Abdominal tachycardia, a rapid and irregular heartbeat originating from the abdomen, can be a debilitating condition that significantly impacts a patient’s quality of life.
Traditionally, treatment options for this condition have been limited and invasive, often involving surgery or the use of medications with potential side effects. However, a cutting-edge treatment called non-invasive radiotherapy is revolutionizing the way abdominal tachycardia is managed, offering patients a safer and more effective alternative.
The Basics of Abdominal Tachycardia
Abdominal tachycardia refers to an abnormal increase in heart rate that originates from the abdomen rather than the heart itself.
This condition is often associated with abnormal electrical activity in the abdominal nerves or ganglia, which disrupts the heart’s normal rhythm. The exact cause of abdominal tachycardia is still not fully understood, but it can be triggered by various factors, including stress, anxiety, certain medications, or underlying medical conditions.
The Limitations of Traditional Treatment
In the past, the treatment options for abdominal tachycardia were limited and often invasive.
Medications, such as beta-blockers or anti-arrhythmic drugs, were commonly prescribed to manage the symptoms, but they often came with side effects like fatigue, dizziness, or gastrointestinal disturbances. In more severe cases, surgical interventions like ablation or sympathectomy were performed, which carried their own risks and potential complications.
An Innovative Approach: Non-Invasive Radiotherapy
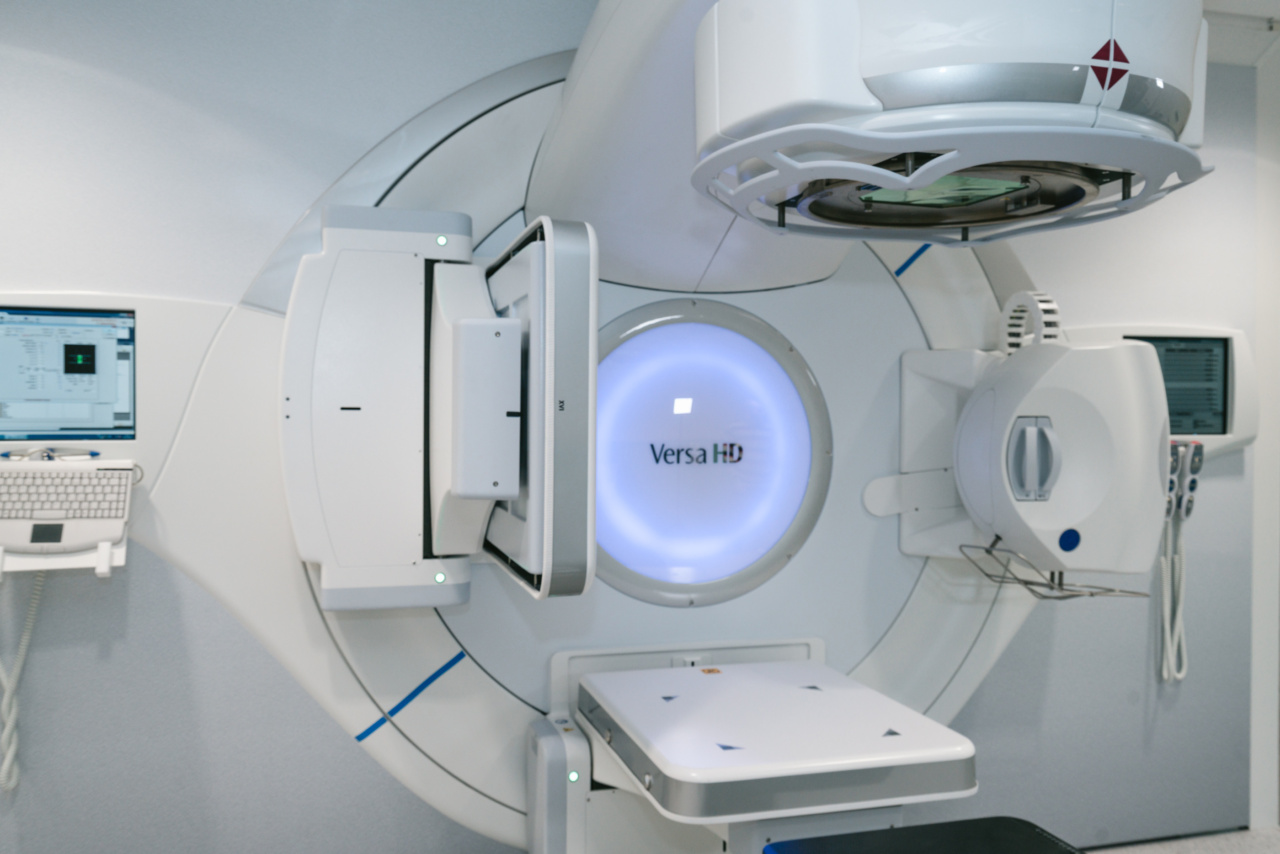
Non-invasive radiotherapy is a cutting-edge treatment modality that is gaining recognition for its effectiveness in managing abdominal tachycardia.
