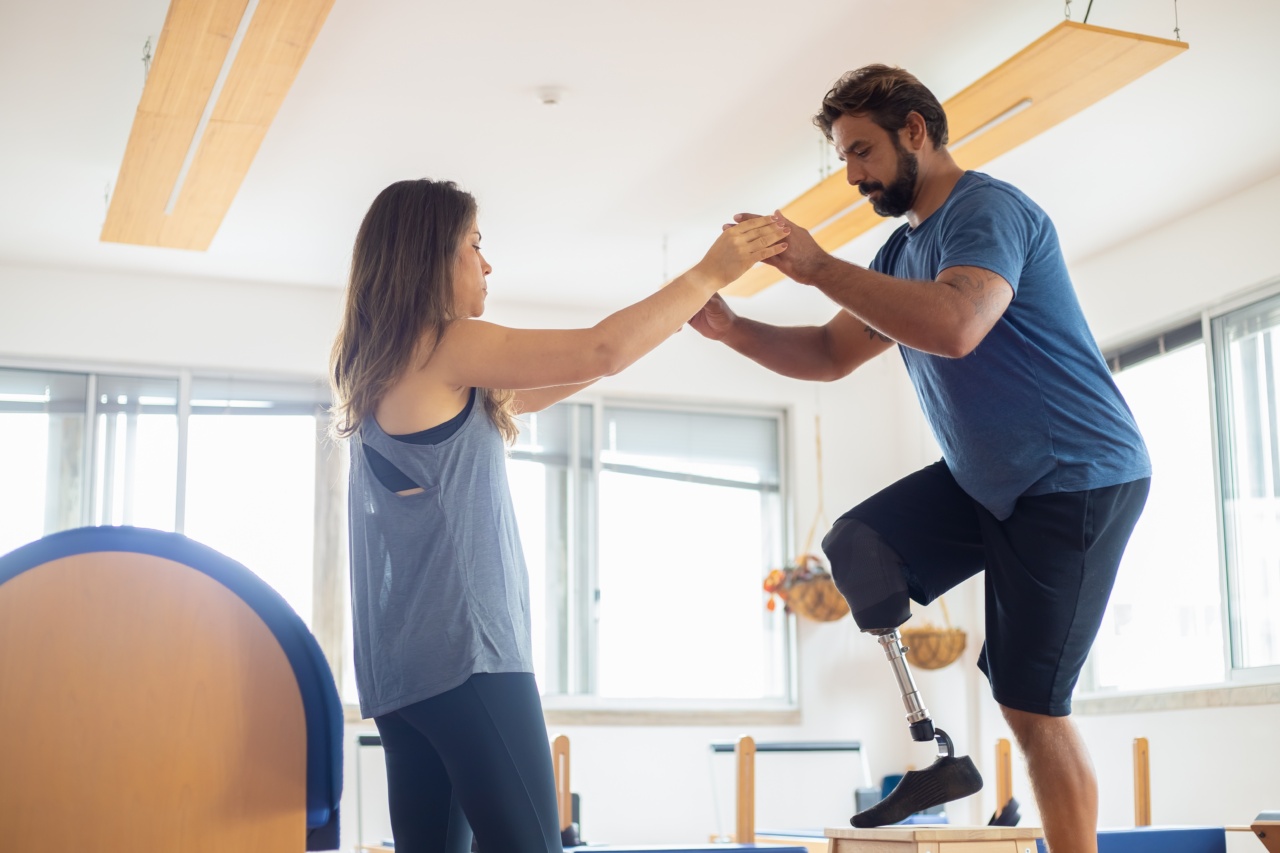
Parkinson’s disease is a neurodegenerative disorder that progressively affects movement. The disease occurs due to a loss in dopamine-producing cells in the brain.
As the disease progresses, motor symptoms such as tremors, stiffness, and balance problems, become more severe and may interfere with daily activities. One of the treatment approaches for people with Parkinson’s Disease is exercise therapy. It is known to improve balance and mobility.
Benefits of Exercise Therapy for Parkinson’s Disease
Exercise therapy is an effective intervention for managing the symptoms of Parkinson’s Disease. It has been shown to improve balance, mobility, and quality of life in patients.
The following are some benefits of exercise therapy for Parkinson’s Disease:.
- Improved balance and gait stability
- Increased muscle strength and flexibility
- Reduced falls and injuries
- Improved cardiovascular health
- Reduced anxiety and depression
Types of Exercise Therapy for Parkinson’s Disease
There are several types of exercise therapy that are beneficial for people with Parkinson’s Disease:.
- Aerobic exercise – This includes activities such as walking, cycling, and running that increase heart rate and breathing rate for a prolonged period of time. Aerobic exercise improves cardiovascular endurance and helps reduce fatigue.
- Resistance training – This involves the use of weights, exercise bands, or body weight to build muscle strength. Resistance training improves overall muscle strength, which can improve balance and reduce the risk of falls.
- Balance training – This includes activities such as standing on one leg, heel-to-toe walking, or Tai Chi that focus on improving balance and stability. Balance training reduces the risk of falls and improves overall mobility.
Exercise Therapy and Improving Balance
Balance problems are common in people with Parkinson’s Disease, which increases the risk of falls and injuries.
Exercise therapy can improve balance by strengthening the muscles involved in balance and promoting the use of proprioception, which is the body’s ability to sense its position in space. The following are some exercises that can improve balance in people with Parkinson’s Disease:.
- Balancing on one leg – Standing on one leg for 30 seconds to one minute improves balance and stability.
- Walking heel-to-toe – Walking with the heel of one foot touching the toe of the other foot improves balance and coordination.
- Practicing Tai Chi – Tai Chi is an ancient Chinese practice that involves slow, gentle movements that improve balance and promote relaxation.
Exercise Therapy and Improving Mobility
Mobility problems are also common in people with Parkinson’s Disease, which can make daily activities such as walking and standing difficult. Exercise therapy can improve mobility by strengthening muscles and increasing flexibility.
The following are some exercises that can improve mobility in people with Parkinson’s Disease:.
- Walking – Walking is an effective exercise for improving mobility and cardiovascular health.
- Cycling – Cycling is a low-impact exercise that improves cardiovascular health and strengthens leg muscles.
- Swimming – Swimming is a low-impact exercise that improves cardiovascular health and strengthens muscles throughout the body.
Conclusion
Exercise therapy is an effective approach for improving balance and mobility in people with Parkinson’s Disease. It has been shown to improve overall quality of life and reduce the risk of falls and injuries.
A combination of aerobic exercise, resistance training, and balance training can provide significant benefits for people with Parkinson’s Disease.