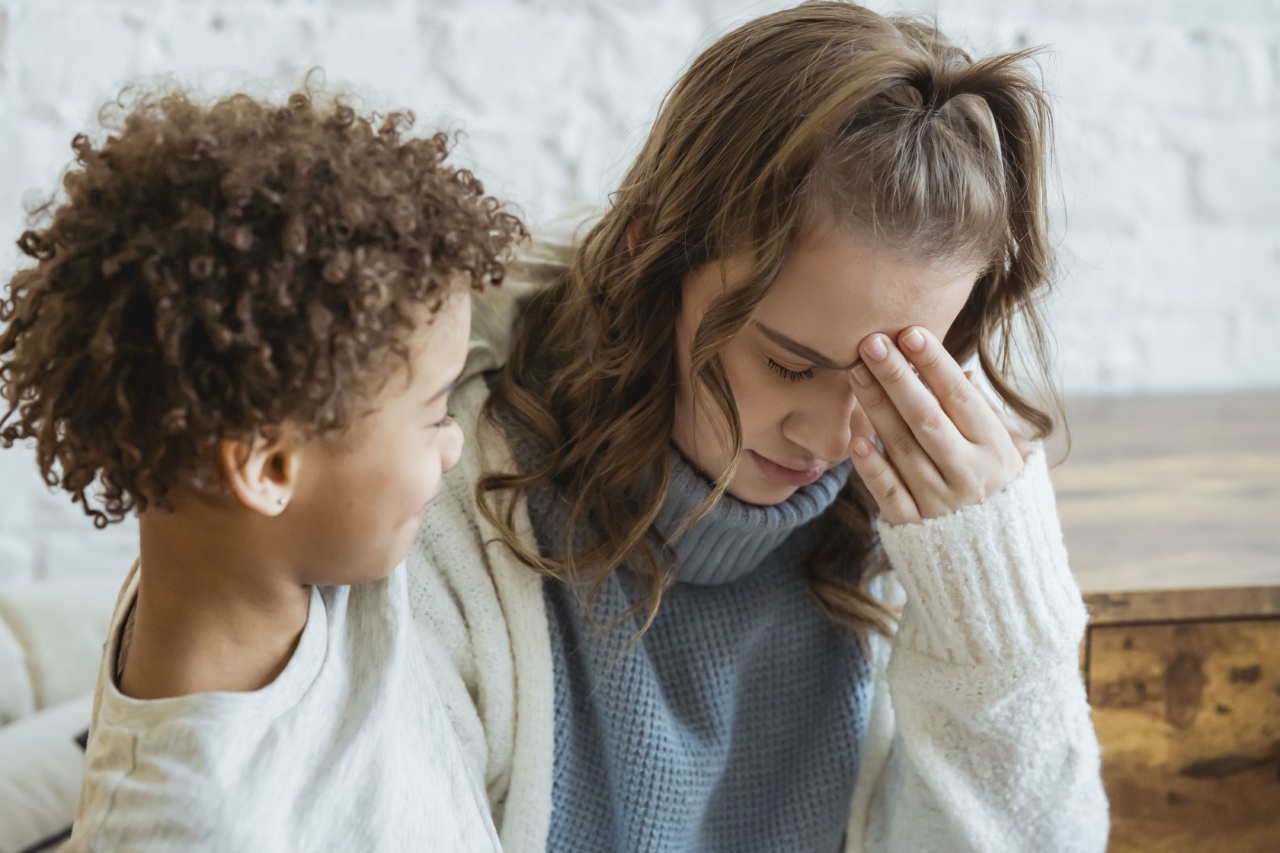
Maternal depression is a serious mental health issue that affects many women during pregnancy and after childbirth.
The impacts of this condition on the mother’s mood and cognitive functions are well-known, but studies also suggest that maternal depression can lead to adverse effects on child brain development.
What is Maternal Depression?
Maternal depression refers to a persistent feeling of sadness, hopelessness, and worthlessness among mothers. It is a medical condition that requires professional intervention to mitigate its impacts.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), depression affects about 10% of pregnant women and 13% of women who have given birth.
Symptoms of Maternal Depression
Some of the common signs and symptoms of maternal depression are:.
- Feeling sad, anxious, or “empty” most of the time
- Lack of interest or pleasure in activities
- Feelings of guilt, hopelessness, or worthlessness
- Changes in appetite and sleeping patterns
- Lack of energy or motivation to do things
- Difficulty concentrating or making decisions
- Thoughts of self-harm or suicide
Impact of Maternal Depression on Child Brain Development
Maternal depression can affect a child’s brain development in different ways:.
Bonding and Attachment
Maternal depression can affect the mother’s ability to bond and attach with her child. Children of depressed mothers may exhibit higher levels of attachment insecurity, which can lead to cognitive and emotional difficulties in the future.
Studies suggest that children of depressed mothers have higher levels of cortisol, a stress hormone that affects brain development.
Cognitive Development
Maternal depression can affect a child’s cognitive development, including language, memory, and attention. Children of depressed mothers may have lower IQ scores, delays in language acquisition, and poor academic performance.
Studies also suggest that maternal depression can affect executive functions such as planning, decision-making, and impulse control.
Emotional Development
Maternal depression can also affect a child’s emotional development, including their ability to regulate emotions and respond to stress. Children of depressed mothers may exhibit higher levels of anxiety, depression, and aggression.
Maternal depression can also affect a child’s social skills, leading to difficulties in making and maintaining friendships.
Preventing Maternal Depression
Preventing maternal depression requires a multi-faceted approach that involves early identification, treatment, and support. Some of the strategies that can help prevent maternal depression include:.
- Regular prenatal care and screening for depression
- Psychotherapy, counseling, or cognitive-behavioral therapy
- Support groups and peer counseling for mothers
- Social support from family, friends, and partners
- Self-care strategies such as exercise, meditation, and sleep hygiene
Treating Maternal Depression
Treatment for maternal depression can involve medication, psychotherapy, or a combination of both. Antidepressant medications can help relieve the symptoms of depression, but they should be used cautiously during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
Psychotherapy, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy, can help women address negative thought patterns and behaviors that contribute to depression.
Conclusion
Maternal depression is a common mental health issue that can have serious impacts on child brain development. It is important for mothers to seek medical attention and support to mitigate the effects of depression on themselves and their children.
By getting help early, mothers can ensure that their children have the best possible chance at healthy brain development and future success.