adulthood.
This article will discuss the causes, symptoms, and various treatments available for acne.
Causes of Acne
Acne is primarily caused by the overproduction of oil, known as sebum, by the sebaceous glands. When excess sebum combines with dead skin cells and bacteria, it can clog pores on the skin’s surface, resulting in acne.
Several factors can contribute to this overproduction of sebum:.
1. Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations during puberty, menstruation, and pregnancy can trigger acne outbreaks.
2. Genetics: Acne can run in families, suggesting a genetic predisposition to the condition.
3. Diet: Consuming high-glycemic foods and dairy products has been linked to acne development.
4. Stress: Increased stress levels can exacerbate acne due to hormonal changes.
5. Medications: Certain medications, including corticosteroids and anticonvulsants, can cause acne as a side effect.
Symptoms of Acne
The symptoms of acne can vary in severity and presentation. Common symptoms include:.
1. Whiteheads: Small, flesh-colored or white bumps that appear on the surface of the skin.
2. Blackheads: Open comedones that appear black due to oxidation of the trapped sebum and dead skin cells.
3. Papules: Small, red, and tender bumps that may be raised or swollen.
4. Pustules: Similar to papules but with a visible yellow or white center, caused by the presence of pus.
5. Nodules: Large, solid, and painful lumps that develop deep within the skin.
6. Cysts: Painful, pus-filled lumps that are deep-seated and can leave scars.
Treatments for Acne
There are various treatment options available for managing acne. The choice of treatment depends on the severity of the condition and individual preferences. The common treatments include:.
1. Over-the-counter Products: These include creams, gels, and cleansers that often contain benzoyl peroxide or salicylic acid to reduce oil production and unclog pores.
2. Prescription Medications: Dermatologists may prescribe topical creams, gels, or oral medications like antibiotics, retinoids, or hormonal treatments for more severe cases of acne.
3. Professional Procedures: Dermatologists can perform various procedures like chemical peels, microdermabrasion, or extracting comedones manually to treat acne.
4. Home Remedies: Some people find relief using natural remedies like tea tree oil, apple cider vinegar, or a honey and cinnamon mask, although evidence supporting their effectiveness is limited.
5. Lifestyle Modifications: Adopting a skincare routine, avoiding excessive sun exposure, washing your face regularly, and maintaining a healthy diet can also help minimize acne breakouts.
Preventing Acne
While acne cannot always be completely prevented, certain measures can reduce the risk of developing it:.
1. Keep the Skin Clean: Regularly cleanse the face with a mild cleanser to remove excess oil, dirt, and dead skin cells.
2. Avoid Touching the Face: Touching the face with dirty hands can introduce bacteria and other impurities to the skin, leading to acne.
3. Remove Makeup before Bed: Sleeping with makeup on can clog pores, increasing the likelihood of developing acne.
4. Wear Non-Comedogenic Products: Choose makeup and skincare products labeled as non-comedogenic, indicating that they are less likely to clog pores.
5. Limit Sun Exposure: While sunlight can temporarily improve acne, excessive exposure can lead to skin damage and make acne worse in the long run.
Conclusion
Acne is a common skin condition that can cause physical and emotional distress. Understanding the causes and symptoms of acne allows for more effective prevention and treatment.
With a combination of proper skincare, lifestyle modifications, and appropriate medical interventions, acne can be managed and minimized, promoting clearer and healthier skin.