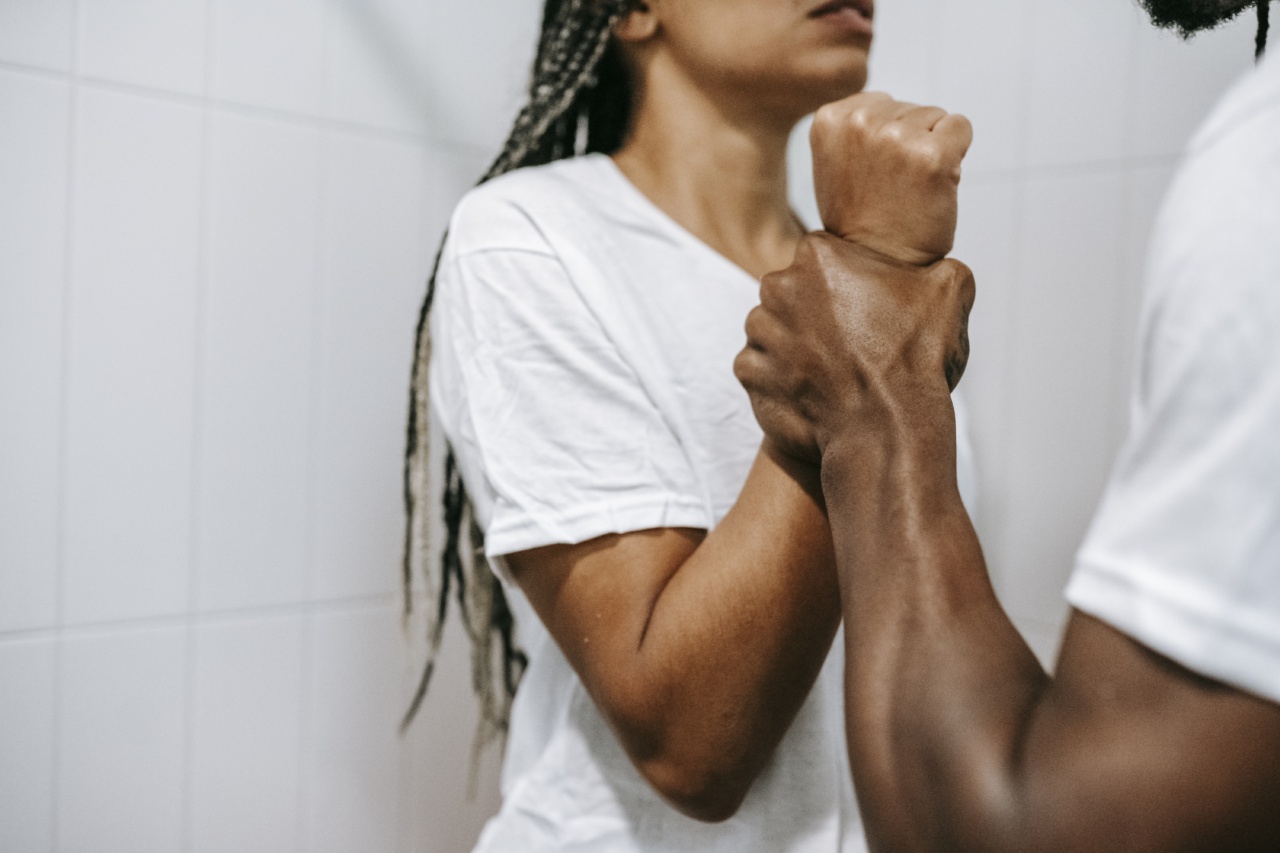
Incarceration is a topic that elicits a myriad of emotions and opinions from people around the globe.
While it is often discussed in the context of crime and punishment, it is imperative to acknowledge the various ways in which incarceration impacts individuals, families, and society as a whole. One crucial but often overlooked aspect is the role of incarceration as a catalyst for domestic violence.
The Link Between Incarceration and Domestic Violence
Domestic violence refers to any form of abuse that occurs within the realm of intimate relationships.
While it is important to recognize that not all individuals who are incarcerated are perpetrators of domestic violence, evidence suggests a correlation between incarceration and increased rates of violence within households.
There are several reasons why incarceration can contribute to domestic violence:.
1. Breakdown of Support Systems
When an individual is incarcerated, their absence leaves a void in the household. This often results in the breakdown of support systems, leaving family members without the emotional and financial assistance they relied upon.
This lack of support can increase stress levels and exacerbate conflict within the household, potentially leading to domestic violence.
2. Economic Strain
Incarceration often leads to financial instability for families. With the loss of the incarcerated individual’s income, families may struggle to meet basic needs and maintain a stable lifestyle.
This economic strain can lead to heightened tension and conflict, increasing the risk of domestic violence.
3. Psychological Impact
Being incarcerated can have profound psychological effects on individuals. The experience of imprisonment can lead to feelings of anger, frustration, and powerlessness.
These emotional struggles, when combined with the challenges of reintegration into society upon release, can contribute to a volatile home environment where domestic violence may occur.
4. Substance Abuse
Research has consistently shown a strong link between substance abuse and domestic violence.
Incarceration can exacerbate issues related to drug and alcohol abuse, as individuals may turn to substance use as a coping mechanism while incarcerated or upon release. Substance abuse can further fuel domestic violence within households.
5. Cycle of Violence
Incarceration can perpetuate a cycle of violence within families. Children who grow up in households where domestic violence is prevalent are at an increased risk of becoming victims or perpetrators of violence themselves.
When a parent or caregiver is incarcerated for committing domestic violence, it reinforces and normalizes violent behavior, perpetuating the cycle of abuse.
Breaking the Cycle
Addressing the issue of domestic violence within the context of incarceration requires a comprehensive approach that focuses on prevention, intervention, and support:.
1. Education and Awareness
Efforts should be made to increase public awareness about the link between incarceration and domestic violence.
Educational programs can help individuals better understand the consequences of their actions and equip them with the tools needed to build healthy and non-violent relationships.
2. Support for Victims
It is essential to provide comprehensive support services for victims of domestic violence. This includes safe shelters, counseling, legal assistance, and access to financial resources.
By empowering victims, we can help break the cycle of violence and ensure their safety and well-being.
3. Rehabilitation Programs
While in prison, individuals should have access to rehabilitation programs that address underlying issues such as anger management, substance abuse, and trauma.
These programs can help incarcerated individuals develop healthier coping mechanisms and reduce the likelihood of reoffending upon release.
4. Family Reintegration
Efforts should be made to facilitate the successful reintegration of individuals back into their families and communities upon release.
This may include providing support services such as job training, housing assistance, and counseling to help individuals rebuild their lives and establish positive relationships within their families.
Conclusion
It is crucial to recognize the role that incarceration plays in perpetuating domestic violence.
By addressing the underlying factors that contribute to violence within households affected by incarceration, we can work towards breaking the cycle of abuse. Through education, support for victims, rehabilitation programs, and family reintegration efforts, we can strive to create a safer and more compassionate society.