This treatment utilizes focused radiation beams to target and disrupt the abnormal electrical signals originating from the abdominal area, restoring the heart’s normal rhythm. The procedure is performed using advanced imaging techniques, ensuring precise delivery of radiation while minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissues.
The Benefits of Non-Invasive Radiotherapy
Non-invasive radiotherapy offers several advantages over traditional treatment methods:.
1. Minimally Invasive:
Unlike surgical procedures, non-invasive radiotherapy does not involve any incisions or invasive techniques. This significantly reduces the risk of complications, such as infection or bleeding, and shortens the recovery time for patients.
2. Targeted Approach:
With the use of advanced imaging technology, non-invasive radiotherapy allows for precise targeting of the abnormal electrical signals in the abdomen. This minimizes damage to surrounding healthy tissues and ensures maximum effectiveness.
3. Non-Toxic:
Unlike medications used to manage abdominal tachycardia, non-invasive radiotherapy does not introduce any chemical substances into the body.
This eliminates the potential side effects associated with medications, such as dizziness or gastrointestinal disturbances.
4. Improved Quality of Life:
By providing a more effective management solution for abdominal tachycardia, non-invasive radiotherapy can greatly improve a patient’s quality of life.
Patients experience fewer episodes of rapid heart rate and related symptoms, allowing them to engage in activities without limitations or anxiety.
The Procedure and Its Efficacy
Non-invasive radiotherapy for abdominal tachycardia is typically performed as an outpatient procedure.
Before the treatment, patients undergo several imaging scans, such as computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), to precisely determine the location and extent of the abnormal electrical activity.
During the procedure, patients are comfortably positioned on a treatment table, and the advanced imaging technology guides the radiation beams to precisely target the affected areas.
The duration of the treatment session can vary depending on the individual case, but it typically lasts between 30 minutes to an hour.
The efficacy of non-invasive radiotherapy for abdominal tachycardia has shown promising results. Multiple studies have reported a significant reduction in the frequency and severity of tachycardia episodes following the treatment.
Long-term follow-up studies have indicated that the beneficial effects of non-invasive radiotherapy can be sustained for several years after the procedure.
Potential Future Applications
Non-invasive radiotherapy is still an emerging field, and ongoing research and development are exploring its potential applications beyond abdominal tachycardia.
Early studies suggest that this treatment modality may also be effective for managing other types of cardiac arrhythmias originating from different areas of the body.
Additionally, non-invasive radiotherapy has the potential to be used in combination with other treatment modalities, such as medications or catheter ablation, to further enhance the effectiveness of managing abdominal tachycardia.
Conclusion
Non-invasive radiotherapy represents a cutting-edge and promising treatment approach for abdominal tachycardia.
By precisely targeting and disrupting the abnormal electrical signals originating from the abdomen, this innovative procedure offers patients a minimally invasive, non-toxic, and effective alternative to traditional treatment options.
As ongoing research and development continue to refine the technique, non-invasive radiotherapy holds the potential to revolutionize the management of abdominal tachycardia and potentially other cardiac arrhythmias.
Through its numerous benefits, this treatment modality has the potential to improve the quality of life for individuals living with abdominal tachycardia, allowing them to regain control over their heart rhythm and live without limitations.