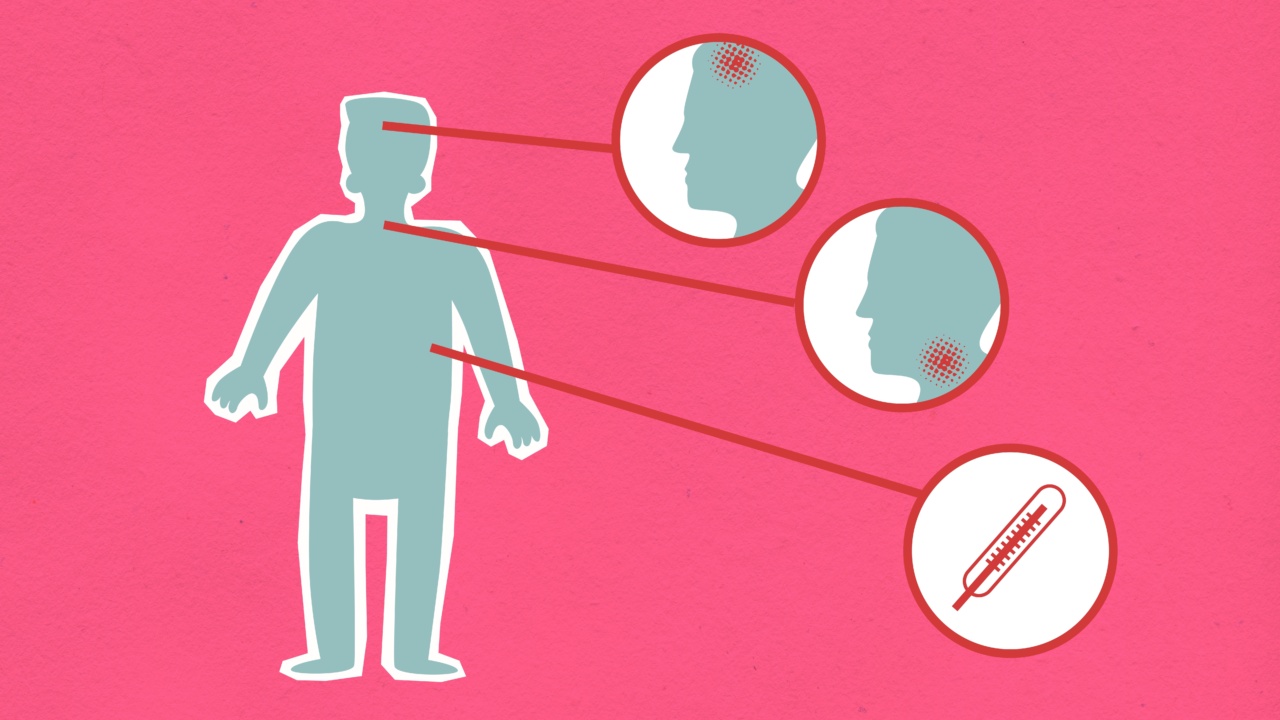
In the midst of the COVID-19 pandemic, it is essential to be able to recognize the various symptoms associated with the virus. One common symptom that often causes confusion is a sore throat.
However, it is important to distinguish between a sore throat caused by COVID-19 and a sore throat caused by other factors, such as coronary issues. By understanding the unique characteristics of each, individuals can seek appropriate medical attention and take necessary precautions.
This article aims to explore the distinguishing features of COVID-19 and coronary sore throats, enabling readers to differentiate between the two.
Understanding COVID-19
COVID-19, also known as the novel coronavirus, is a highly contagious respiratory illness. It primarily spreads through respiratory droplets when an infected individual coughs, sneezes, or talks.
The virus can enter the body through the nose, mouth, or eyes, and it then targets the respiratory system, causing various symptoms that range from mild to severe.
COVID-19 and Sore Throat
A sore throat is one of the many symptoms associated with COVID-19, but it is not always present in every case. The severity of the sore throat can also vary among individuals.
