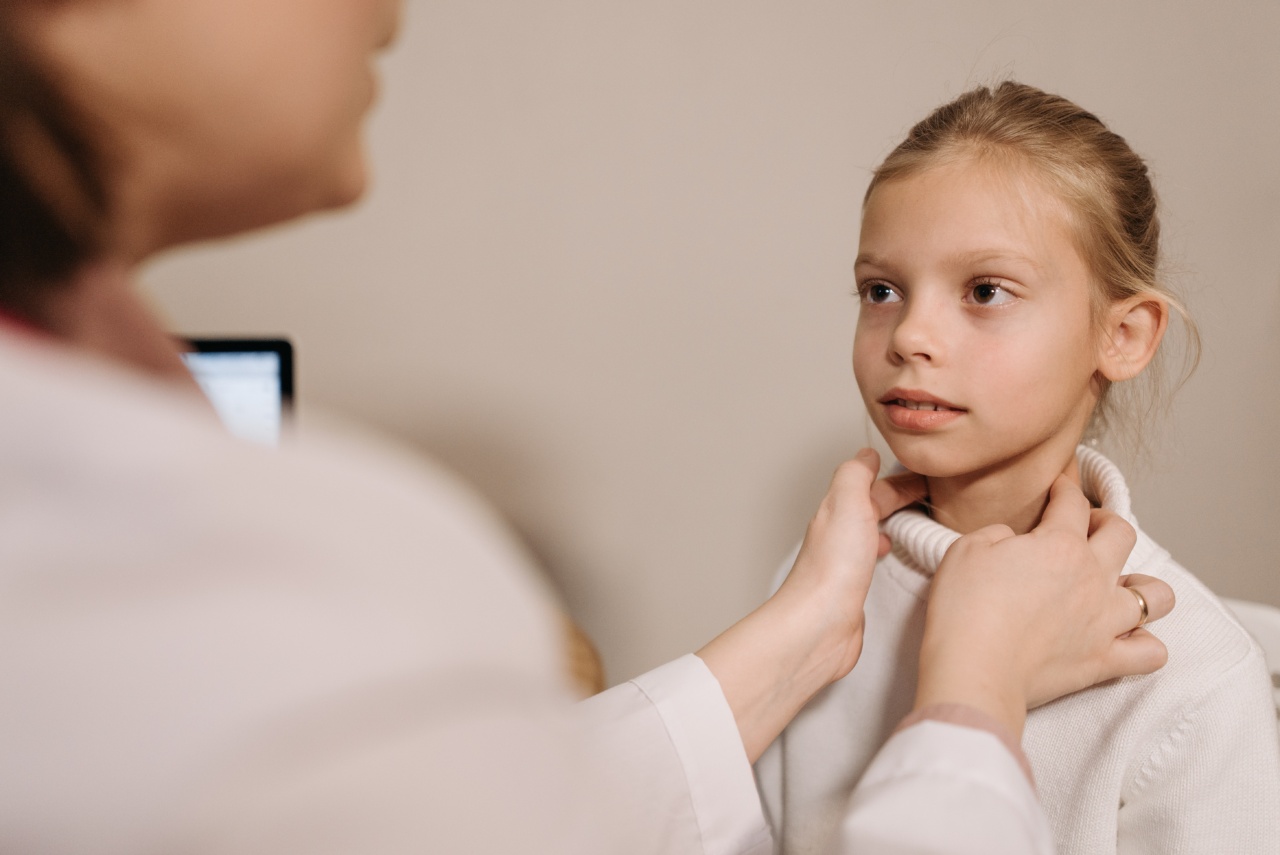
Swollen tonsils with pus, also known as tonsillitis, is a common condition that affects people of all ages. It is marked by the irritation and inflammation of the tonsils, which are two small masses of soft tissue located at the back of the throat.
These masses, which are part of the immune system, help protect the body against infection by trapping bacteria and other germs that enter the body through the mouth and nose.
What Are the Symptoms of Swollen Tonsils with Pus?
Swollen tonsils with pus can cause a range of symptoms, which can vary in severity from person to person. The most common symptoms of the condition include:.
- Sore throat
- Fever
- Painful swallowing
- Difficulty breathing
- Swollen lymph nodes in the neck
- Bumps or sores on the tonsils
- White or yellow spots on the tonsils
What Causes Swollen Tonsils with Pus?
The most common cause of swollen tonsils with pus is a bacterial or viral infection. Bacterial infections are usually caused by streptococcus bacteria, which can cause strep throat and other types of infections.
Viral infections, on the other hand, can be caused by a variety of viruses, including the flu, the common cold, and the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV).
Other factors that can increase the risk of developing swollen tonsils with pus include:.
- Exposure to allergens and pollutants
- Cigarette smoke
- Chronic sinus infections
- Chronic tonsillitis
- Immune system disorders
How Is Swollen Tonsils with Pus Diagnosed?
To diagnose swollen tonsils with pus, a doctor will typically perform a physical exam and ask about the patient’s symptoms and medical history.
They may also order tests, such as a throat culture or a blood test, to confirm the presence of a bacterial or viral infection. In some cases, a CT scan or MRI may be needed to check for complications, such as an abscess or damage to the tonsils.
What Is the Treatment for Swollen Tonsils with Pus?
The treatment for swollen tonsils with pus depends on the underlying cause of the condition. Bacterial infections are usually treated with antibiotics, while viral infections are treated with rest and fluids to help the body fight off the infection.
Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, can also be used to ease pain and reduce fever.
In severe cases, where the tonsils are severely infected, surgery may be required to remove them. This is known as a tonsillectomy and is typically reserved for cases where other treatments have failed to resolve the condition.
How Can Swollen Tonsils with Pus Be Prevented?
Preventing swollen tonsils with pus involves taking steps to reduce the risk of bacterial or viral infections. This includes:.
- Washing hands frequently with soap and warm water
- Avoiding close contact with people who are sick
- Covering the mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing
- Avoiding touching the face, especially the nose and mouth
- Keeping surfaces clean and disinfected
- Staying hydrated
When Should You See a Doctor?
If you have symptoms of swollen tonsils with pus, it is important to see a doctor promptly. This is especially true if you experience difficulty breathing, high fever, or severe throat pain.
These symptoms can indicate a more serious infection that requires prompt treatment.