Some may experience a mild irritation, while others may experience significant discomfort. However, it is important to note that a sore throat alone is not a definitive indication of COVID-19. It should be considered alongside other common symptoms, such as fever, cough, and shortness of breath.
COVID-19 sore throats often manifest as a dry, scratchy, or itchy sensation. Swallowing might be painful, and the throat can feel inflamed and swollen.
In some cases, individuals may also experience a loss of taste or smell, which are unique symptoms associated with COVID-19. If you are experiencing a sore throat with any of these additional symptoms, it is crucial to seek medical advice and get tested for COVID-19.
Coronary Sore Throat
A sore throat is not exclusively related to COVID-19 and can be caused by various factors, including coronary issues.
Coronary artery disease occurs when the major blood vessels that deliver oxygen, nutrients, and vital substances to the heart become damaged or diseased. As a result, a person may experience chest pain (angina) or a sore throat.
A sore throat caused by coronary issues may have different characteristics compared to a COVID-19 sore throat. It often begins as a dull, aching sensation that can radiate to the jaw or neck. The pain may worsen with physical exertion or emotional stress.
Unlike a COVID-19 sore throat, coronary-related sore throats are not typically accompanied by other respiratory symptoms or a loss of taste or smell.
Differentiating between the Two
While there are some distinguishing features between a COVID-19 and a coronary sore throat, it can still be challenging to determine the exact cause based on symptoms alone.
Consulting a medical professional is vital to receive an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Here are a few factors that can help differentiate between the two:.
1. Accompanying Symptoms
Pay attention to other symptoms accompanying the sore throat. If you experience symptoms such as fever, cough, shortness of breath, body aches, fatigue, or a loss of taste or smell, it may indicate COVID-19.
On the other hand, if you have a sore throat along with chest pain, difficulty breathing, or a history of coronary issues, it is more likely related to a cardiac problem.
2. Medical History
If you have a pre-existing heart condition, such as coronary artery disease, and have been experiencing chest pain or other symptoms related to cardiac health, it is crucial to consider the possibility of a coronary sore throat.
Similarly, if you have been in contact with someone who has tested positive for COVID-19 or have visited an area with a high number of cases, it is important to consider the possibility of COVID-19 as the cause of your sore throat.
3. Timeframe
COVID-19 symptoms often develop within two to fourteen days after exposure. If your sore throat occurs within this timeframe and is accompanied by other common COVID-19 symptoms, it is crucial to get tested and follow appropriate isolation protocols.
However, if you have a history of coronary issues and have been experiencing a sore throat for an extended period along with chest discomfort or other cardiac symptoms, consult with your healthcare provider immediately.
4. Risk Factors
Consider your risk factors for both COVID-19 and coronary artery disease. Age, underlying health conditions, and exposure to the virus can increase the likelihood of COVID-19.
On the other hand, factors such as smoking, a sedentary lifestyle, high blood pressure, high cholesterol levels, and a family history of coronary issues can predispose individuals to a sore throat caused by coronary problems.
Seeking Medical Advice
Regardless of the cause of your sore throat, it is essential to seek medical advice if you experience persistent or severe symptoms.
Healthcare professionals can provide a proper diagnosis and guide you through the appropriate steps to manage your condition.
If you suspect COVID-19 is the cause of your sore throat, follow the guidelines provided by local health authorities and get tested. It is crucial to isolate yourself to prevent the spread of the virus to others while awaiting test results.
If you believe your sore throat is related to coronary issues, consult with your primary care physician or a cardiologist. They can evaluate your medical history, perform necessary tests, and recommend appropriate treatment options.
Conclusion
While a sore throat can be a common symptom of both COVID-19 and coronary artery disease, understanding the distinguishing features can help in identifying the cause.
A sore throat accompanied by other respiratory symptoms, a loss of taste or smell, and epidemiological factors may indicate COVID-19. On the other hand, if the sore throat is accompanied by chest pain, shortness of breath, or is associated with coronary issues, it is more likely related to the heart.
Regardless, it is always important to seek medical advice to receive an accurate diagnosis and proper treatment. By staying informed and vigilant, individuals can take appropriate measures to protect their health and the well-being of others.